Contents:
- Medical Video: Stages of Kidney Disease
- What are the functions of the kidney?
- Parts of the human kidney
- 1. Kidney cortex
- 2. Kidney medulla
- 3. Kidney pelvis
- Various kidney diseases
- 1. Acute kidney failure
- 2. Kidney stones
- 3. Glomerulonephritis
- 4. Acute nephritis
- 5. Urinary tract infections
- 6. Acidosis
- 7. Uremia
- 8. Polycystic Kidney (PKD)
- 9. Chronic kidney failure
- Type of examination of kidney function
- 1. Blood test
- 2. Urine test
- How do you keep kidney function healthy?
- 1. Avoid salty foods
- 2. Regular exercise
- 3. Meet the needs of body fluids
- 4. Pay attention to the medication consumed
- 5. Stay away from risk factors
Medical Video: Stages of Kidney Disease
Everyone has a pair of kidneys in his body. Just like other organs, you must maintain kidney health so that this one organ can work optimally and be free from kidney disease. To make it easier, you must first understand the functions of the kidney, kidney parts, and types of kidney function checks.
Relax, all the information you need has been provided in full through the following review.
What are the functions of the kidney?
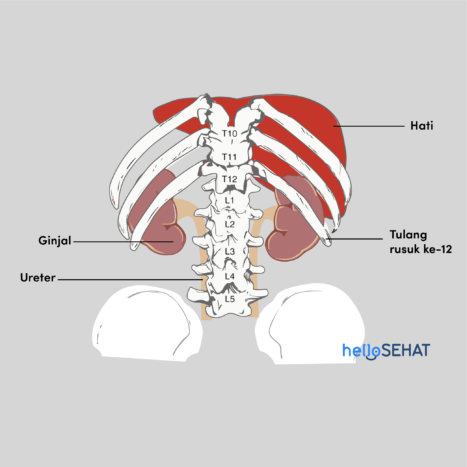
The kidneys are located along the muscular wall of the back (posterior muscle) of the abdominal cavity. The shape of the kidney is similar to a nut that is about the size of a fist, about 12 centimeters long and 6 centimeters wide.
Just like other organs, kidneys play an important role in the human body. The main function of the kidney is to filter out waste (waste) in the body, both from food, drugs, and toxic substances.
The kidneys filter 200 liters of blood every day. Of the many blood that is filtered, there are 2 liters of waste that must be removed through urine. For this reason, the kidney is equipped with a pair of ureters, a bladder, and a urethra that will carry urine out of the body.
In addition to removing residual substances in the body, the function of other kidney parts is to reabsorb substances needed by the body, namely amino acids, sugar, sodium, potassium, and other nutrients. The function of this part of the kidney is affected by the adrenal glands located at the top of each kidney.
The adrenal gland produces the hormone aldosterone. This hormone functions to absorb potassium from urine into blood vessels so that it can be used again by the body.
The function of the kidney part does not stop there. The kidneys are also responsible for producing hormones that are beneficial to the body, including:
- Erythropoietin (EPO), a hormone that stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells.
- Renin, functions to regulate blood pressure.
- Calcitriol, an active form of vitamin D that helps maintain bone health.
Parts of the human kidney
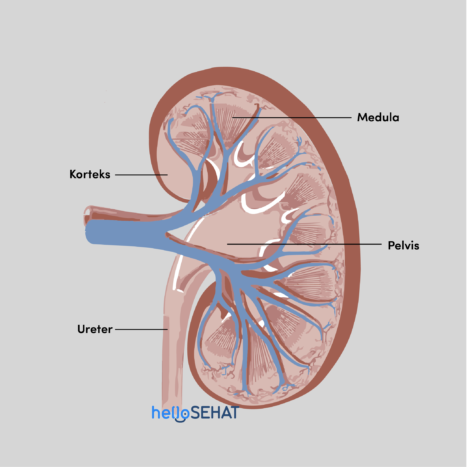
In general, the anatomy or parts of the human kidney consist of three parts, namely the renal cortex, renal medulla, and renal pelvis.
1. Kidney cortex
The cortex is the outermost part of the kidney surrounded by kidney capsules and a layer of fat. These kidney parts function to protect the structure in the kidneys from damage.
2. Kidney medulla
The kidney medulla is one of the subtle kidney parts. The kidney medulla consists of the arch of Henle and the kidney pyramid, a small structure that contains nephrons and tubules. This tubule serves to transport fluids into the kidneys and transport urine out of the kidneys.
3. Kidney pelvis
The kidney pelvis is the deepest part of a funnel-shaped kidney. The function of this part of the kidney is as a pathway for the fluid to move from the kidney to the bladder.
Pelvic kidney consists of two parts. The first part of the kidney pelvis consists of calyces, which is a cup-shaped chamber that serves to collect fluid before going to the bladder. Furthermore, the liquid will enter the hilum, which is a small hole that will drain the fluid into the bladder.
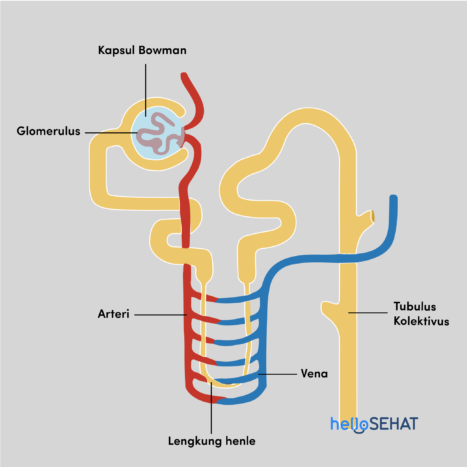
Apart from the main kidney parts, the kidney also consists of nephrons. These nephrons are located along the cortex to the kidney medulla. The function of the nephron itself is to filter blood, absorb nutrients, and drain waste substances into urine.
Nephrons consist of several parts, namely:
1. Malphigi body, also called the kidney corpus. Malphigi's body consists of two parts, namely the glomerulus or a collection of capillaries that absorb protein from the blood; and Bowman's capsule.
2. Kidney tubules, which is a collection of tubes that spread from Bowman's capsule to the collecting tube (collectivus tubules). The renal tubules consist of the proximal tubule, the Henle arch, and the distal tubule.
Various kidney diseases
If you do not maintain the health of kidney parts optimally, you must be careful about the risk of kidney disease. Because, most kidney disease does not cause any symptoms until the disease enters an advanced stage.
However, some of the most common symptoms of kidney disease include:
- Hard to sleep
- Anxious
- Difficult to concentrate
- Dry and itchy skin
- Changes in frequency of urination
- Pain when urinating
- Bloody urine
- Foaming urine
- Swelling around the eyes and legs
- Decreased appetite
- Muscle cramp
As we get older, almost all organs of the body will experience a decline in function. The same is true for the kidneys. As a result, the ability of the kidneys to filter blood is not optimal. For this reason, the elderly generally experience one or more of the symptoms of kidney disease above.
Unlike the decline in kidney function caused by kidney disease, this can lead to more serious health problems. If kidney function is reduced by 10 to 15 percent, this means that someone is considered to suffer from kidney failure. As a result, patients need dialysis (dialysis) or even kidney transplants so that their kidneys can continue to work optimally.
Various kidney diseases that can occur are as follows:
1. Acute kidney failure
Kidney failure is a condition when the kidneys are no longer able to filter out residual substances from the blood. This can be caused by urinary tract stones, drugs, severe dehydration, or trauma to the kidneys.
Symptoms of kidney failure can be a decrease in the amount of urine, swelling in the legs, shortness of breath, chest pain, anxiety, seizures, to coma. If not treated immediately, this can be life threatening to the sufferer.
2. Kidney stones
Kidney stones are crystals that form in the kidney. You may be more familiar with it as stone urine. Although the name is focused on the kidney parts, this disease is actually not only lodged in the kidney. Kidney stones can also move along your urinary tract, either in the ureter, the bladder, or the urethra.
If the kidney stone has moved to the urinary tract, the crystal can swipe and injure the walls of the urinary tract. This can cause blood spots to appear in the urine.
3. Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is inflammation of the glomerulus or small blood vessels that filter blood. Because the glomerulus is inflamed, the kidneys cannot filter blood normally and you can experience kidney failure.
Similar to other kidney diseases, glomerulonephritis symptoms can include bloody urine, high blood pressure, infrequent urination, abdominal pain, foaming urine, and swelling of the face, hands, feet and abdomen due to fluid buildup in the body.
4. Acute nephritis
Acute nephritis is inflammation (swelling) of the kidney nephron. This condition causes abnormal cells from the blood to enter the urine and cause inflammation. These cells are usually in the form of eosinophils or a type of white blood cell.
When inflammation has caused nephritis, patients will experience fever, vomiting, hypertension, back pain, and urinary disorders (burning sensation, frequency changes, foaming urine, or bloody urine).
5. Urinary tract infections
Urinary tract infections occur when bacteria infect your urinary tract, from the kidneys to the urethral tract. Symptoms are fever, pain during urination, and increased frequency of urination. Usually the doctor will suggest drinking enough water and giving antibiotics to treat the infection.
6. Acidosis
Acidosis is a condition when the body is filled with acidic blood. Normally, the body's pH is not too acidic or not too basic, which is around 7.4.
In conditions of acidosis, body pH tends to be less than 7.35. This can be caused by the amount of carbon dioxide in the body, diarrhea, decreased amount of insulin, or because the kidneys fail to filter alkaline substances in the body.
7. Uremia
Uremia is a buildup of urea in the blood which causes irritation to the nervous system. At first, uremia sufferers do not feel any symptoms. However, over time the sufferer will experience leg cramps, loss of appetite, headache, severe fatigue, vomiting, and difficulty concentrating.
8. Polycystic Kidney (PKD)
If there is one family member affected by polycystic kidney disease, that means you are at risk of developing the same disease. Yes, polycystic kidney disease is a hereditary disease caused by the presence of several cysts in the kidney.
Polycystic kidney sufferers often do not feel any symptoms. Symptoms of a new kidney cyst will be felt if the cyst has started to grow by three centimeters or larger. Symptoms include bloody urine, suppressed stomach, urinary tract infections, and so on.
9. Chronic kidney failure
Chronic kidney failure is a decrease in kidney function below the normal limit of more than 3 months. If you suffer from chronic kidney failure, this means that the function of your kidney part is no longer able to filter out impurities, control the amount of water in the body, as well as salt and calcium levels in the blood.
This disease is generally caused by hypertension and diabetes that are not immediately treated. Symptoms of chronic kidney failure are characterized by shortness of breath, vomiting, bone pain, swelling around the eyes and feet, fainting, numb hands and feet, and weight loss.
Type of examination of kidney function
One way to find out whether your kidney function is good or bad is by checking kidney function. Especially if you are at high risk of kidney disease, for example, have diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, or have a family history of kidney disease. If so, you should routinely check kidney function at least once a year.
There are two types of kidney function checks, namely blood tests and urine tests. Let's peel one by one.
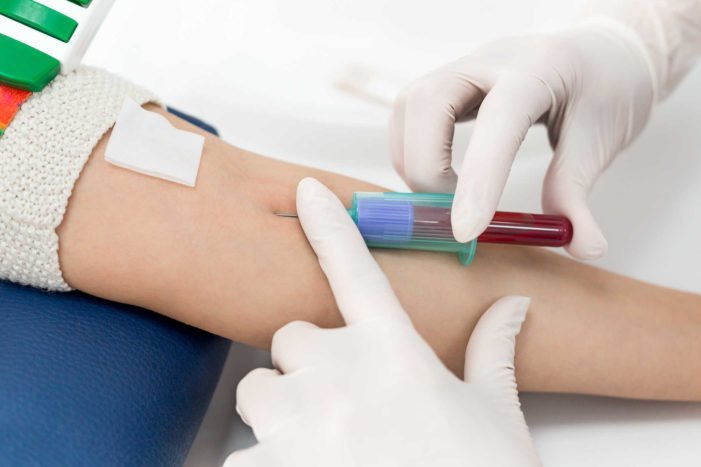
1. Blood test
A blood test is needed to find out how optimal your kidney parts are in filtering blood. This examination of kidney function is referred to as the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
On this test, your blood will be tested by looking at its creatinine levels. Creatinine is a waste product produced by muscle tissue and will be excreted through the excretion process.
When a person has kidney disease, his kidneys will have difficulty removing creatinine from the blood. So, the greater the creatinine, the better your kidney function.
Even so, this blood test does not only refer to the amount of creatinine. This creatinine result will be combined with your age, race, height, weight, and gender to determine the final value of GFR.
There are five phases of GFR that describe the severity of a person's kidney function, namely:
- Phase 1: GFR> 90, kidney function tends to be normal
- Phase 2: GFR 60-89, mild level kidney function disorder
- Phase 3a: GFR 59-45, moderate level renal function disorder
- Phase 3b: GFR 30-44, moderate level of kidney function to severe
- Phase 4: GFR 15-29, severe kidney function disorders
- Phase 5: GFR <15, kidney failure
If the results of examination of kidney function with a GFR show a number of less than 60, then the doctor will advise you to do other medical examinations, such as ultrasound, CT scan, or kidney biopsy. This is done to see the possibility of kidney stones, tumors, or other causes of kidney disease.
2. Urine test
Examination of kidney function is done by looking at the patient's urine condition. The aim is to see how much albumin (a type of protein) is involved in dissolving with urine.
Healthy kidneys will not allow albumin to enter the urine. The reason is, albumin should be in the blood, not residual substances that must be released through the urine. The presence of albumin in urine is called albuminuria.
Reporting from the National Kidney Foundation, there are two ways you can do to check albumin levels in urine, namely:
- Urine dipstick test, which is testing by dipping a strip into a urine sample. The strip will change color if there are abnormalities such as excess amounts of protein, blood, pus, bacteria, and sugar.
- Comparison of urine albumin and creatinine (UACR), namely the procedure for examining kidney function by comparing the amount of albumin with creatinine in the urine for 24 hours. If the UACR results exceed 30 milligrams per gram, then this can be a sign of kidney problems.
How do you keep kidney function healthy?
The kidneys are important organs that must be taken care of. The reason is, this organ can affect other body organs. If your kidney has a problem or gets kidney disease, then other organs will come into trouble, especially the heart.
For kidney function to remain normal, there are various healthy ways you can do, namely:
1. Avoid salty foods
Most eat salty foods can interfere with the balance of minerals in the blood. This can aggravate the work of the kidneys and interfere with the function of the kidney. Over time, you run the risk of kidney disease.
So, exchange processed foods that contain high salt with healthier foods. Examples of fresh fruit and vegetables, lean meat and nuts.
2. Regular exercise
Hypertension is a risk factor for chronic kidney disease. That is why, you are encouraged to control blood pressure so that your kidney function is maintained.
Rather than taking a shortcut by taking hypertension medication, you should do a healthier way with exercise. Regular exercise at least 20 minutes a day can help control your blood pressure. As a result, your kidney parts will stay healthy, work optimally, and avoid the risk of kidney disease.
3. Meet the needs of body fluids
If you want to avoid kidney disease, make sure your body is fluid enough. Because, drinking enough water can help optimize the function of the most important part of the kidney, namely removing toxins or poisons in the body.
How much your fluid needs every day depends on your gender, age and type of activity. Ask your doctor about your daily fluid needs.
4. Pay attention to the medication consumed
Are you taking certain drugs? Come on, check the medicine content again. Because, some types of drugs can affect your kidney health.
NSAID drugs are one of the over-the-counter drugs that can actually interfere with kidney health at any time. Consult a doctor to get recommendations for other drugs that are safer for your kidney function.
5. Stay away from risk factors
To keep kidney function healthy, make sure you avoid various risk factors. Some risk factors that can increase your chances of getting kidney disease are diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and a family history of kidney disease.
If you feel you have one of the risk factors, this means you need to check kidney function regularly. This aims to control the risk factors so as not to develop into kidney disease.