Contents:
- Medical Video: Diabetes Treatment : How to Treat Diabetes With Insulin
- How does insulin affect diabetes?
- Types of insulin
- Insulin injection
- Insulin reaction
Medical Video: Diabetes Treatment : How to Treat Diabetes With Insulin
Insulin is a hormone made in the pancreas, a gland located behind the stomach. Insulin allows the body to use glucose as energy. Glucose is a type of sugar found in many carbohydrates. After eating or snacking, the digestive tract breaks down and converts carbohydrates to glucose. After releasing glucose into the bloodstream, insulin causes cells throughout the body to absorb this sugar and use it as energy.
Insulin also plays a key role in balancing blood glucose levels. When too much glucose in the bloodstream, insulin signals the body to store excess sugar in the liver. This sugar is not released until your blood sugar drops, such as between meals or at times of stress when your body needs additional energy boost.
How does insulin affect diabetes?
Diabetes occurs when your body does not use insulin properly, or when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Type 1 diabetes is a type of autoimmune disease in which the body no longer produces insulin. In this disease, the body's failure to produce insulin occurs because the immune system has destroyed all the cells that produce insulin in the pancreas. This disease is more common in young people, although it can develop in adults. Type 2 diabetes also affects people of all ages, but usually develops later in life.
Unlike type 1 diabetes, the main problem in people with type 2 is a decreased response to the effects of insulin by body cells that need glucose (insulin resistance). Therefore, in many cases of type 2 diabetes, patients may actually have excess insulin in an effort to keep blood sugar levels normal. However, over the years, this excess can cause the cells producing insulin in the pancreas to disintegrate. At that time, the patient was dependent on insulin treatment.
Insulin injections can treat both types of diabetes. However, many people with type 2 diabetes can manage their blood sugar with lifestyle changes and medications. Sometimes, patients with type 2 diabetes cannot achieve normal blood sugar levels by only using eating drugs and lifestyle modifications, and these people may need insulin to maintain a healthy blood sugar level. Because people with type 1 diabetes cannot make insulin, they must use insulin to control this disease.
Types of insulin
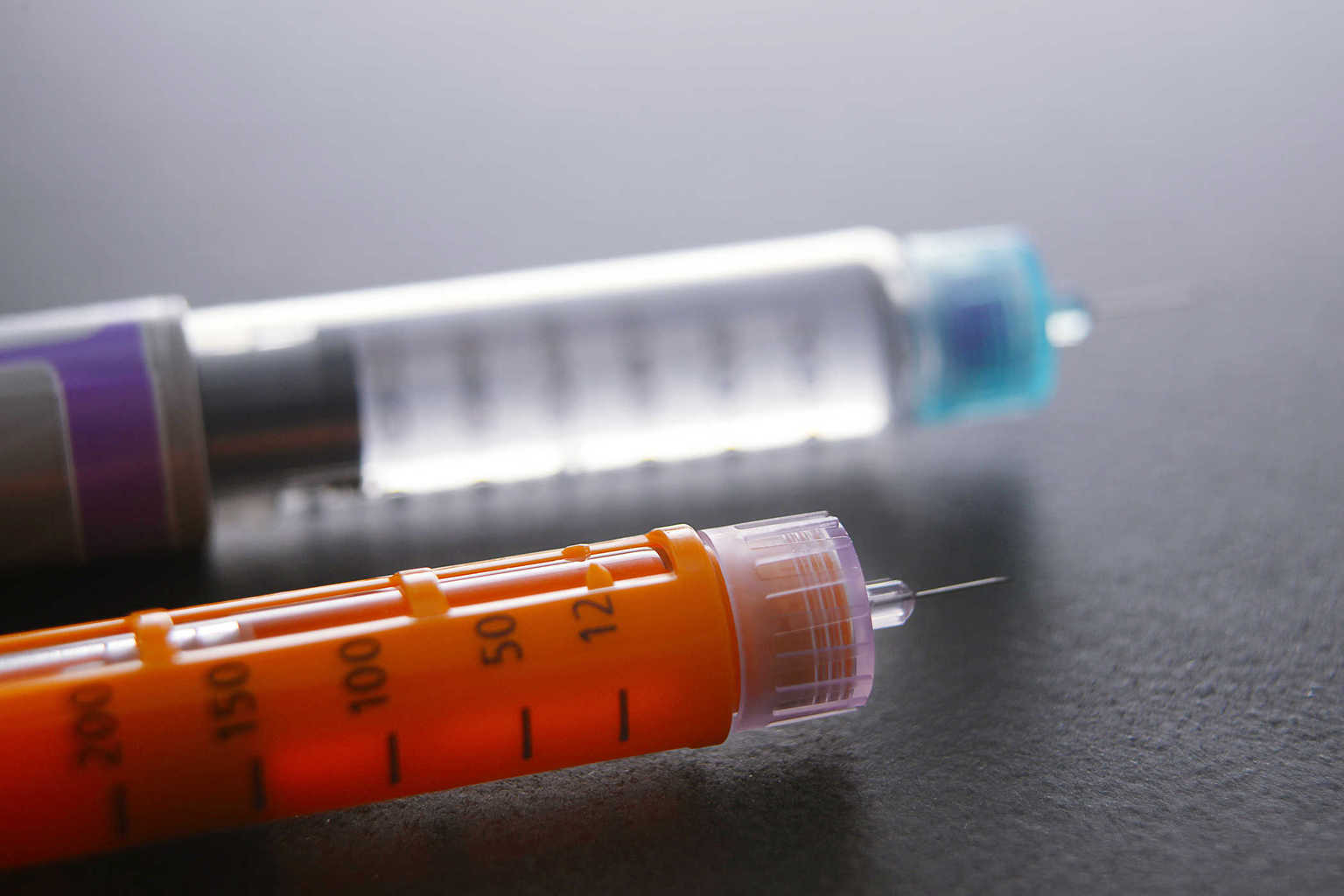
Insulin cannot be taken by mouth. Insulin must be injected with a syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump. Although at the cellular level all insulin has the same effect, the chemical modification of insulin protein has enabled the development of various types of insulin for the treatment of diabetes. The main difference between the various types of insulin used in the treatment of diabetes is the reaction speed and duration of the drug effect.
- Insulin Direct Effects
The type of insulin that starts working about 15 minutes after the injection. The injection can last for 3-5 hours, and is often done before eating. - Short Insulin Effects
Performed before meals, insulin starts working in about 30-60 minutes after the injection, and lasts 5-8 hours. - Old Insulin Effects
Insulin does not work immediately until 1 hour after the injection, but can last up to 26 hours. - Medium Effect Insulin
The type of insulin that starts working in 1-3 hours after injection, and can last 12-16 hours.
Insulin injection
Insulin is injected under the skin, and the doctor or nurse can provide instructions on how to do the injection. You can inject insulin in many different parts of your body, such as your thighs and stomach. Do not inject insulin 2 inches from the navel. You must vary the location of the injection to prevent skin thickening.
Diabetes treatment varies for everyone. Your doctor may instruct you to use insulin 60 minutes before meals, or after meals. The amount of insulin you will need each day depends on various factors including your diet, level of physical activity, and how severe your diabetes is.
Some people only need one supply of insulin a day, while others need three or four supplies a day. Your doctor may also combine direct effects of insulin with long-acting insulin.
Insulin reaction
Insulin reaction (hypoglycemia) can occur in people who use insulin to treat their diabetes. When you use insulin, its use needs to be balanced with food or calories. If you exercise too much or don't eat enough, the level of sugar in your blood can drop too low and trigger a reaction. Signs of insulin reaction include:
- Fatigue
- Yawn often
- Unable to speak
- Sweating
- Confusion
- Lost consciousness
- Seizures
- Twitching muscles
- Pale skin
To stop the effects of an insulin reaction, bring at least 15 g of carbohydrates that have an immediate effect on you at any time. As an example:
- About half a cup of non-diet soda
- ½ cup of fruit juice
- 5 sweets
- 2 tablespoons of raisins
Insulin can keep your blood sugar level in a healthy range and reduce the risk of diabetes complications, such as blindness and amputation of limbs. It is important for you to monitor your blood sugar regularly, and make lifestyle changes to prevent blood sugar levels from getting too high.