Contents:
Medical Video: My Skin Could Kill Me (Medical Documentary) - Real Stories
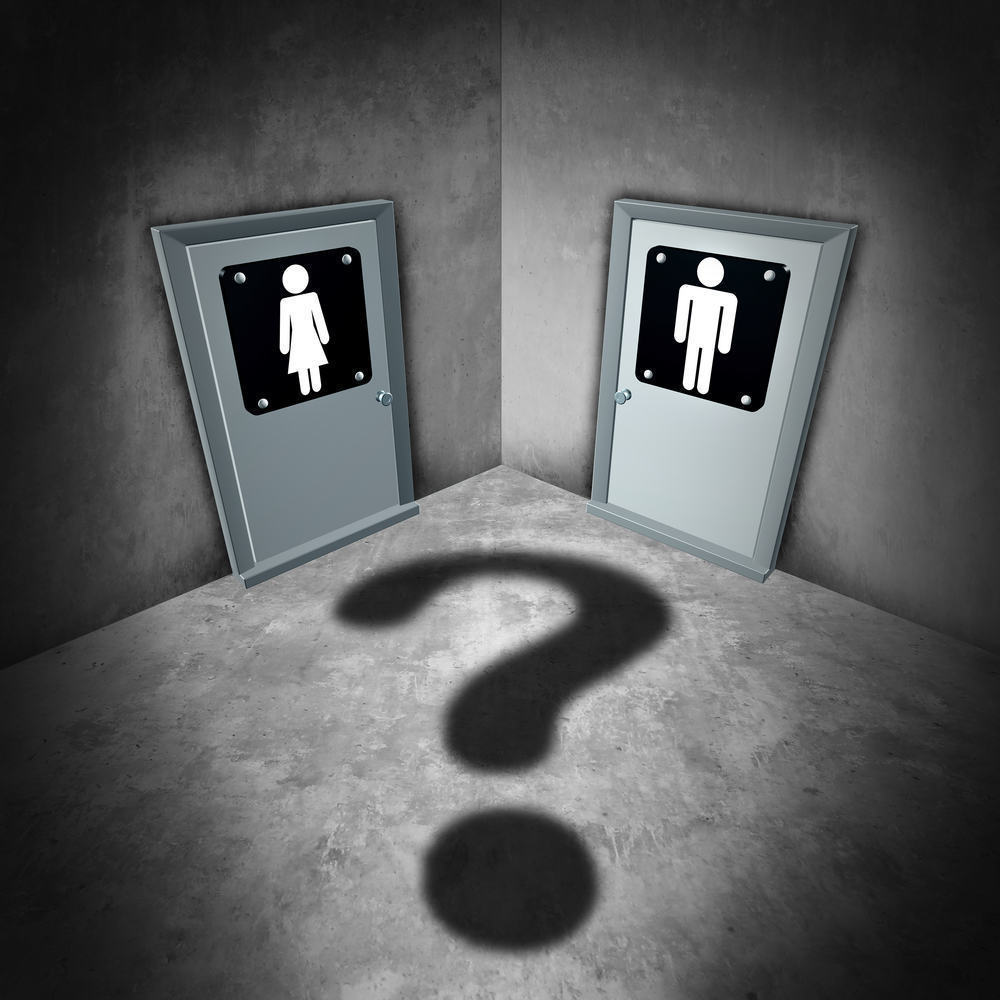
Gender dysphoria, previously known as gender identity disorder, is a condition that affects people known as transgender, in which a person experiences discomfort or feeling depressed because there is a mismatch between the biological sex and their gender identity.
Quoted from WebMD, the biological sex obtained by a person at birth depends on the appearance of his genitalia. However, gender identity is a gender identity that is trusted and believed by that individual. For example, someone who has a penis and other physical characteristics that represent a man, in general, will identify himself as a man.
But, even though a person's gender and gender identity can be harmonious for most people, this is not certain for others. Some people may have male physical characteristics, but feel and believe they are a woman, while others may feel they are both or do not feel that they are 100 percent female or male (regardless of their physical appearance), aka genderqueer.
What causes gender dysphoria?
Gender dysphoria is a real medical condition that is recognized by American Psychiatric Assocation, and in certain cases medical treatment is needed. However, gender dysphoria is not a mental illness.
Reporting from News Medical, a number of studies indicate that this condition is not only due to the irregularities of the brain's work, but can be caused by biological causes related to the development of gender identity before birth.
Gender dysphoria may be caused by a rare medical condition, such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia / CAH, and an intersex condition (also known as hermaphroditism).
At CAH, female fetuses have adrenal glands that produce high levels of male sex hormones that make the vagina swell, so that misunderstandings can occur as a baby boy.
Intersex or hermaphroditism is a rare condition in which a baby is born with two genitals, vagina and penis. In this case, after banning the sex normalization procedure without the owner's consent by The United Nations, children will be allowed to grow with two genitals until they are mature enough to choose one, and do surgery.
Even so, more research is needed to be able to ascertain the causes of gender dysphoria.
Signs and symptoms of gender dysphoria
According to the psychiatric guidebook Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), for someone to be diagnosed with gender dysphoria, there must be a real difference between the gender he believes and gender that is perceived by others, and must be sustained for at least six months. In children, the desire to change gender must be real and visible, and expressed directly from the individual.
The real wishes and beliefs mentioned above are not only desires to get social and cultural benefits from different sexes, but come from within on the basis of the belief that they should not be in a particular sex group, and show consistent attitudes and behaviors from gender opposite.
Gender dysphoria is manifested in many ways, including a persistent desire to live and be treated like a gender that he believes in, eliminate and / or change their sexual characteristics, or a strong belief that they have general feelings, behavior patterns, and reactions from the opposite gender himself.
Some transgenders choose to carry out medical therapy (hormone or surgery) to make their physical appearance more consistent with their gender identity.
According to NHS Choices, it is not known how much people with gender dysphoria, because many people who experience this condition have never and / or can seek help. A survey of 10,000 people conducted by the Equality and Human Rights Commission in 2012 found that one percent of the world's population is included in the transgender and genderqueer groups, to a certain extent.
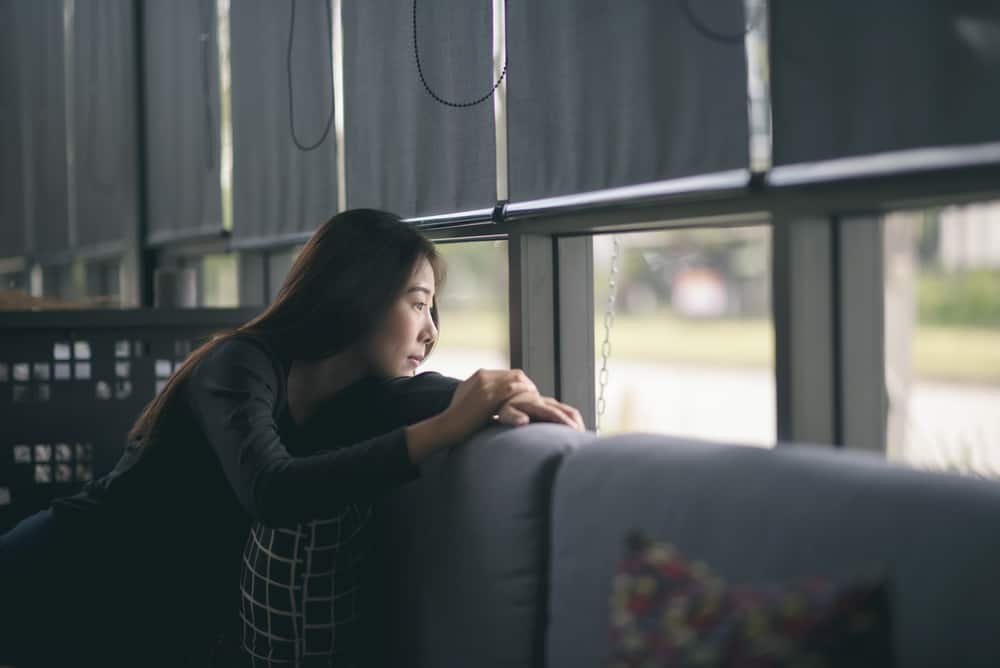
Not infrequently, transgender people suffer from depression and experience exile
Gender dysphoria causes stress or clinical depression in social, occupational, or other fields that can hinder the quality of life of individual sufferers.
The impact of the disorder can be very broad, so that the mental life of the person is only centered on a number of certain activities that can reduce the pressure due to the gender stigma they face. People with gender dysphoria are often preoccupied with appearances, especially at the beginning of the transition to living with their "new" gender. Relationships with parents may also be very disturbed. It is not uncommon for transgender people or people with gender dysphoria to accept exile from family and friends.
Some men with gender dysphoria choose to do illegal treatment with hormones or maybe, although very rarely, do self castration without a doctor's supervision. Many transgenders are involved in prostitution, placing them at a high risk of HIV infection.
Mismatch between gender and gender identity experienced by someone with gender dysphoria can cause stress, nervousness, and prolonged depression. Attempts to commit suicide and substance and drug abuse are common to people with gender dysphoria and / or transgender.
Some adult men have a history of fetishism and other parafilia. Associated personality disorders are more common in men with gender dysphoria than women.
READ ALSO:
- Get to know the reasons people want to commit suicide and immediately reach out to help
- Psychopaths and sociopaths, one of them tends to kill. Which one?
- Various false assumptions about condoms