Contents:
- Medical Video: WHAT IS EYE STROKE Eye Stroke Symptoms Risks and Treatment
- The effects of drugs on the brain that you must watch out for
- Manipulate feelings, mood, and behavior
- Spur excessive brain work
- Triggers hallucinations
- Effects of drugs on the nervous system
- How can drug users become dependent?
- Drug users will continue to increase the usage dose until overdose
Medical Video: WHAT IS EYE STROKE Eye Stroke Symptoms Risks and Treatment
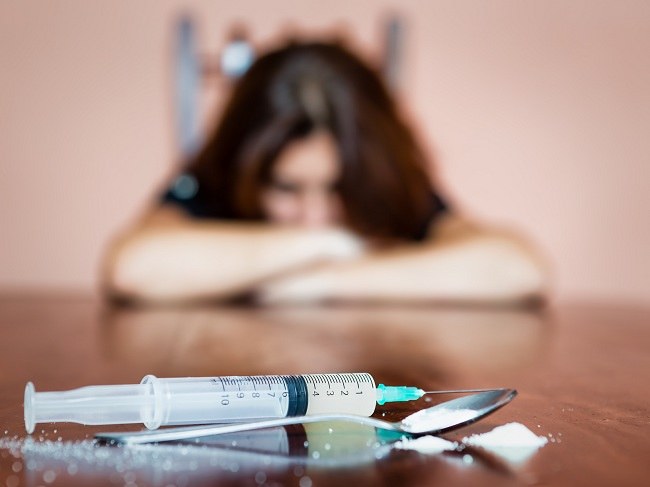
You certainly have heard a lot about the dangers caused by drug abuse. Of the many effects, do you know that the use of narcotics, psychotropic substances and other addictive ingredients can affect the work of the brain which functions as the center of the body's control? As a result this will affect all of your body's functions. So, what are the effects of drugs on the brain?
The effects of drugs on the brain that you must watch out for
Manipulate feelings, mood, and behavior
Because drugs affect the brain's work, drugs can change the atmosphere of the wearer's feelings, ways of thinking, awareness and behavior. That is why narcotics are called psychoactive substances. There are several kinds of effects of drugs on the brain, such as inhibiting the work of the brain, called depresansia, this will reduce awareness so that drowsiness arises. Examples are opioids such as opium, morphine, heroin, pethidine), sedatives (sedativa and hypnotics) such as BK, Lexo, Rohyp, MG and alcohol pills.
Narcotics affects the part of the brain responsible for the 'life' feeling, called the limbus system. The hypothalamus as a pleasure center in the brain is part of the limbus system.
Spur excessive brain work
Drugs can also stimulate the work of the brain or often called stimulants, so that a sense of freshness and enthusiasm arises, increased self-confidence, and relationships with other people become familiar. However, this can cause you to not be able to sleep, anxiety, faster heartbeat and increased blood pressure. Examples are amphetamine, ecstasy, meth, cocaine, and nicotine contained in tobacco.
Triggers hallucinations
There are also drugs that cause delusions, or which are also often called hallucinogens. Example is LSD. In addition to LSD, there is marijuana that causes various influences, such as changing perceptions of time and space, and increasing imaginary power, so that marijuana can be classified as hallucinogenic.
In brain cells there are various chemicals called neurotransmitters. These chemicals work on one nerve cell connection with other nerve cells (synapse). A number of neurotransmitters are similar to some types of drugs.
All psychoactive substances (narcotics, psychotropics and other addictive ingredients) can change a person's behavior, feelings and thoughts through their influence on one or several neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters that have the most role in the occurrence of dependence are dopamine.
Effects of drugs on the nervous system
Narcotics abuse has an influence on the workings of the nervous system. Anything? Here's the explanation.
- Sensory nerve disorders. This disorder causes a feeling of numbness and blurred vision so that it can cause blindness.
- Autonomic nerve disorders. This disorder causes unwanted movements through motor motion. So that people who are drunk can do anything outside their consciousness. For example, when drunk, these users can disturb people, fight and so on.
- Motor nerve disorders. This movement without coordination with the motor system. For example like someone else ‘on ', the head can shake on its own, the movement only stops if the drug's effect disappears.
- Vegetative nerve disorders. This is related to language that comes out of consciousness. Not only that, the effect of drugs on the brain can cause fear and lack of confidence if you don't use it.
In the long run, drugs can slowly damage the nervous system in the brain from mild to permanent. When using narcotics, the electrical charge in the brain is excessive, if it is addicted, the nerves can be damaged over time. Do you want to be blind, impaired consciousness, or intentionally imprisoned just for drugs?
How can drug users become dependent?
Then, what happens to someone who is dependent? Dependence is a kind of 'learning' of brain cells in the pleasure center. When you try to take drugs, the brain will read your body's response. If you feel comfortable, the brain secretes dopamine neurotransmitters and will give a pleasant impression.
The brain records it as something that is sought as a priority because it is considered fun. As a result, the brain makes the program wrong, as if the person needed it as a basic need and there was addiction or dependence. In a state of dependence, addicts feel very uncomfortable and in pain. To get drugs, he will do everything like steal, even kill.
In cases of dependence, a person must always use drugs, if not, withdrawal symptoms arise (also called sakau), if the use is stopped or the amount is reduced. Symptoms depend on the type of drug used.
Symptoms of sacio opioids (heroin) are similar to those with severe flu, which are runny nose, tears out, standing body hair, muscle aches, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and difficulty sleeping. Narcotics also interfere with the function of other organs, such as the heart, lungs, liver and reproductive system, so that various diseases can arise.
Drug users will continue to increase the usage dose until overdose
So, the feeling of pleasure, comfort, calm or joy that is sought by drug users, must be paid dearly by its adverse effects, such as dependence, damage to various organs, various diseases, broken relationships with family and friends, damage to moral life, dropping out of school unemployment and the destruction of his future.
Consuming drugs continuously causes an increase in body tolerance so that the user cannot control their use and tends to continue to increase the usage dose until finally the body cannot receive it anymore. This is called overdose.
The nerve is one of the important organs in humans that regulates the body's system. If it is damaged, it can cause permanent and difficult disability to repair. You do not want to not, disabled just because of drugs?