Contents:
- Medical Video: How To Reduce High Blood Pressure Naturally | How To Prevent High Blood Pressure Naturally
- What is this research?
- Who was the research conducted at?
- Then, what are the results?
- What is the purpose of the results of this study?
- Conclusion
Medical Video: How To Reduce High Blood Pressure Naturally | How To Prevent High Blood Pressure Naturally
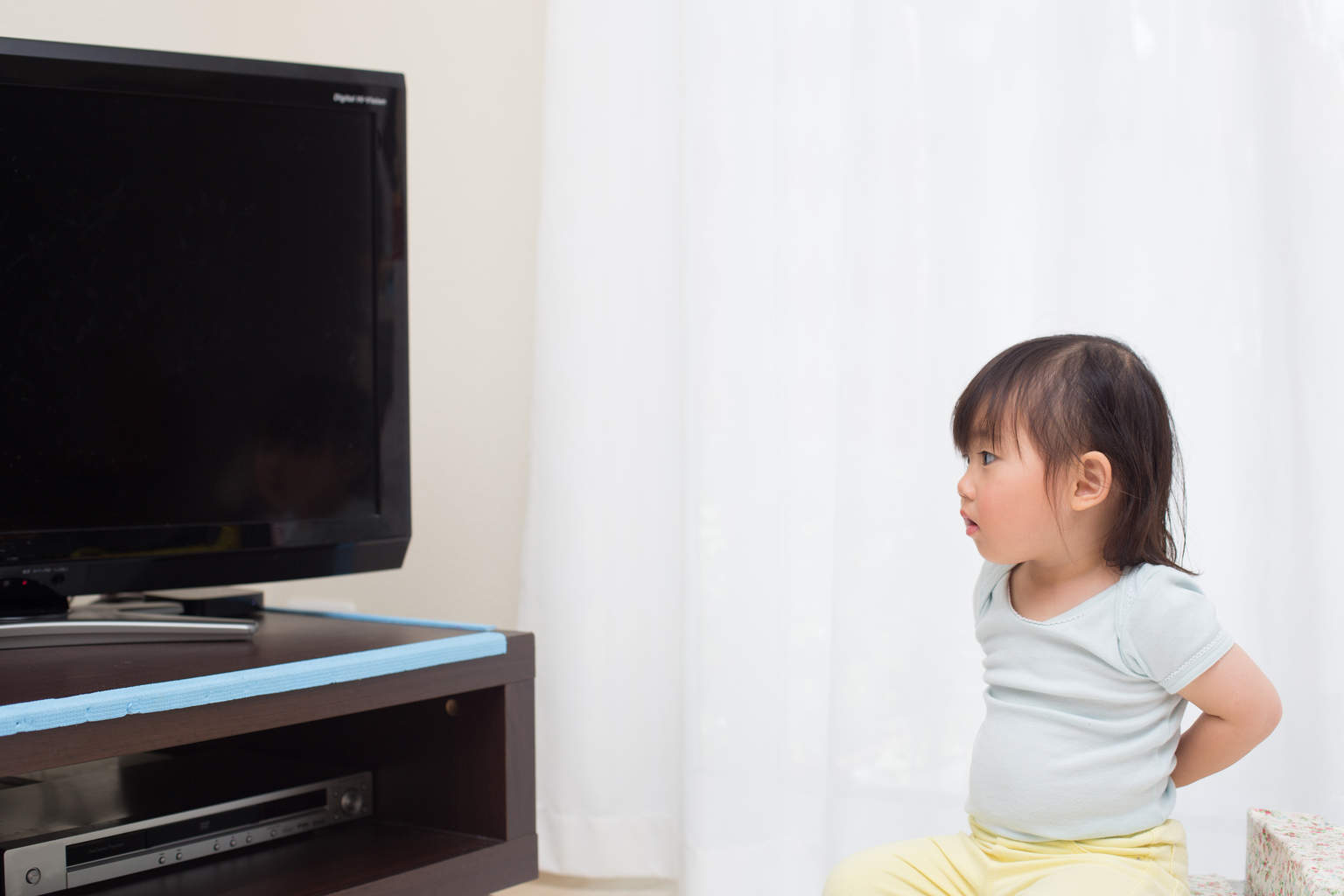
"Watching TV for more than two hours per day increases the risk of high blood pressure in children," The Daily Telegraph reported.
A large study involving more than 5,000 children, carried out for more than 2 years, found a relationship between watching TV and increasing blood pressure.
The study found that more than 1 in 10 children showed signs of high blood pressure, the main risk factor for cardiovascular disorders as they grow older. Cardiovascular disorders are health conditions that can damage the heart and blood vessels, such as strokes.
Children who spend more than two hours per day sitting in front of a TV in 2 years show a significant increase in risk, similar to children who rarely engage in physical activity.
This study supports previous evidence of a "lazy motion" lifestyle and a low frequency of physical activity, which is associated with causes of high blood pressure, although it does not prove that the phenomenon specifically causes this condition.
There are many factors that can affect high blood pressure, including genetics, fetal development during womb, socioeconomic status, and weight.
In short, the more time wasted in front of the TV (watching or playing video games), the less time your child will have to do physical activity.
Children aged 5-18 years are recommended to at least do 60 minutes of physical activity every day. The study was conducted by a group of joint researchers from several health institutions in various countries, including the University of Glasgow in the UK.
What is this research?
This study is a joint observation study that looks at the incidence of pre-hypertension and hypertension in children in Europe, and its relation to the frequency of physical activity and "lazy motion" behavior.
The study's authors say that high blood pressure is one of the most important factors in cardiovascular disease, and other studies have shown similarities to high blood pressure in children and adolescents with adults. However, little is known about the risk factors for high blood pressure in childhood. Their hypothesis is, the combination of low frequency of physical activity and "lazy motion" lifestyle behavior might contribute to high blood pressure.
"Lazy motion" behavior is determined based on reports from parents about the time their children spend only sitting in front of the screen — watching TV, movies, or playing computer video games. This behavior does not include other "lazy motion" behaviors, such as reading.
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and recorded in two categories:
- Systolic pressure - blood pressure when the heart pumps blood out
- Diastolic pressure - blood pressure when the heart is resting between beats, which shows how strong your arteries hold blood flow
In children, high blood pressure is defined as blood pressure that exceeds the 95th percentile of their age, height, and gender.
Who was the research conducted at?
The researchers used data from a study conducted on 16,224 children from 8 European countries (Spain, Germany, Hungary, Cyprus, Estonia, Sweden, and Belgium) to see the effect of diet and lifestyle on health. The analysis is currently based on 5,221 children aged 2-10 at the time of the study began, as an age group with complete data available at that time. 5,061 children from the total participants were then re-examined after 2 years.
These children measured their systolic and diastolic pressure at the time the study began, and 2 years later as a follow-up. Pre-hypertension is defined as systolic or diastolic pressure with a range from the 90th to 95th percentile for age and height; and high blood pressure classified as a percentile range exceeding 95 for age and height.
Physical activity in children is measured by an accelerometer - an electronic device that measures the level of intensity of activity. The tool must be used for at least 6 hours per day, 3 days a week (2 working days and 1 day on weekends).
The researcher calculated the time that children used to carry out moderate physical activities and which were more energy intensive. Moderate physical activity includes cycling, while activities that are draining include running, playing football, and dancing.
That way, researchers can group these children into two groups: those who meet the guidelines for physical activity (spend at least 60 minutes on activities), and those who don't. Then these children will be further classified according to changes in the level of physical activity during the 2 years of the study.
The parents of these children were then asked to fill out a questionnaire about the "lazy behavior" of their children, calculated from the amount of time spent watching TV / DVD / playing video games throughout the week. The researcher uses this information to calculate "total TV time" per day. Then, children are classified into two groups: those who fulfill the total TV time guide, which is at least less than 2 hours per day, and those who don't. The researcher also calculated changes in "lazy motion" behavior for two years.
Researchers also consider other factors, including season, gender, age, parental education, and waist circumference.
The researchers estimated the relationship between levels of physical activity, the duration of watching TV reported, and the risk of developing high blood pressure or high blood pressure.
Then, what are the results?
Researchers found that the annual incidence of pre-hypertension reached 121 events in 1,000 children, and the incidence of high blood pressure reached 110 per 1,000 children.
Children who maintain "lazy motion" behavior more than 2 hours per day for two years during the current study show that the risk of high blood pressure increased by 28%.
Children who do not meet the recommended time of physical activity (60 minutes per day) at the time the study begins show a 53% increased risk of high blood pressure.
There is no relationship between pre-hypertension and child behavior.
What is the purpose of the results of this study?
The researchers said the incidence of pre-hypertension and high blood pressure was high in children in Europe, and children who underwent physical activity of less than 60 minutes per day or spent more than 2 hours in front of the screen per day had a higher risk . Researchers suggest that routine physical activity should be encouraged and "lazy motion" behavior in children should be reduced to prevent high blood pressure and its consequences as they grow older.
Conclusion
This study showed a high incidence of alarming blood pressure problems in children, amounting to 10% of initial estimates which only reached 5%. The study also found that the frequency of irregular physical activity and spending too long in front of the screen will increase the risk.
Although researchers have adjusted their analysis for other factors that might affect blood pressure (called blending), there are still a number of other factors that are not counted as variables but can affect the results. Furthermore, this study relies on estimating the amount of time from "lazy behavior" of children every day reported by parents, which may be exaggerated or even reduced. The use of an accelerometer can also affect the amount of physical activity performed, which can also affect results.
It is common knowledge that a generation of children today spend too much time sitting in front of the screen and very rarely do activities outside the home. The real question is, what can we do to overcome this problem?
Furthermore, the evidence shows that limiting the use of glass screens (TV, DVD, computers, mobile phones) towards bedtime can improve the quality of children's sleep. This can help them to restore their energy and ability to move the next day.