Contents:
- Medical Video: Massage for Muscle Spasms & Cramps
- Causes of muscle cramps while exercising
- Signs and symptoms of muscle cramps while exercising
- How to deal with muscle cramps while exercising
- Prevent muscle cramps while exercising
Medical Video: Massage for Muscle Spasms & Cramps
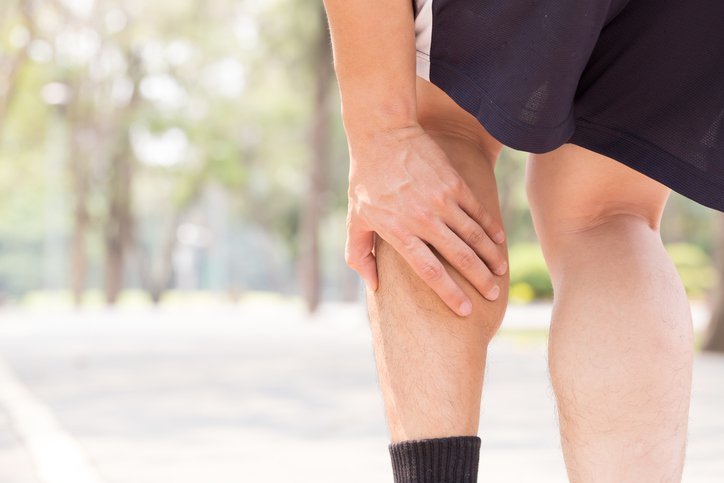
Muscle cramps are one of the conditions experienced by almost everyone. When we use muscles that we can control like the muscles of the arms and legs, the muscles will make alternating contractions and relaxation. Muscles that contract outside the will are called "spasm", and when the spasm that occurs is strong and sustained, cramps occur. Muscle cramps are often seen or palpated as hardened muscles.
Cramps that occur during physical activity or exercise in people who do not have metabolic, endocrine and neurological abnormalities are called Exercise Associated Muscle Cramps (EAMC). Apart from during exercise, this cramping is also reported to occur within 8 hours after exercise. Research conducted by Norris reported that the incidence of cramps during exercise was experienced by 95% of students majoring in sports, 26% of whom also complained of having experienced cramping some time after exercising. Although not a dangerous condition, muscle cramps can cause discomfort for patients and can interfere with daily activities.
Causes of muscle cramps while exercising
Unbalanced body dehydration and electrolytes are thought to be the main factors causing muscle cramps. When exercising, the body will lose a lot of fluid that is not replaced, resulting in dehydration and lack of electrolytes such as sodium, calcium, and magnesium. This causes the nerve muscles to become sensitive and contractions occur unwillingly. This theory is also supported by the incidence of muscle cramps in professional athletes which are more common in summer than other seasons.
Excessive use of muscles or in certain positions in excessive time can also cause cramps. Cramps can also be caused by the presence of pinched nerves or reduced blood flow to the muscles.
Signs and symptoms of muscle cramps while exercising
Cramps often occur in the leg muscles, especially the calves. Can occur during or after exercise, and usually takes place in seconds to ten minutes. When cramps occur, patients generally feel sudden pain and muscles that cannot be moved. Muscles can look swollen and when held feels hard. After cramping improves, the patient usually still feels pain for several hours afterwards. There is no special examination to diagnose cramps, generally cramps can be easily recognized by most people. Cramps usually improve on their own, but if the following symptoms are found, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- Causes severe pain
- Redness or skin changes arise
- Accompanied by muscle weakness
- It often happens and does not improve
- Occurs when you are not active or exercising
How to deal with muscle cramps while exercising
Although it can improve on its own, here are some things that can be done when the muscle cramps attack:
- Stretch the muscles that experience cramps. If it occurs in the leg muscles, you can lie down while stretching your legs, asking your friends to pull your feet towards your head. Another technique that can be done is to stand as far as 1 meter or more from the wall, lean your body forward, place both palms on the wall, with your back and knees straight and your feet touching the floor. On cramps that occur due to writing too long, pressing the hand towards the wall with the finger facing down can relax the muscles of the hand.
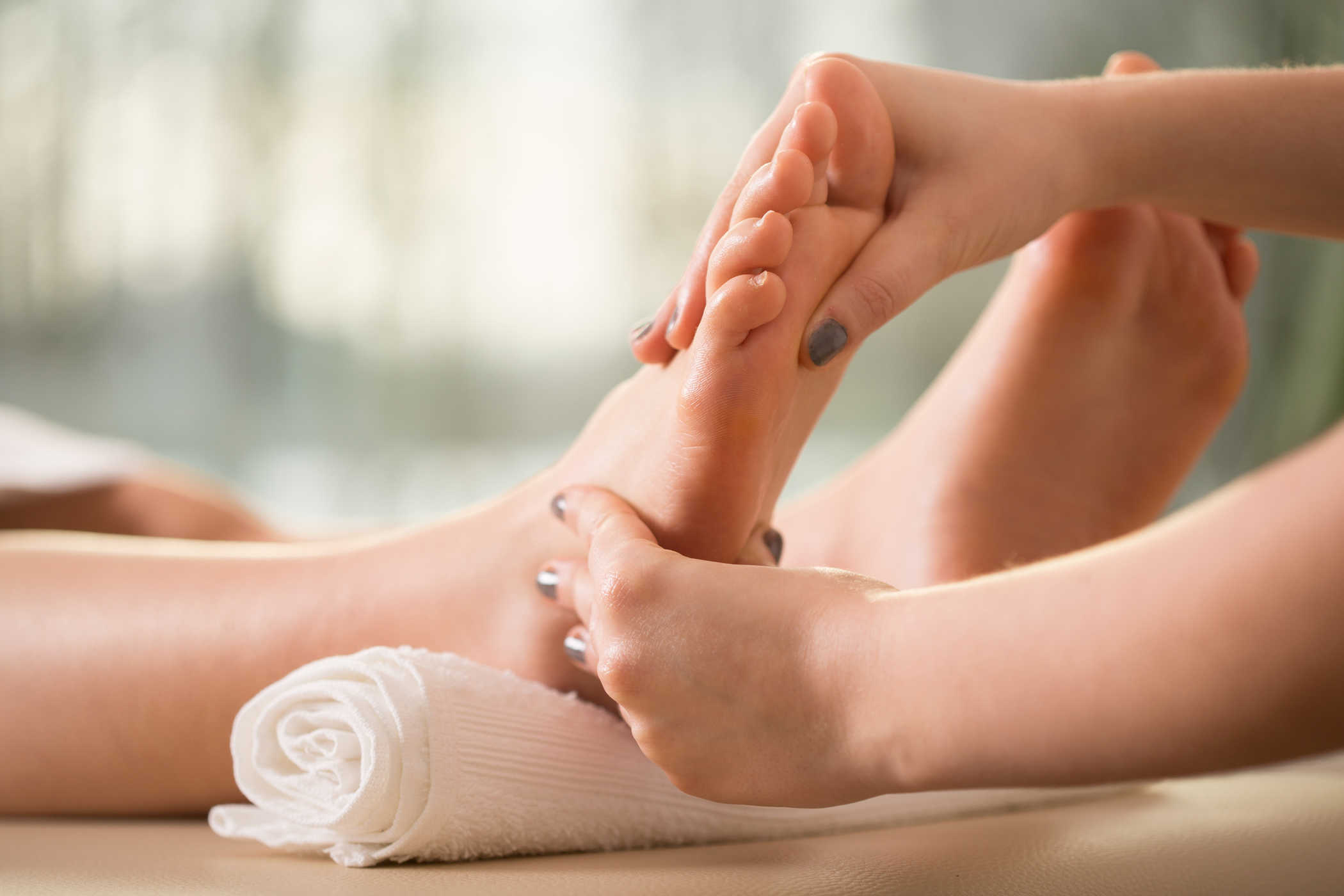
- Gently massage the muscles that experience cramps to help relax.
- Soak with warm water or warm compresses.
- Give fluids and electrolytes to treat dehydration due to heavy physical activity.
- The doctor can give medicine muscle relaxant in certain conditions or when injured.
Prevent muscle cramps while exercising
The incidence of muscle cramps can be reduced by doing the following:
- Stretch and warm up before and after exercise. Stretching makes your muscles more flexible so it is more difficult to get cramps.
- Make sure you get enough fluids. Each person's fluid needs vary, but generally the body loses 0.4-1.8 liters of water for every one hour of exercise.
- Consumption of fluids or foods that contain lots of electrolytes before and after exercise.
- Avoid excessive physical activity and exercise during hot weather.
READ ALSO:
- 7 Ways to Not Run Out of Breath When Running
- Effective Sports in 7 Minutes: 7 Minute Workout Guide
- 8 Sports That Can Train Sex Agility in Men