Contents:
- Medical Video: Neck Anatomy - Organisation of the Neck - Part 1
- What is the male pelvic anatomy like?
- The organs are protected in the anatomy of the male pelvis
Medical Video: Neck Anatomy - Organisation of the Neck - Part 1
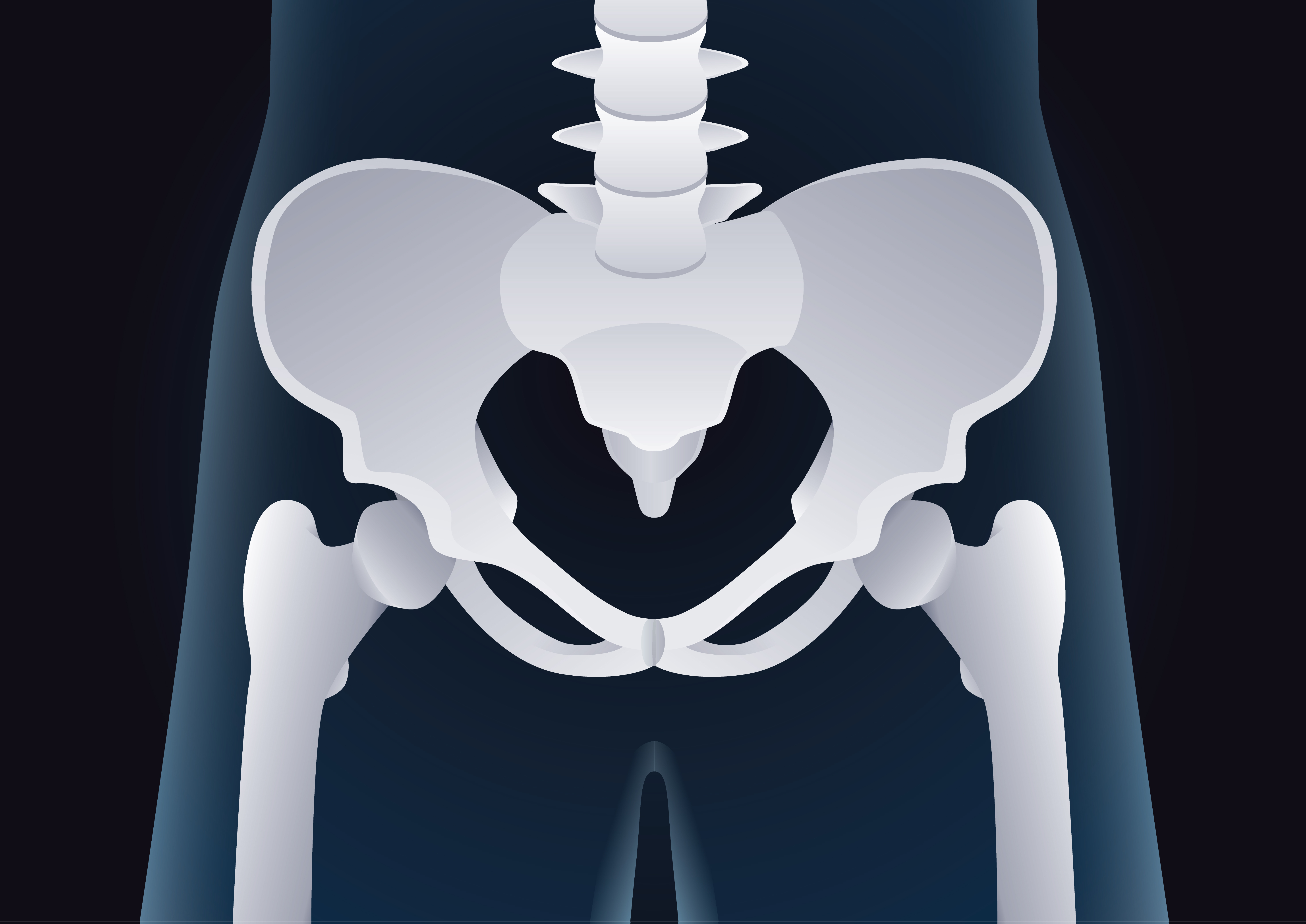
The pelvis is a collection of bones located below the waist and serves as a buffer for organs in the abdominal area. The pelvis also connects the upper and lower body. Did you know that a woman's pelvis with a man's pelvis is much different? Men have smaller pelvic size than women. So, what are the functions and parts of the pelvis? Come on, see the review of the male pelvic anatomy below.
What is the male pelvic anatomy like?
Pelvis in men has different functions and sizes than women. The size of the pelvis in women is generally wider and shallow because it functions as a means of movement, as well as undergoing pregnancy and childbirth. While in men, the pelvis is more optimized as a means of gesture.
A man's pelvic cavity is narrower than a woman's and the segment between his sitting bones is also not as wide as a woman's. This is because the pelvis is designed as a means of gesture in men, different from women who use the segment as a birth canal.
The difference between the male and female pelvic bones can be seen in the picture below.

The pelvic bone consists of three constituent bones, namely the hip bone, the sacrum, and the coccyx. The hip bone itself, consists of three component parts namely ilium, ischium, and pubis. These three parts of bone are separated from birth and then fuse when entering puberty.
1. Ilium
Among the three bones that make up the hip bone, ilium is the biggest part. If you notice, ilium expands and forms like a curved wing, located at the top of the acetabulum. Ilium has two surfaces:
- Inner surface - shaped concave known as the iliac fossa, its function as a place attached to the iliac muscle.
- A convex outer surface known as the gluteal surface, bound to the gluteal muscle.
In addition to its curved shape, the composition of the constituent parts of ilium also thickens which will form the iliac crest. This section extends from the front of the iliac bone to the back of the iliac bone.
2. Pubis
Pubis is the frontal part of the hip bone. Both pubic parts are united by the symphysis pubis. The position of the pubic symphysis is parallel to the coccyx, although its location may vary in some people. Pubic symphysis tends to be central to a person's body.

3. Ischium
Ischium forms the posteroinferior part of the hip bone. In ischium there are two important ligaments:
- The sacrospinous ligament - located from the spine to the sacrum, forms a large sciatic foramen
- Sacrotuberous ligament - located from the sacrum to the ischial tuberosity, forming a smaller sciatic foramen
As mentioned before, in addition to the hip bones there is a tailbone and sacrum which also make up the hip bones. The location of the coccyx is under the sacrum. The pelvis forms the spine and socket of the hip joint on the body.
The organs are protected in the anatomy of the male pelvis
The pelvic bone in men functions to protect important organs in it, such as the main digestive organs and reproductive organs.
In the digestive organs, there is the small intestine which is the longest part of the digestive tract, the task is to receive food and start processing it while absorbing nutrients for the body. The small intestine is connected to the large intestine in the lower right part of the abdominal cavity. To prevent food returning to the small intestine is the duty of a muscle sphincter (a special valve that automatically opens and closes when food enters).
While the male reproductive organs have their own muscles, the penile muscles, the corpora cavernosa, are located on the sides of the penis. When an erection occurs, the corpora cavernosa is usually filled with blood and makes the penis tighten. When the penis is erect, there is an inner layer called the corpus spongiosum, still in a springy and supple state.
This layer protects the urethra - the channel that carries urine and semen out of the body - from the erection to the discharge of semen during ejaculation. The release of urine from the body is regulated by the prostate gland. The location of the prostate gland is above the bladder, which is a place to store urine.