Contents:
- Medical Video: Laryngospasm: Sudden, Terrifying Difficulty Breathing
- Bronchospasm is a disease that attacks the respiratory tract
- What are the causes and risk factors for bronchospasm?
- What are the symptoms of bronchospasm?
- How can bronchospasm be diagnosed?
- How to overcome bronchospasm?
- Short-acting bronchodilator
- Long-acting bronchodilator
Medical Video: Laryngospasm: Sudden, Terrifying Difficulty Breathing
Bronchospasm may be unfamiliar to your ear compared to bronchitis. Although it attacks the same part of the respiratory tract, the bronchi. Bronchospasm is a disease that you need to be aware of because it is prone to occur in people who have a history of asthma or allergies. To be clearer, consider the following reviews of bronchospasm.
Bronchospasm is a disease that attacks the respiratory tract
Bronchospams are the condition of the muscles that line the bronchi in the lungs to tighten and tighten. When this muscle tightens, the airways will narrow, so that air is difficult to get in and out.
Oxygen that should enter the lungs and carbon dioxide that should be released is hampered and limited in number. The narrowing of the airways can reduce the amount of air flow by 15 percent or more.
Bronchospasm is prone to occur in people with asthma, allergies or other respiratory diseases. This condition usually attacks children and adults aged over 65 years.
What are the causes and risk factors for bronchospasm?
The cause of bronchospasm is the presence of swelling, inflammation, irritation of the respiratory tract. That is why many diseases can develop into bronchospasm, such as:
- Asthma
- Allergy to dust, mites, pet dander, or flower powder
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, such as chronic bronchitis or emphysema
- Fungal, viral, or bacterial infections of the lungs
Meanwhile, other factors that can make a person at risk for bronchospasm include:
- Often exposed to smoke from chemicals or combustion
- Have smoking habits, both from tobacco and e-cigarettes
- Get general anesthesia during surgery that can irritate the respiratory tract
- Using blood thinning drugs
What are the symptoms of bronchospasm?
Symptoms of bronchospasm vary, depending on the severity of the disease, how much the bronchial duct narrows or how much air flow is reduced. Common symptoms of bronchospasm include:
- Feeling tight and tight on the chest
- Pain in the chest can penetrate to the back
- Eject wheezing when breathing
- Cough
- Easily dizzy and also tired
- It's hard to breathe freely like other normal people
How can bronchospasm be diagnosed?
To get a diagnosis of bronchospasm, you should consult a specialist in respiratory diseases or pulmonary experts.
The doctor will ask for your symptoms and find out your medical history, whether you have asthma, allergies or other respiratory diseases or not. Next, the doctor will see how you breathe.
In addition, you need to take several health tests to measure how well your lungs function, such as:
- Test breathing with a spirometry tube to measure air tightness when you breathe
- Lung volume tests to measure how much oxygen can be captured by the lungs
- Test of diffusion capacity of the lungs to determine hemoglobin levels in the blood
- Test pulse oximetryto measure the level of oxygen in the blood
- Test eucapnis voluntary hyperventilation,diagnose bronchospasm by inhaling a mixture of oxygen and carbon dioxide to stimulate breathing exercise
- X-rays and CT scans to look for signs or other problems in the lungs
How to overcome bronchospasm?
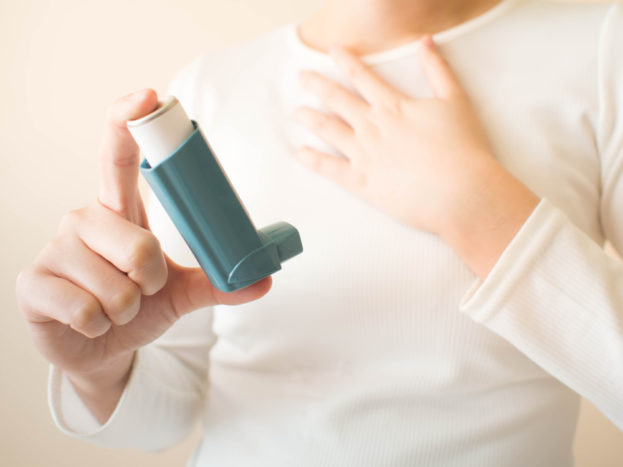
Although this disease can be treated with tablets, or injections, the most effective drug is inhalation. Usually the doctor will prescribe a bronchodilator to treat bronchospasm.
This drug can help patients to dilate the narrowed airways so that air flow will increase. There are three types of bronchodilators commonly used, namely beta-agonists, anticholinergics, and theophylline.
There are two types of bronchospasm treatment with bronchodilators, namely:
Short-acting bronchodilator
This drug will start working in a few minutes and the effect can last up to several hours. The doctor will prescribe this treatment, if the patient experiences sudden tightness and may only be used once or twice a week. Short-acting bronchodilators commonly used, including:
- Metaproterenol
- Xopenex
- Maxair
- Ventolin
Long-acting bronchodilator
For chronic bronchospasm, the doctor will provide long-term care, namely a combination of bronchodilators with inhaled corticosteroids. The use of bronchodilators is carried out two or three times per day and at the scheduled times by the doctor. Drug combinations can help relieve the symptoms of strains in the bronchial muscles quickly.
Long-acting bronchodilators and commonly used inhaled corticosteroid drugs, including:
- Foradil
- Prednisolone
- Advair
- Flovent