Contents:
- Medical Video: What Is The Best Vitamin D | Get Vitamin D3 Colecalciferol or Cholecalciferol | Sun For VitaminD
- Vitamin D is a nutrient that can be obtained from food and sunlight
- Then, the best source of vitamin D is?
- Too often exposure to the sun is also not good
Medical Video: What Is The Best Vitamin D | Get Vitamin D3 Colecalciferol or Cholecalciferol | Sun For VitaminD
Based on the results of a published study Journal of Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutic, it is estimated that around 50% of people around the world experience vitamin D deficiency. In fact, vitamin D is a vitamin that is needed by the body to strengthen bones and teeth and to maintain endurance. Most of the intake of vitamin D can be easily obtained from sun exposure. However, you can also provide daily vitamin D from the various foods you consume everyday. So, which is better: basking in the hot sun or from food?
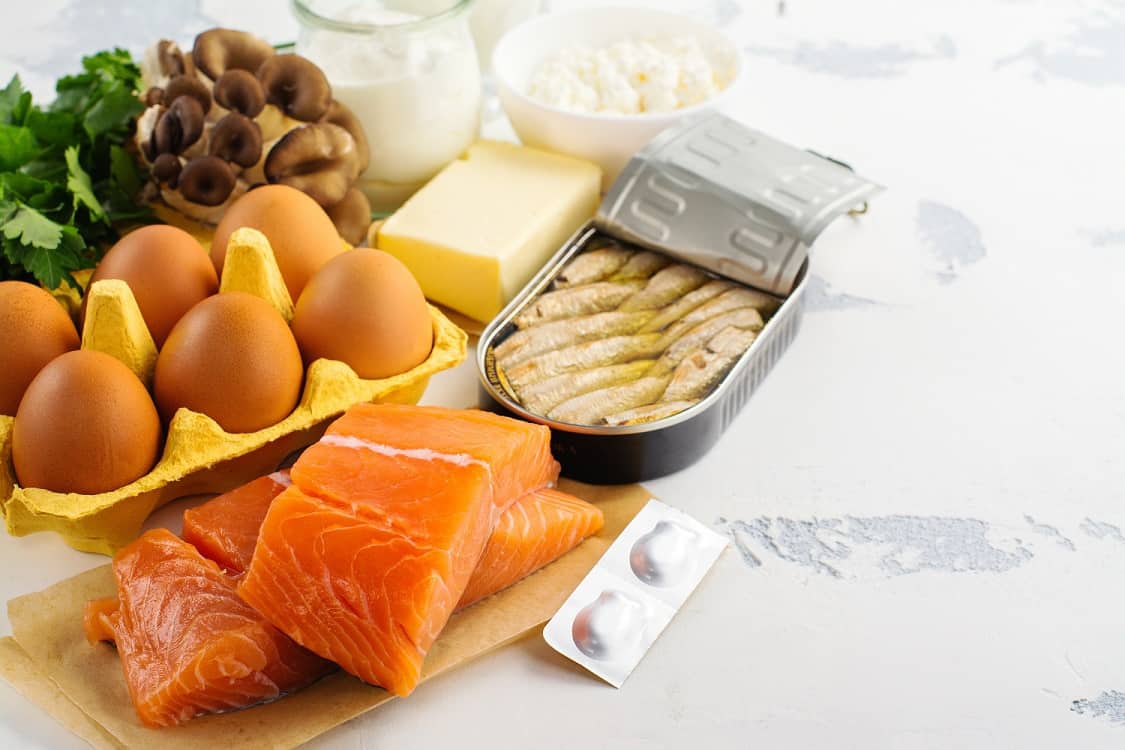
Vitamin D is a nutrient that can be obtained from food and sunlight
Another name for vitamin D is "sun vitamins" because nearly 80% of the vitamin D needed by the body comes from sunlight. However, vitamin D itself consists of two forms, namely vitamin D2 and vitamin D3.
Vitamin D3 is actually called vitamin sun. Your body will produce vitamin D automatically when exposed sunlight by converting cholesterol to the skin into calcitriol. Calcitriol will be directly channeled to the liver and kidneys to produce vitamin D3 (calciferol) needed by the body.
Meanwhile, vitamin D2, which has another name ergocalciferol, can be found in a number of plant-based food sources, such as almond mushrooms, soybeans, and coconuts. These plants produce their own vitamin D2 content by processing the UV radiation they receive.
Then, the best source of vitamin D is?
The quality of vitamin D3 (calciferol) derived from sunlight is reported to be far superior to vitamin D from food. Because, vitamin D3 is more easily digested by the body but can last longer in blood circulation. Karsiferol is considered 87% stronger in increasing and maintaining the concentration of vitamin D in the blood.
When obtained at the same time as the same portion, levels of vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) dropped dramatically after 14 days, while calciferol levels peaked on day 14 and remained stable for 28 days after the first intake.
Therefore, vitamin D3 is more effective for helps the body to quickly absorb calcium, which is an essential nutrient for bone health. Calciferol has been shown to be more effective in maintaining bone density in older adults thereby reducing the risk of fractures when compared with ergocalciferol (vitamin D2). In addition, vitamin D3 is also reported can reduce the risk of heart disease, joint pain, depression, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, and skin cancer.
Too often exposure to the sun is also not good
Even though sunlight from D3 is proven to be better by many studies, it does not mean you have to and may linger in the sun. The World Health Organization (WHO) states that you only need to be exposed to sunlight at least Just 5 to 15 minutes for two to three times a week without using sunscreens to meet the body's vitamin D intake.
Sunbathing longer than recommended and without adequate protection is actually dangerous. Excessive exposure to UV radiation can increase risk sunburned skin, melanoma skin cancer, even heat stroke which can be fatal.
Sunlight recommended by experts is from 10am to 2pm. This time is considered the most appropriate time to get the benefits of sunlight while reducing the risk of danger of ultraviolet radiation.
Even so, get intake vitamin D from food sources also remains important, especially for people whose daily activities dwell indoors and are rarely exposed to the sun. Therefore, the best step to getting enough vitamin D is to balance between a healthy diet and outdoor physical activity (for example, by exercising).