Contents:
- Medical Video: Diabetic Foot Ulcers 101
- Causes of foot ulcers in diabetics
- 1. Poor blood circulation
- 2. Nerve damage
- 3. Infected wounds
- 4. Decreased immune system
- Ulcers in diabetics do not always hurt
- How do you treat ulcers in diabetics?
- 1. Take care and check the wound regularly
- 2. Clean the wound
- 3. Check with the doctor
- 4. Avoid physical contact and put pressure on the wound
- 5. Wear safe and closed footwear
Medical Video: Diabetic Foot Ulcers 101
According to the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons, diabetics have a 15% risk of getting ulcers (diabetic ulcers). Ulcers that occur in diabetics usually occur due to the effects of neuropathy or damage to nerve tissue which is a complication of diabetes. Diabetes is also a major cause of (non-traumatic) amputation in the United States. About 14 to 24% of diabetic patients have to undergo amputation due to injuries to the body and not being treated properly.
Causes of foot ulcers in diabetics
Ulcers that occur in diabetics are usually caused by several things, namely:
1. Poor blood circulation
Damage to blood vessels starts from small blood vessels, which are usually found in the hands and feet. However, the body parts that most often experience ulcers (diabetic ulcers) occur in the lower body, this is due to the lower body like feet away from the main blood circulation. It is known that 10-20% of ulcers that occur in diabetics occur in the lower legs.
Poor blood circulation is one of the complications of diabetes. This will slow wound healing, because the wound cannot get the intake and "medicine" that should be obtained from the blood flowing. If this continues, it can cause an infected wound and then ulcers appear.
2. Nerve damage
According to the Indonesian Ministry of Health, 54% of diabetics suffer nerve damage as a complication of diabetes. Nerve damage is caused by high blood sugar in diabetics. Sugar is the main ingredient in cell metabolism. When sugar is not properly channeled into cells in the body, the cell will experience 'starvation'. If this happens continuously can cause cell death. Death to nerve cells can cause damage to nerve tissue. This nerve damage then decreases the body's sensitivity, one of which is sensitivity to the feet in feeling sharp objects.
3. Infected wounds
Associated with the two previous factors, wounds that do not heal are caused by poor blood circulation and the sugar is not well channeled. Wounds are difficult to heal and become a place for developing bacteria and viruses.
4. Decreased immune system
Diabetics have a low immune system, which then causes wounds to heal longer and easily get infected.
Ulcers in diabetics do not always hurt
Pain is not the main symptom that occurs in wounds suffered by people with diabetes, because usually they do not even feel pain in the injured leg. The first thing that often arises is pus or fluid that comes out on the wound, then redness and swelling will appear on the wound and over time cause a bad smell.
Other symptoms caused if the wound is getting worse is the wound looks black because more and more cells die from not getting food from the blood vessels. Then it will become gangrene, where more dead cells will appear and appear on the surface around the wound. When this happens, usually the medical action taken is to carry out an operation to remove the dead tissue or the ulcer.
How do you treat ulcers in diabetics?
If there are injuries to diabetics, what can be done to prevent them becoming a serious problem and speeding up the healing of these wounds are:
1. Take care and check the wound regularly
Do not underestimate small wounds, because from small wounds that are not properly treated, can be a place for the growth of bacteria that can cause infection.
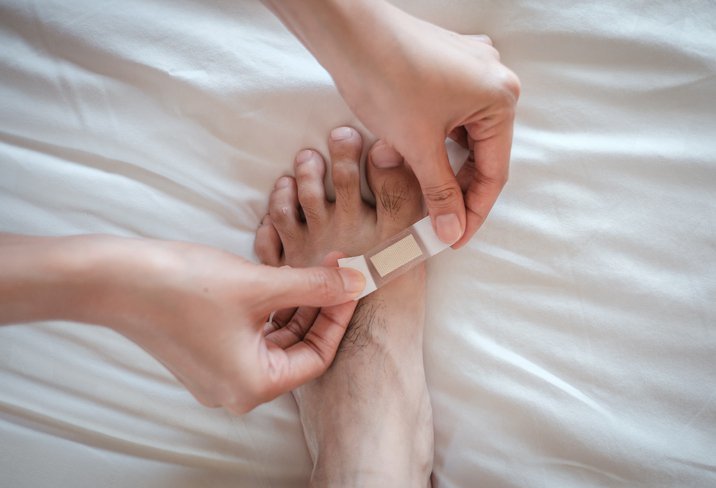
2. Clean the wound
Rinse the wound with running water to remove dirt on the wound, do not use soap, because it can cause irritation. Use an antibiotic ointment to prevent infection and cover by using a sterile bandage. Change the bandage regularly every day and clean the skin around the wound using soap. Be vigilant and watch for wounds whether or not an infection appears.
3. Check with the doctor
Check the wound to the doctor, even if only a small wound does not wait for the wound to become severe and getting bigger. The smaller and the earlier the wound is examined by a doctor, the higher and faster the healing process.
4. Avoid physical contact and put pressure on the wound
In diabetics often found a wound on the bottom of the foot, you should not put pressure. For example if the wound is on the sole of the foot, then try not to walk too much.
5. Wear safe and closed footwear
Wearing closed and thick footwear will prevent diabetics from being exposed to things that have the potential to hurt the skin.
READ ALSO:
- 4 Sports that are Right for People with Diabetes
- Is Diabetes Really Reducing Male Fertility?
- Can People with Diabetes Have Milk?