Contents:
- Medical Video: Migraines in children: Guidelines for primary care management of headache
- Various risk factors for hydrocephalus in children
- Signs and symptoms of a child experiencing hydrocephalus
- Symptoms of hydrocephalus in newborns
- Symptoms of hydrocephalus in children
- Are there ways to reduce the risk of hydrocephalus in children?
Medical Video: Migraines in children: Guidelines for primary care management of headache
Hydrocephalus is a condition characterized by the size of a baby's head that enlarges abnormally due to a buildup of fluid in the ventricular cavity of the brain. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) reports that around two out of 1000 babies born in the world experience hydrocephalus. Meanwhile, cases of hydrocephalus in Indonesia can reach an average of 4 per thousand births. So, what are the risk factors for hydrocephalus in children?
Various risk factors for hydrocephalus in children
The brain normally contains clear fluid produced in the ventricular cavity of the brain. This fluid is called cerebrospinal fluid. Cerebrospinal fluid flows from the spinal cord to the entire brain to support various brain functions.
But when the amount is excessive, this will actually result in permanent damage to brain tissue which causes disruption of children's physical and intellectual development.
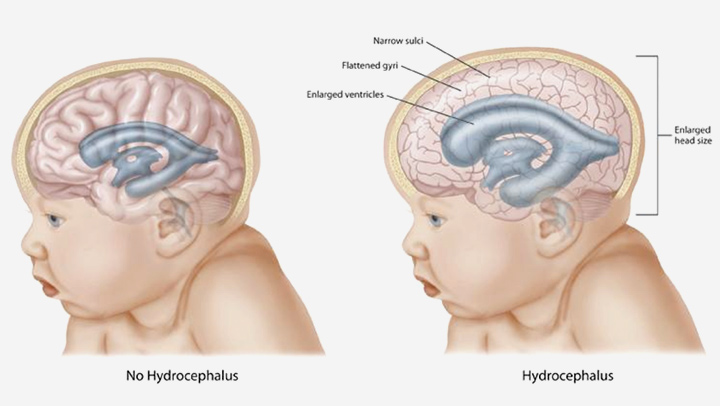
Enlargement of head size occurs because of the excessive amount of cerebrospinal fluid production so that it compresses the skull, or because the cerebrospinal fluid cannot flow properly in the brain.
Most cases of hydrocephalus in children occur from birth (congenital birth defects / congenital abnormalities). In addition there are several conditions that increase the chances of hydrocephalus in newborns, such as:
- The central nervous system does not develop normally so it blocks the flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- The presence of bleeding in the ventricles of the brain, which triggers the possibility of premature babies born.
- The mother has an infection that attacks the uterus during her pregnancy, causing inflammation in the fetal brain tissue. For example rubella infection, toxoplasma, goiter or chicken pox.
In the case of a new hydrocephalus that occurs after a child has grown up, the risk factors include head injury that affects the brain, or:
- A tumor grows in the brain or spinal cord.
- Infection of the brain or spinal cord.
- Bleeding in brain blood vessels.
- Head surgery.
Signs and symptoms of a child experiencing hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus can cause permanent damage to the brain and the child's head cavity. That is why it is important to recognize what signs and symptoms might occur if your child has hydrocephalus, so that he can seek medical help as soon as possible.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus in newborns
- An abnormal soft lump appears on the top of the head
- Rapid change in head circumference
- The size of the head is not normal
- Downward eye view
- Easy to fuss
- Refuse to eat
- Easy to sleep
- Muscles weaken
- Growth stunted
Symptoms of hydrocephalus in children
- Headache
- Blurred vision or squint eyes
- Changes in facial structure
- Growth stunted
- Easy to sleep
- Having trouble eating
- Body balance is not stable
- Loss of muscle coordination
- Easy to get angry
- Cognitive ability is impaired
- Seizures
- Nausea and vomiting
- Difficult to concentrate
Are there ways to reduce the risk of hydrocephalus in children?
Hydrocephalus in children is actually not a preventable condition. However, you can breathe a little relieved because at least there are still ways to reduce the risk of this disease.
If you are or are planning to become pregnant, make sure to always get proper care during pregnancy, for example by routinely checking pregnancy. This method can help you to detect abnormalities in the fetus, and reduce the risk of premature babies who can be a risk factor and / or complications of hydrocephalus.