Contents:
- Medical Video: What Is Prediabetes?
- What is prediabetes?
- What are the symptoms of prediabetes?
- What are the trigger factors?
- What are the tests to diagnose this condition?
Medical Video: What Is Prediabetes?
There are types of diabetes, ranging from prediabetes, type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Prediabetes is a sign of risk that your body can get diabetes further. What is prediabetes?
What is prediabetes?
Prediabetes is not a disease but a warning sign that you may have type 2 diabetes in the near future. In prediabetes, your blood sugar is higher than normal but not enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes.
Having prediabetes means you are at high risk for type 2 diabetes within 10 years.
If you are diagnosed with prediabetes, you should feel lucky because you can prevent type 2 diabetes from developing in yourself by reducing excess weight and changing your lifestyle.
What are the symptoms of prediabetes?
Usually, you have no specific symptoms or signs until you are in serious complications of diabetes. However, there is one sign that indicates a possible risk of type 2 diabetes, namely the skin becomes darker or almost brown in some parts of the body, called acanthosis nigricans. Often appears on the neck, armpits, elbows, knees and knuckles. The following are other symptoms:
- urinate more often
- tired or tired
- blurred vision
You should tell your doctor if you are worried about diabetes or if you notice signs or symptoms of type 2 diabetes, increased thirst and frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision.
What are the trigger factors?
Factors that increase the risk of prediabetes are the same as type 2 diabetes, which includes:
1. Excess weight.
Being overweight is a major risk factor for prediabetes. The more fat you have — especially in and between the muscles and skin around your stomach — the more resistant your cells are to insulin.
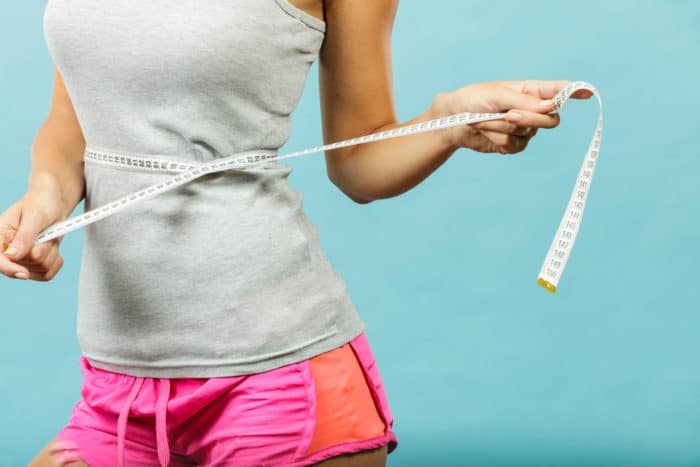
2. Waist size
Large waist circumference can indicate insulin resistance. The risk increases in men with a waist greater than 100 cm and for women with a waist size greater than 88 cm.
3. Lifestyle
The more you are less active, the greater the risk of prediabetes. Physical activity helps you control weight, uses sugar as energy and makes your cells more sensitive to insulin.
4. Age
Even though diabetes can develop at any age, the risk of prediabetes increases as you get older, especially those over 45 years of age. This might be because people tend to lack exercise, lose muscle mass and gain weight as you get older.The risk of developing this condition will also increase if your parents or siblings have type 2 diabetes.
6. Sleep
Research has linked sleep problems, such as obstructive sleep apnea, with an increased risk of insulin resistance. Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that causes breathing to be disrupted several times during sleep, causing poor sleep quality. People who work on shifts or night shifts, may cause sleep problems, also may have an increased risk of prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
What are the tests to diagnose this condition?
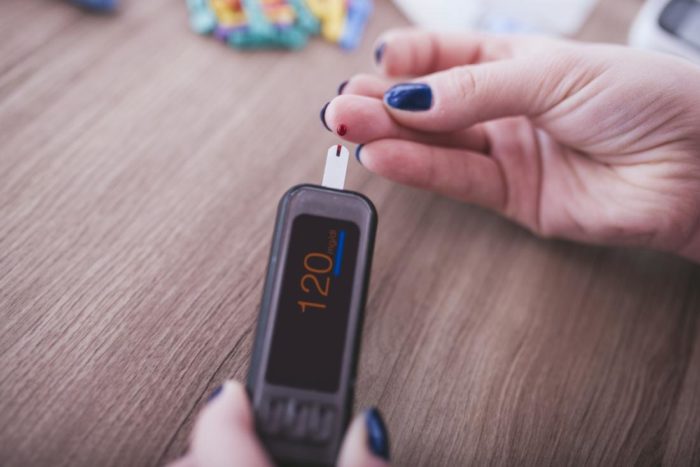
- Glycated hemoglobin test (A1C). This blood test shows the average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. This test works by measuring the percentage of blood sugar attached to hemoglobin, an oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells. The higher your blood sugar level, the more sugar is attached to the hemoglobin you have.
- Fasting blood sugar test. Blood samples will be taken after you have fasted for at least eight hours or overnight.
- Oral glucose tolerant test. This test is rarely used to diagnose diabetes except during pregnancy. Blood samples will be taken after you have fasted for at least eight hours or overnight. Then, you will drink a sugar solution, and your blood sugar levels will be measured again after two hours.
If your blood sugar levels are normal, your doctor may recommend a screening test every three years. If you have pre-diabetes, further examination may be needed. For example, your doctor should check your fasting blood sugar, A1C, cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, low lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglyceride density at least once a year, possibly more often if you have additional risk factors for diabetes.
What should I do to control prediabetes?
You can restore blood sugar levels to normal range by choosing a healthier lifestyle. Even though there are some people who suffer from type 2 diabetes even when they have lost weight, at least you can reduce risk.
Here are some recommendations that can help you prevent prediabetes to progress to diabetes:
- Eat healthy food
- Reduce a few pounds of excess body weight. Losing 5% to 10% of your body weight can make big changes.
- Do sports every day. Choose something you like to do, like walking. Try to do at least 30 minutes every day, 5 days a week. You can start with a shorter time and slowly increase your time to half an hour if you need to. Check with your doctor before doing more.
- Quit smoking
- Treat blood pressure and high cholesterol
- Take medication as directed. Depending on your other risk factors, your doctor may prescribe medications to lower cholesterol or blood pressure or to help prevent diabetes.