Contents:
- What is birth en caul?
- What causes this condition?
- Is birth en caul dangerous for babies?
- What is the process of removing a baby from the intact amniotic sac?
In general, the amniotic sac will rupture before the baby comes out of the uterus. There are also cases of membranes that rupture earlier before the time to give birth. Same is the case with caesarean delivery. The doctor will tear the amniotic layer with a scalpel to remove the baby.
But in a few cases, babies can be born into the world still wrapped intact in the complete amniotic sac with their fluids. This rare birth is called en caul. Even so rare, many obstetricians have never witnessed birth en caul with his own eyes throughout his career.
What is birth en caul?
The amniotic sac is a thin, elastic bag that wraps the baby in the womb. This bag contains a baby, placenta, and amniotic fluid. The amniotic sac serves to protect the baby from impact trauma while he is still in the womb until the seconds of labor. Usually, this bag will break and the liquid will flow out to allow the baby to come out.
Interestingly, some lucky babies can be born in their fetal sacs. This is what is called birth caul, which means "helmet" in Latin. There are two types caul, that is caul and en caul. Birth caul occurs when the amniotic sac only partially breaks, so the remaining intact wrap around the baby's head and face, which makes it look like he is wearing a glass helmet. Another "variation" of birth caul is the amniotic sac that wraps the baby from the head to the baby's chest, while the abdomen to the end of the leg is free.
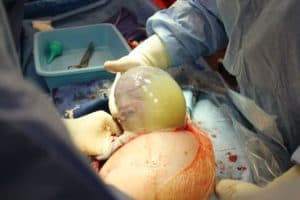
Birth caul itself alone is quite rare, but birth en caul it turns out more rarely. In 1 in 80,000 births, babies can be born into a world still completely encased in the amniotic sac the whole one without defects - like being trapped in a clear cocoon.
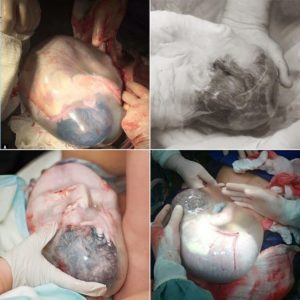
Although classified as very rare, birth en caul most likely to occur in preterm labor. This is because the size of a very small baby can allow the amniotic sac to remain intact. A 2010 study found that in cases of very premature babies, giving birth en caul can protect them from traumatic pressure in the uterus.
Napoleon, Sigmund Freud, Charlemagne and David Copperfield are some of the most important figures in world history born through birth caul.
What causes this condition?
The birth of caul, whether that is partially (caul) or intact like a cocoon (en caul), is a very rare phenomenon. Even so rare, many obstetricians who may not have or at all have never witnessed birth en caul with his own eyes throughout the history of his career. Therefore, it is still a mystery about what caused this rare birth.
Is birth en caul dangerous for babies?
Reporting from What to Expect, "The birth of caul, regardless of the type, is absolutely safe," said Dr. Susan Benson, one of the lucky obstetricians to have witnessed 3 births caul throughout the 12 years of his career. Babies are not at high risk of experiencing complications arising from birth caul or en caul. Most babies born in this condition are born healthy, unless they have a problem that preceded it since pregnancy.
While still in the womb of the mother, the baby continues to receive nutrients and oxygen through the umbilical cord, and he also breathes the amniotic fluid that surrounds it in the bag. This process will still be carried out by the baby even if he was born into the world but still trapped in the intact amniotic sac. But of course your team of doctors will not let the baby linger wrapped in this condition to let him breathe.
What is the process of removing a baby from the intact amniotic sac?
If your doctor or midwife finds that your baby is still in his fetal sac, he will immediately make an incision over the baby's nostrils so he can take a breath for the first time. After the incision is made, the liquid will be drained and the doctor will peel the "skin" of the amniotic sac starting from the face and ears, the most vital and complex area, then the rest of the body parts.
The doctor may also rub the lining of the amniotic sac with a thin piece of paper, which will then be peeled off from the skin just like removing a temporary tattoo sticker. But the amniotic sac that has been "broken" will stick to the baby's skin. Then the peeling process will be very slow and extra careful. Because if not, the skin layer of the amniotic sac that attaches tightly to the skin may cause permanent scars when pulled tight.
After successfully peeling the amniotic sac, the doctor will continue the labor process as usual, i.e. cut the umbilical cord, suck mucus out of the baby's nose and mouth, and cleanse his body of blood and mucus.