Contents:
- Medical Video: Health Alert: Blood clots and the HPV vaccine
- Who can get HPV?
- How to prevent HPV infection?
- How does the HPV vaccine work?
- Side effects of the HPV vaccine
Medical Video: Health Alert: Blood clots and the HPV vaccine
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a group of viruses consisting of 130 types of HPV. HPV infection can occur to anyone regardless of age, even teenagers or children who have not been sexually active can be exposed to this virus. HPV 6 and HPV 11 are HPV viruses that cause genital warts. HPV 16 and HPV 18 are HPV viruses that need to be watched out because they can cause cervical cancer.
To find out more about HPV, see the explanation below.
Who can get HPV?
HPV infection is a problem for both men and women. In women, HPV infection can cause cervical cancer. HPV infection can also cause problems that cause cancer in the vagina, vulva, anus, mouth, and throat. In men, HPV infection may cause cancer of the penis, anus, mouth, throat and genital warts
HPV infections can be transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, oral, and anal sex. Many people who are exposed to the HPV virus in their body do not feel any signs or symptoms, so they can transmit the virus without realizing it.
How to prevent HPV infection?
Primary prevention measures or the most important thing to prevent cervical cancer is to vaccinate HPV. HPV vaccination makes the body form antibodies to the HPV virus, so the incoming virus will die and not cause cervical cancer.
The HPV vaccine is an inactive vaccine (containing a protein similar to the HPV virus shell structure that does not contain viral DNA). So, this vaccine is very safe and is unlikely to infect humans. After being injected, the HPV vaccine will stimulate the formation of an immune response in the body, thus creating protection against cervical cancer.
There are 2 types of HPV vaccinations:
- Quadrivalent: provides protection from HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18.
- Bivalent: only protects against HPV types 16 and 18.
If the purpose is to prevent cervical cancer, one of the two vaccines can be used, because it is good Bivalent and Quadrivalent both beneficial against cervical cancer caused by HPV types 16 and 18.
But the HPV vaccine quadrivalent should be used if you expect additional protection against pre-cancerous vulva, pre-vaginal cancer, pre-anal cancer caused by HPV types 16 and 18, and genital warts caused by HPV types 6 and 11.
HPV vaccine Quadrivalent can be given to women aged 9-45 years and men aged 9-26 years. While the HPV vaccine Bivalent can be given to women aged 9-25 years.
How does the HPV vaccine work?
- The Quadrivalent vaccine, given as many as 3 doses each on the month schedule 0, 2, and 6.
- Bivalent vaccine, given as many as 3 doses at 0, 1, and 6 months.
HPV vaccination is recommended as early as possible in adolescence, 9 to 13 or 14 years. This age range is considered effective because at this time the body provides a better immune response protection than the age above it. This also underlies that the administration of the HPV vaccine at this age range is sufficiently given 2 doses in the month of 0.6 or 0.12.
But for those of you who have had sex, of course you can still get HPV vaccination. This is still the best way to protect yourself from viruses that might not have developed in you.
The spread of cervical cancer can also be prevented by secondary prevention measures, namely through early detection by carrying out a pap smear test. This test is recommended to be done once a year for women who have had sexual relations. Women who are pregnant can also take a pap smear test because the procedure is safe
Side effects of the HPV vaccine
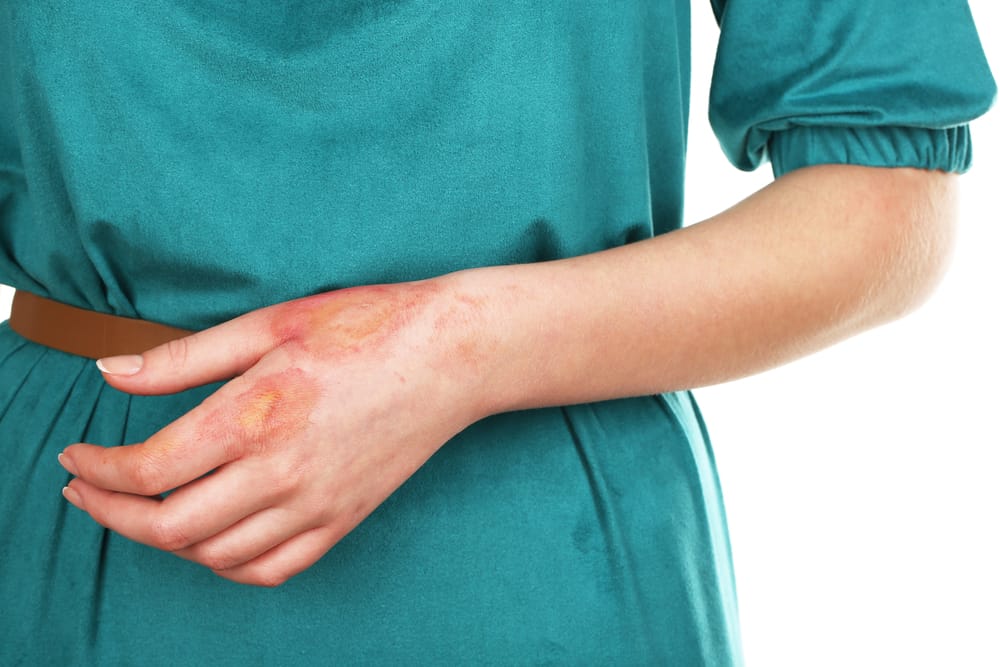
Side effects that might occur after the injection of the HPV vaccine are as follows:
- Local reactions: Pain at the injection site, erythema / redness, swelling.
- Systemic reactions: headaches, pyrexia, nausea, fatigue(fatigue)