Contents:
- Medical Video: What are the signs and symptoms of diabetic shock ? | Health for All
- What is insulin shock?
- How insulin works
- What causes insulin shock?
- How does insulin shock affect the body?
- Treat insulin shock
- How to prevent insulin shock
Medical Video: What are the signs and symptoms of diabetic shock ? | Health for All
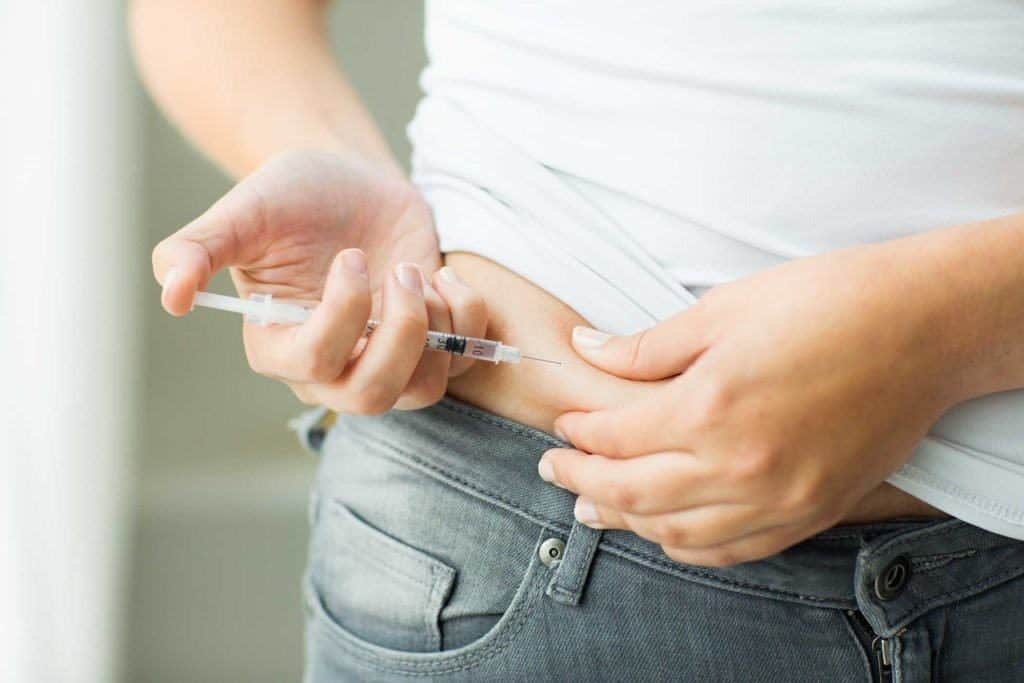
Insulin plays an important role in regulating blood sugar levels in the body. If you suffer from type 1 diabetes, you may need additional insulin intake. However, using too much insulin is also not good for your body. Because, excessive insulin intake can actually trigger a serious condition, called insulin shock.
What is insulin shock?
If someone with diabetes forgets to eat after getting an injection of insulin, it will cause too much insulin levels in the blood. Furthermore, this can cause mild hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar. If someone ignores symptoms of mild hypoglycemia, uses too much insulin accidentally, or skips meals, they may suffer a much more serious condition called insulin shock.
Insulin shock is an emergency condition of diabetes. This condition causes frightening symptoms that if left untreated can cause diabetes coma, brain damage, and even death.
How insulin works
When consuming foods or drinks that contain carbohydrates, carbohydrates are then converted into glucose. Glucose is a type of sugar which is a fuel for the body, providing the energy needed to perform daily functions. Well, insulin is a hormone that works like a key. This hormone opens the door in the cells of the body so that they can absorb glucose and use it as fuel.
People with diabetes may lack insulin or their body cells cannot use insulin properly. If the body's cells cannot absorb glucose properly, this causes excess glucose in the blood. This is called "high blood sugar" which is then associated with a number of health problems. Yes, high blood sugar can cause eye and foot problems, heart disease, strokes, kidney problems, and nerve damage.
Insulin injections help people with diabetes to use glucose more efficiently. Using insulin injections before meals helps the body absorb and use glucose from food. The result is a more balanced and healthy blood sugar level. Usually, this can work well. Even so, sometimes injecting insulin also doesn't work properly.
What causes insulin shock?
Insulin levels that are too high in the blood can cause low blood sugar. If your blood sugar drops too low, your body no longer has enough energy to carry out its functions. Insulin shock can cause your body to become so hungry because of reduced energy intake.
If you have diabetes and use insulin to help control blood sugar, you can experience excessive insulin levels in the blood. This usually happens if you inject too much insulin or skip meals after an insulin injection. If left too long, this condition can make the system on your body unbalanced.
Other causes of insulin shock include:
- Don't eat all day
- Doing sports with high intensity
- Drink alcohol on an empty stomach
How does insulin shock affect the body?
If your blood sugar drops slightly below normal, you may experience mild to moderate symptoms, such as:
- Dizzy
- Kliyengan
- Sweating
- Starving
- Feeling anxious or anxious
- Irritability
- Fast pulse
At this stage, you can take immediate steps for recovery. You can eat 15 grams of carbohydrates for first aid. Eating glucose tablets or high-sugar foods, such as fruit juices, raisins, honey, or sweets can also help stabilize your blood sugar. If you feel better in 15 minutes or more, you may be able to recover fully. If not, you should continue to eat 15 grams of carbohydrates until your blood sugar rises or at least your condition improves.
If you experience insulin shock, you may experience some of the symptoms above, but these symptoms will develop faster if left unchecked. Low blood sugar can also cause:
- Headache
- Confusion
- Fainted
- Poor coordination, frequent tripping, and falling
- Muscle tremor
- Seizures
- Coma
Insulin shock can also occur at midnight. In this case, symptoms that might occur include:
- Nightmare
- Cry when sleeping
- Confused or very angry easily
- Sweating very much
- Aggressive behavior
Treat insulin shock
Mild to moderate hypoglycemia can usually be treated by consuming sugar. If you begin to experience symptoms of severe hypoglycemia, it's time for more intensive care. If you or someone near you begins to experience insulin shock, take the following steps:
- Seek emergency medical help, especially if the person is unconscious.
- Give sugar to the person's body immediately, as described above.
- If the person is unconscious, give a glucagon injection if you have it. If not, emergency medical personnel will provide it. Don't give someone something that is not to be swallowed because it might make it choke.
How to prevent insulin shock
Insulin shock is not a pleasant experience. However, there are things you can do to prevent this from happening, including:
- Always prepare glucose tablets for you or bring candy to anticipate when your blood sugar drops too low.
- Always eat after using your insulin injection.
- Be sure to always ask the doctor to teach you how to use new drugs.
- Eat sweet snacks while exercising. Consult your dietitian about foods that are good to eat before exercise.
- Be careful when drinking alcohol. Talk to your doctor about what's best.
- Be careful after high-intensity exercise because it can reduce blood sugar for hours after exercise.
- Diligently check your blood sugar.
- If you experience symptoms of low blood sugar while driving, immediately pull over.
- Tell your family and friends about the symptoms of hypoglycemia so they can help you if you start experiencing these symptoms.
- Ask your doctor to give glucagon, because everyone who uses insulin must always have a supply of glucagon.
- Wear a medical identity so that emergency medical nurses can treat you quickly.
With the right precautions, you can manage your diabetes and use insulin drugs to keep your blood sugar levels stable.