Contents:
- Medical Video: What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Tuberculosis?
- What are the symptoms of pulmonary TB?
- Symptoms of tuberculosis other than in the lungs
Medical Video: What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Tuberculosis?
According to WHO, every second there is at least one person infected with tuberculosis in the world. Indonesia ranks second as the country with the most TB cases in the world after India. TB is even the number one cause of death in Indonesia. Unfortunately, there are still many who do not realize or even do not know about this disease, including symptoms. Knowing the symptoms of tuberculosis as early as possible can help doctors determine the best treatment and treatment. Here are the various symptoms of TB that you need to know.
What are the symptoms of pulmonary TB?
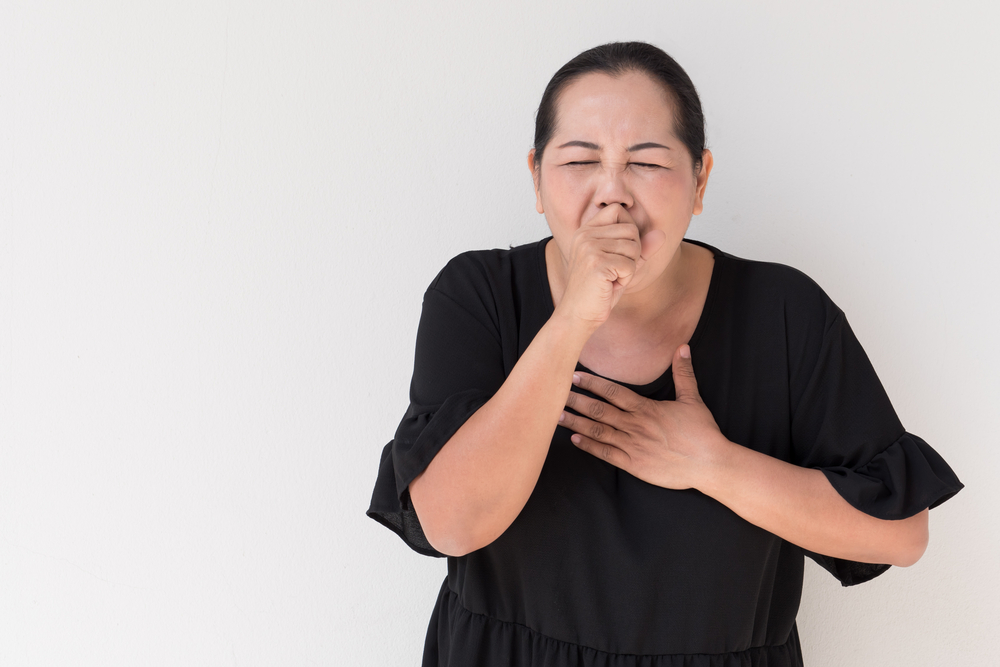
Complaints felt by TB patients vary, although there are also TB sufferers who do not complain of anything. Complaints that usually arise are:
- Cough with phlegm or dry for more than 3 weeks.
- Coughing up blood.
- Chest pain and shortness of breath.
- Appetite decreases and weight decreases.
- Missing high fever. This condition makes the patient feel as if he has never recovered from a fever. Suspect TB symptoms if the fever is more than 3 weeks and the cause is unclear.
- Sweating at night even though it's not warm.
- Extreme fatigue, muscle pain.
TB usually develops slowly and may take several weeks to realize that you have contracted an infection. The bacteria that cause TB will usually start actively attacking and causing symptoms if your immune system is weakened. In some cases, symptoms may not appear for months or even years after the initial infection.
In Indonesia, the diagnosis of pulmonary TB disease is usually inaugurated by seeing symptoms, results of radiological examination, and sputum of SPS.
Symptoms of tuberculosis other than in the lungs
Symptoms of TB can vary depending on which part of the body is attacked.
Tuberculosis infection usually develops in the lungs. However, some other organs can also be attacked, although rarely. Other parts of the body that may be infected include lymph nodes, bones and joints, the digestive system, bladder and reproductive system, and the nervous system.
Common symptoms of non-pulmonary TB can include:
- Lymph nodes that continue to swell.
- Stomach ache.
- Pain and difficulty moving in the affected bone or joint.
- Confusion.
- Constant headaches.
- Seizures.
Just like pulmonary TB, TB-causing bacteria can fall asleep for a long time and will attack until they cause symptoms when your body's resistance is weakened.