Contents:
- Medical Video: Understanding Muscle Atrophy (Muscle Loss): Fitness Exercises For Strengthening Your Muscles
- Why does muscle weakness occur?
- How to control and overcome atrophy?
- What should I remember?
Medical Video: Understanding Muscle Atrophy (Muscle Loss): Fitness Exercises For Strengthening Your Muscles
If you have had a stroke, you may suffer from weakness in the face, arms or legs. Usually, only one side of the body will be affected. Strokes that affect body coordination can lead to difficulty moving even when your muscles do not become weak.
In addition, after a stroke, many stroke sufferers suffer from confusion, communication difficulties, difficulty swallowing, headaches, mood swings, and various other problems that make it difficult to get up and move safely.
Patients suffering from severe and life-threatening stroke complications can be monitored in the intensive care unit until the danger is dealt with. Sometimes, patients who are not physically stable need to lie in bed for safety.
Rehabilitation is an important part of stroke recovery and some patients are fortunate enough to be able to start physical therapy or occupational therapy after a stroke.
Why does muscle weakness occur?
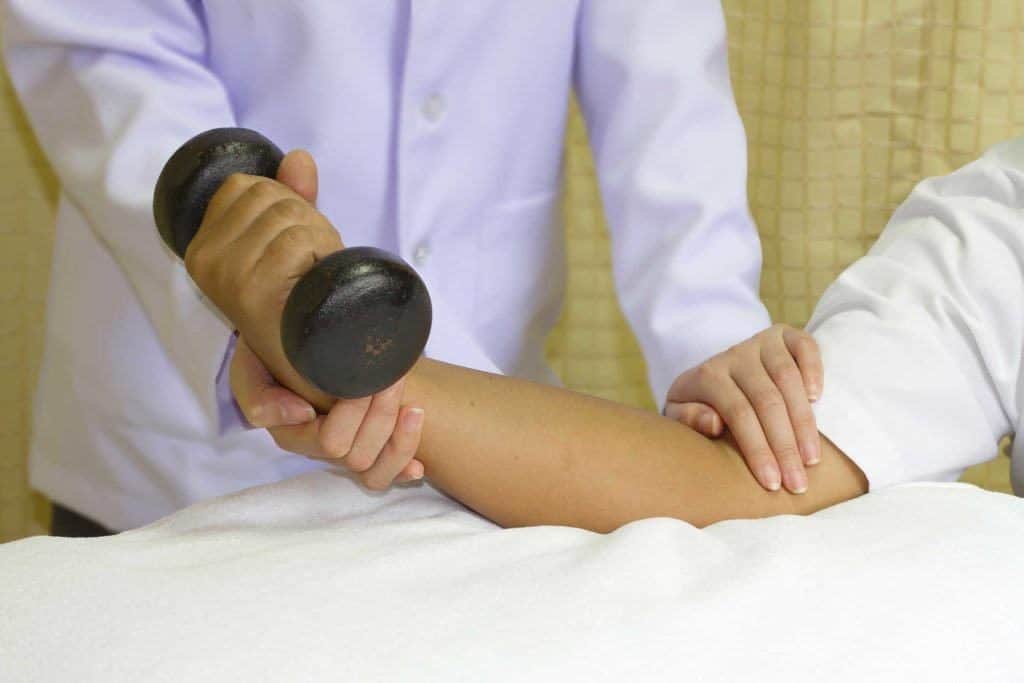
When muscles are not used, a condition called atrophy often occurs. Atrophy is the shrinking of muscle tissue. If physical exercise in the gym will train the muscles, trigger the muscles to grow stronger and bigger, atrophy is just the opposite. Atrophy is a decrease or loss of muscle mass due to muscle use not too long.
Lack of activity causes the muscles to shrink and become weak. After stroke sufferers are ready to reactivate, weak muscle atrophy plus weakness due to stroke makes exercise a difficult challenge.
How to control and overcome atrophy?
One method that is used to start physical activity before the patient is ready for therapy is to slowly move the patient's arms and legs. This is often done for stroke patients in hospitals that are unable to carry out activities. There are several benefits of moving passive muscles, which helps to avoid injury due to pressure on one part of the body when lying in bed or sitting in a chair for a long time. This can help prevent blood clots that can occur in the arms or legs due to lack of movement. Passive movement is also believed to be a method of preventing blood clots. Passive movement can help to minimize some nerve damage and muscle stiffness that usually occurs during long periods of muscle inactivity.
Even though atrophy is an unpleasant condition, this can be cured. Many stroke patients become depressed when they observe their thin bodies that appear weak and malnourished. After a stroke, eating disorders are a common thing for stroke sufferers so that body weight drops immediately after a stroke. Even with optimal efforts to provide food in hospitals, many patients have difficulty swallowing so that the weight of the body continues to drop dramatically. Families are often very concerned about seeing the skinny muscles of their loved ones.
However, continuing nutrition and physical activity slowly can help cure atrophy, allowing muscles to improve their size and shape. It takes some time to develop and rebuild muscles. After stroke sufferers begin to continue physical activities with safe physical therapy at home, appetite will begin to improve. Often it takes special planning and attention to maintain good protein intake and sufficient calories. Light activities such as walking a few steps or even taking a shower may seem tiring at first. Gradual expectations and improvements can help prevent despair. Disrupted muscles due to stroke can still improve thanks to long-term passive movements. This helps coordination and overall health.
What should I remember?
Atrophy is a common consequence of lack of muscle use. With good time, practice and nutrition, stroke sufferers can recover from atrophy.