Contents:
- Medical Video: Gestational Diabetes: Managing Risk During and After Pregnancy Video - Brigham and Women’s Hospital
- Various factors that increase the risk of gestational diabetes
- How to prevent and treat gestational diabetes?
Medical Video: Gestational Diabetes: Managing Risk During and After Pregnancy Video - Brigham and Women’s Hospital
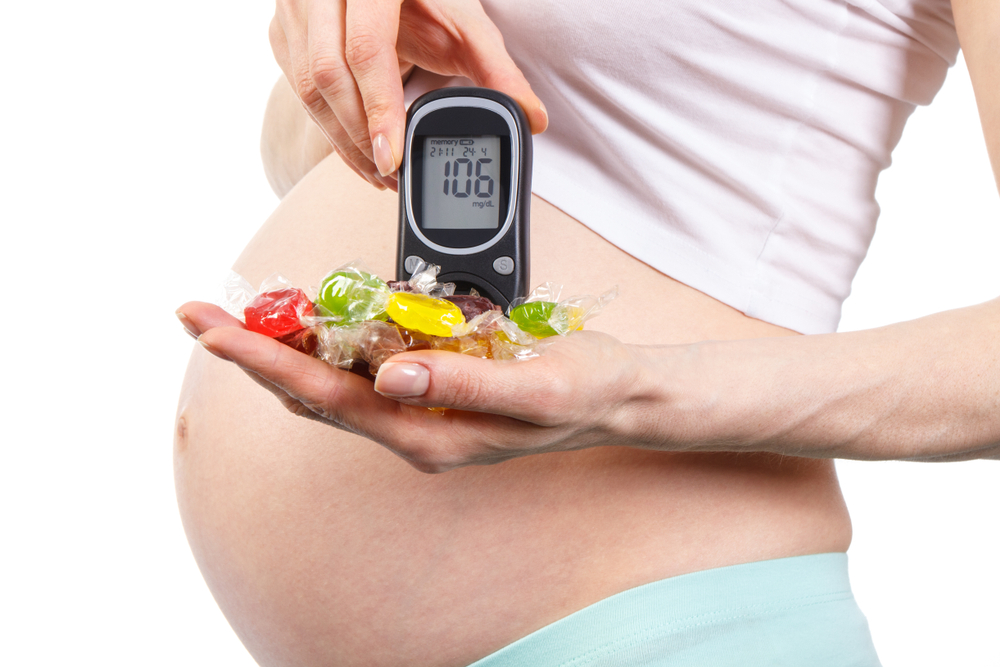
Gestational diabetes is diabetes that occurs during pregnancy, and includes complications of pregnancy which are fairly common.
Gestational diabetes causes high blood sugar which can affect pregnancy, such as increasing a mother's risk of preeclampsia in the last stages of pregnancy. In addition, this disease can also affect your baby, such as birth defects and respiratory disorders.
This type of diabetes will disappear after the mother gives birth. However, mothers who suffer from this disease have a higher risk of other diabetes attacks. Women who before pregnancy do not have a history of diabetes also have a risk of developing gestational diabetes.
There are several conditions that can increase the risk of diabetes during pregnancy in women. Anything? Check out the answer below.
Various factors that increase the risk of gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes can occur in every woman, but some women have a higher risk, especially women who have the following conditions:
- Overweight. You are likely to get gestational diabetes if you are significantly overweight with a body mass index of 30 or more.
- Age more than 25 years. Women over the age of 25 are more likely to develop gestational diabetes.
- Family or personal health history. The risk of gestational diabetes increases when you have prediabetes, a slight increase in blood sugar which may be a clue to type 2 diabetes, or if a family member, such as a parent or sibling, has type 2 diabetes. You are likely to get gestational diabetes if you have this diabetes.
- The previous baby's birth condition. If you give birth to a baby who weighs more than 4.1 kilograms, or if you experience a stillbirth (stillbirth) without explanation, or even if you have had a miscarriage.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or other health conditions related to insulin. More than half of women with PCOS can experience diabetes or prediabetes before the age of 40 years. This may be due to the relationship between excess insulin and the androgen hormone which is one of the PCOS factors.
- High blood pressure (hypertension). High blood pressure can affect insulin secretion from the pancreas, which leads to higher blood sugar.
- Have high cholesterol and heart disease. Cholesterol is also influenced by blood pressure and blood glucose. If your blood glucose and blood levels are high, your cholesterol may also decrease. All of these are risk factors for diabetes and heart disease, and the more risk factors you have, the higher the risk.
- Unhealthy eating patterns and lack of exercise.
How to prevent and treat gestational diabetes?
Women who plan to become pregnant or are pregnant can prevent gestational diabetes by eating healthy foods, regular exercise, and controlling blood sugar.
Controlling blood sugar can prevent a difficult birth and make you and your baby healthy.
In gestational diabetes, blood sugar will return to normal soon after giving birth. However, if you have ever had diabetes while pregnant, you have a seven times greater risk of having type 2 diabetes in the future.
You should monitor and manage your blood sugar regularly to see a doctor. Because for most women, diabetes during pregnancy does not cause obvious signs or symptoms.
When you have diabetes during pregnancy, you need to regularly check your blood sugar levels. The frequency of blood sugar testing will depend on the results of the test after you give birth to your baby.