Contents:
- Medical Video: How Antioxidants Work and Where to Get Them
- How do antioxidants work in the body?
- What are the sources of antioxidants?
- Antioxidants and prevention of diseases
Medical Video: How Antioxidants Work and Where to Get Them
Have you ever heard of free radicals? Components that are mentioned can cause various kinds of this disease that turns out to be around you everyday. Free radicals are a by-product of food processing into energy. In addition you can also get free radicals from food, air, even from your body's reaction to sunlight. Well, our body has a special defense mechanism to counteract the bad effects of free radicals, namely antioxidants.
There are two types of antioxidants, namely endogenous produced by the body, and exogenous which is obtained from outside the body, especially from food. Although it can produce its own antioxidants, the body tends to depend more on antioxidants from outside. These antioxidants will work by giving electrons to free radical molecules so that they neutralize the bad nature of these free radicals.
How do antioxidants work in the body?
The way antioxidants work is related to how free radicals work. Free radicals in the body in the form of molecules that have free electrons, where electrons should be pairs. These free electrons make free radicals very reactive so they can cause damage to the surrounding cells. Because of the pairing of electrons, free electrons in these free radical molecules can donate electrons or receive electrons from healthy body cell molecules. Healthy body cell molecules will then be the same as free radicals, causing many other free radicals. Reactive free radicals then affect the membrane to the cell nucleus and damage the components contained in a cell, triggering the cell to destroy itself. Although it can attack all types of cells, free radicals mainly attack fat cells, nucleic acid cells, and proteins.
The main function of antioxidants is to donate electrons to unpaired electrons in free radical molecules, preventing the free electrons from pulling electrons from healthy cells. What is special about the work of antioxidants is that after giving electrons, antioxidants will not turn into free radicals like other cells that give electrons. So that antioxidants work like neutralizing the reactive nature of free radical molecules.
What are the sources of antioxidants?
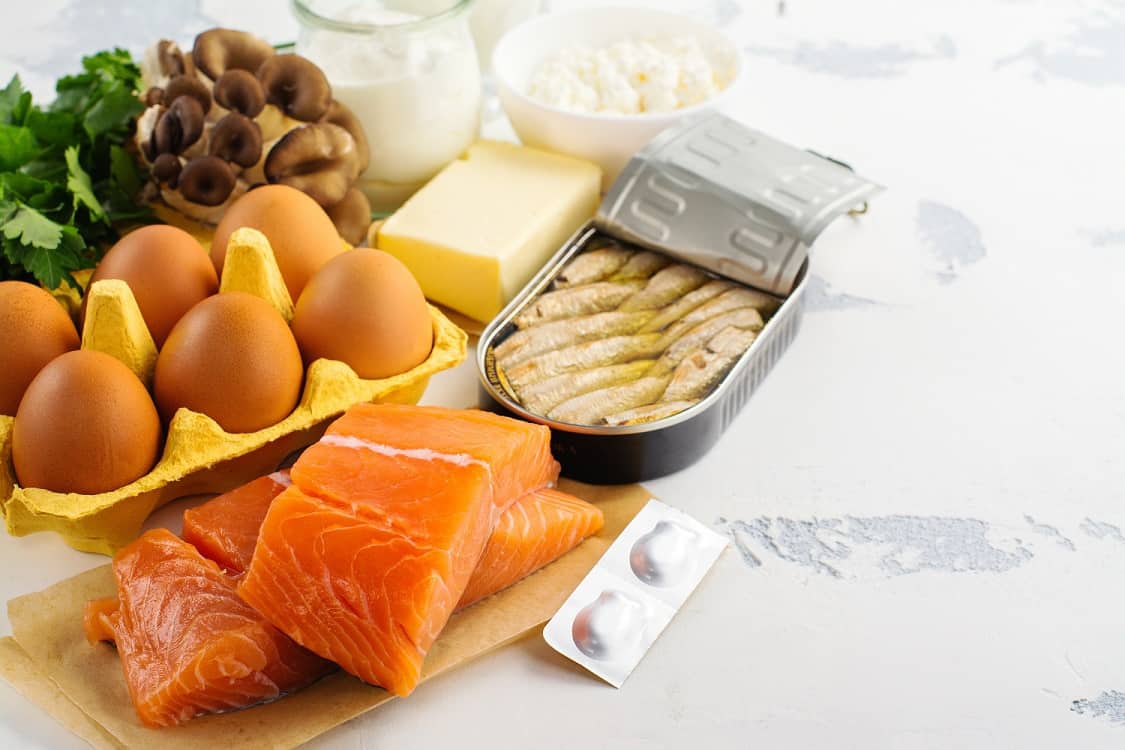
There are lots of vitamins and phytonutrients, antioxidants you can easily find in your food and drinks everyday. Examples of antioxidants are vitamin C, vitamin E, and carotenoids such as lutein, beta carotene, and lycopene where there are many in vegetables and fruits. Vitamin E helps protect body cells from damage that can cause cancer, heart disease, and eye diseases. Vitamin E usually works together with vitamin C to prevent various degenerative diseases. You can find Vitamin E in plant oils, products whole grain, grains, and nuts.
Besides vitamin E, vitamin C is probably the most widely known type of antioxidant. Helps protect the body from infection, prevents cell damage, to help collagen production which functions to attach bone to muscles are some of the benefits of vitamin C. You can find vitamin C in citrus fruits, mangoes, papaya, strawberries, vegetables such as tomatoes, broccoli, and potatoes.
In addition to derived from vitamins, antioxidants can also be found in phytonutrients, a component that is only found in vegetables and fruit and plays a role in giving the color or aroma typical of these fruits. Phytonutrients from the carotenoid group contain lots of antioxidants. For example there are beta carotene, lycopene, and lutein which are mostly found in carrots, tomatoes, and dark green vegetables such as broccoli and kale.
Antioxidants and prevention of diseases
As explained earlier, antioxidants are counteracting free radicals. If left unchecked, free radicals can cause damage to healthy body cells. Free radicals are thought to be the cause of various diseases such as cancer, heart disease, reduced visual ability, to Alzheimer's. Antioxidants as neutralizing the reactive properties of free radicals can prevent these diseases, but the effect will be greater if antioxidants are consumed in their natural form, not consumed in supplement form.
Several studies have shown that consuming antioxidant supplements has little effect on the prevention of diseases caused by free radicals. Although these studies have their own limitations, research related to the benefits of eating vegetables that are rich in antioxidants actually gives positive results to counter the adverse effects of free radicals.
READ ALSO:
- Get to know phytonutrients: Different food colors, different nutrients
- Two Vitamins that Make the Flu Clear to Approach
- Vitamin C Is Better Than Food or Supplements?