Contents:
- Medical Video: How to Give an Injection with an Insulin Pen | Cincinnati Children's
- Get to know the insulin pump component
- How does the insulin pump work?
- Why should you use this tool?
- Where is the right place to put an insulin pump?
- What are the disadvantages of using an insulin pump?
- Take off the insulin pump
Medical Video: How to Give an Injection with an Insulin Pen | Cincinnati Children's
Insulin injections are the most popular method of controlling blood sugar for diabetics, in addition to lifestyle changes and medication. However, what happens if diabetics have fear of needles and have to inject?
When you find out that you are diagnosed with diabetes, a series of treatments have popped up in your head. Starting from a diet, eating patterns that are not as free as before, taking various drugs, until injections every day fill your mind even when you are still in the doctor's examination room.
As diabetics, your main goal is to control blood sugar levels to stay within safe limits so as to avoid various complications. Unfortunately, this is often constrained given the control of diabetes requires high discipline. An insulin pump can be the solution, especially for those of you who are often lazy or forget about the injection schedule, even needle phobia.
An insulin pump is one way to administer insulin into the body, in addition to using a syringe or injection pen (insulin pen). An insulin pump is a device with a battery that helps provide insulin automatically for your body throughout the day. By using an insulin pump, you don't need to be busy remembering or stopping your activities just for injecting insulin.
This tool can be used for type 1 diabetes patients and type two diabetes.
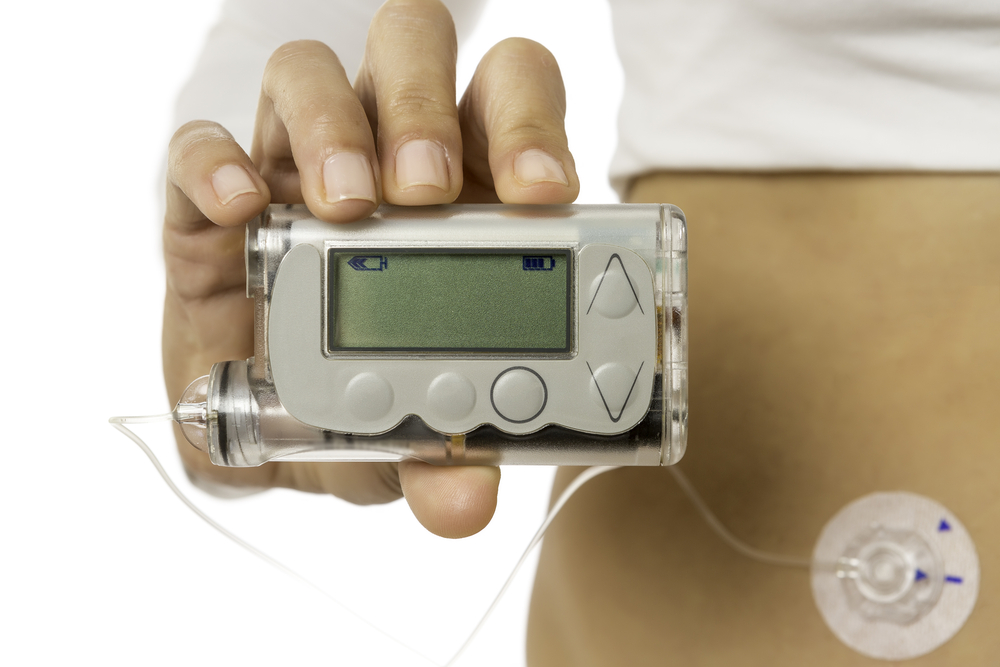
Get to know the insulin pump component
An insulin pump is a small electronic device that helps diabetics control blood sugar. The size is usually as big as a cellphone and is easy to carry anywhere. Usually pinned on a belt or in a pants pocket. An insulin pump can supply insulin needs throughout the day in accordance with the prescribed dose, and can be added with bolus doses if needed. The bolus dose is additional insulin given at around meal times.
An insulin pump helps you adjust insulin administration to your lifestyle, not the other way around if you have to inject insulin. Insulin injections make it you who have to adjust to the insulin administration schedule.
The insulin pump has several components that you need to pay attention to and know well, so that its use can run optimally. The components in this pump consist of:
- Container / reservoir. This is where insulin is stored. You must make sure that the insulin container is filled to keep the supply of insulin into the body
- Catheter. It is a small needle and a hose that is placed under the fat tissue in the area of your skin that will deliver insulin into the body. You must replace it regularly to avoid the risk of infection
- Operation button. This button allows you to adjust the insulin supply to the body throughout the day and adjust the bolus dose when the meal schedule arrives
- Tube. It is a thin tube that will channel insulin from the pump to the catheter.
How does the insulin pump work?
Using this pump, you don't need to feel burdened with the possibility of missed injections or dealing with your fear of needles. You could say, you can forget about needles when using an insulin pump.
The way the insulin pump works is similar to how the pancreas works in the body. The pancreas works for 24 hours by releasing insulin little by little to keep blood sugar levels within safe limits. So is the insulin pump.
The insulin pump is channeled rapid or short acting insulin for 24 hours through a catheter that has been installed in the body. Your insulin dose can be divided into:
- Baseline dose / basal dose
- Bolus dose to maintain sugar levels after eating due to carbohydrate breakdown
- Dosage correction or additional dose
Basal insulin is distributed throughout the day and keeps your blood sugar levels normal. Usually you can adjust the amount of insulin given at night or during the day.
When eating schedules, you can use the existing button to give bolus doses. If you eat more than usual, you can simply add the number of bolus doses to release more insulin.
Additional doses are given when you find high blood sugar levels in a condition you should not, such as before eating. This additional dose is useful for correcting sugar levels to return to normal limits.
Using an insulin pump means you have to monitor this device and the point where the catheter is installed. You may need to replace the catheter placement point every two or three days to prevent infection. Also remember to keep the insulin tube filled. In order to make it easier for you to remember, check your insulin tube every time you change the catheter point.
Check your blood sugar at least four times a day to see if you have the right dose of insulin. Usually dose adjustments will also be made to adjust the activities carried out with the eating habits that you live. Don't change your insulin dose without consulting your doctor first.
Why should you use this tool?
Some doctors recommend administering insulin with this method because of its slow release of insulin, as is done by the pancreas. Research also states that the use of insulin mixed in the pump results in better blood sugar control compared to daily injection.
Where is the right place to put an insulin pump?
You may have understood how the insulin pump works. However, your next question is where can the insulin pump be placed? Remembering these objects will stick to you all day wherever you go.
You can attach an insulin pump to your belt or pants pocket. You can even attach it to underwear, just like when you pin headset.
Because the insulin pump works for 24 hours, you also have to use this tool when you sleep. Make sure that the insulin pump stays at the limit where the hose can reach it so that it doesn't come loose. You can try lying side by side on your bed. You can also pin it on a blanket, pajamas or pillow.
An insulin pump is a waterproof device, but that doesn't mean you can take it when taking a shower. Usually, this device is equipped with features to remove it when doing activities such as swimming or bathing. You can put it in a place that is protected from water or you can buy a storage container.
What are the disadvantages of using an insulin pump?
An insulin pump is a safe and comfortable way to administer insulin to control blood sugar levels. This method can also provide more precise amounts of insulin. Even so, there are still shortcomings brought about by this tool.
Users of insulin pumps must be diligent in checking blood sugar levels and calculating carbohydrates in order to determine the bolus dose that must be given. They also must be able to calculate the number of calories that come out through the activities carried out.
Using an insulin pump requires proper training and direction to operate it. Because, even though administration is done automatically, you must pay attention to how your body responds to the treatment given to avoid side effects.
The risk of infection at the point of catheter placement may also occur. That is why, replace the point of catheter placement regularly, about two or three days to avoid the risk of infection.
Take off the insulin pump
There may be times when you have to remove the device, for example when taking a shower. When deciding to remove the insulin pump, remember that you will stop all the supply of insulin that enters your body.
Here are some things you need to pay attention to when removing this tool.
- If you stop the insulin pump when a bolus dose is being given, you cannot give (continue) the remaining dose when putting the insulin pump back on. You may have to repeat the new dose from the beginning
- Make sure that the bolus dose can meet the basal dose that might be lost because you released the insulin pump. If your blood sugar is below 150 mg / dl, you can wait an hour for bolus doses
- Don't let yourself not get insulin for more than one or two hours
- Monitor your blood sugar levels every three to four hours