Contents:
- Medical Video: Children’s Cavities | How to Keep Your Kid’s Teeth Healthy
- Is it true that the teeth are toothless and never grow new teeth?
- What are the causes of a child's permanent teeth growing late?
- 1. Genetic
- 2. Nutritional status
- 3. Gender
- 4. Body posture
- 5. Certain diseases
- So, how can a child's permanent teeth grow again?
Medical Video: Children’s Cavities | How to Keep Your Kid’s Teeth Healthy
As a parent, you do not need to be anxious when you see the tooth of a toothless child in its infancy. Because the dislodged teeth will soon be replaced by permanent teeth - aka adult teeth. However, what if the permanent teeth do not grow for years? What caused it? Find out through the following reviews.
Is it true that the teeth are toothless and never grow new teeth?
Humans will generally experience twice the period of tooth growth. First, the milk teeth begin to grow when the baby is 6 months old and continues for 2 to 3 years.
Entering the age of five years, the child will experience dislodged milk teeth and then be replaced by permanent teeth or adult teeth. This permanent dentition usually takes one week to six months since the milk teeth are dislodged.
However, in fact some children whose milk teeth are dislodged do not directly grow new teeth. This even lasted for years. As a result, the tooth of the child is toothless and sometimes makes him not confident.
Dennis J. McTigue, a professor of pediatric dentistry from Ohio State University in the United States, revealed to Baby Center that this condition was normal thing. This case is referred to asdelayed eruption, namely late permanent dentition.
What are the causes of a child's permanent teeth growing late?
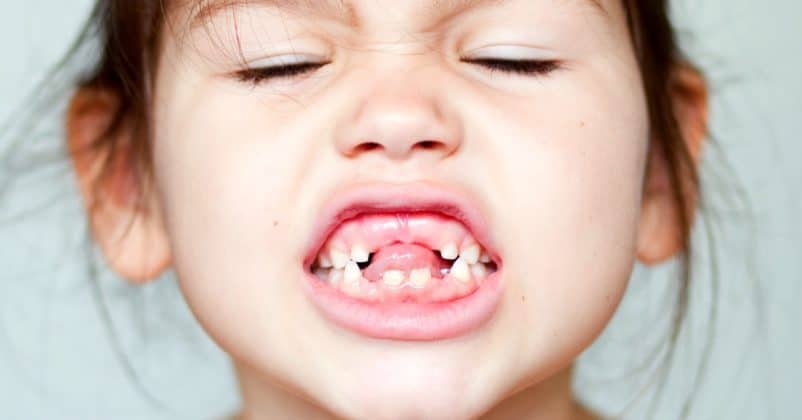
Basically, permanent teeth originate from the seed of the tooth that is inside the gum from birth. As long as there are teeth, the teeth that are dislodged will certainly be replaced with new teeth.
However, some people don't actually have the seeds of permanent teeth in their gums. That is, when her milk teeth dislodged, she did not have a reserve of teeth that could replace the dislodged tooth. This is what may be one of the causes of toothless children's teeth for a long time.
Child permanent teeth that do not grow can also be caused by dental trauma. Tooth trauma can be dislodged because of a fall or a hard blow on the head or directly on the tooth.
When the teeth are dislodged prematurely, this will cause the area around the dislodged tooth to bleed inside the gums. This can cause the child's teeth to appear black and permanent teeth to be difficult to grow.
However, there are several other factors that can cause a child's permanent teeth to not grow quickly after the milk teeth are dislodged, including:
1. Genetic
Genetic or genetic factors can affect a child's development, including tooth growth. If you have experienced a delay in the growth of permanent teeth compared to your peers, chances are that your child will also experience the same problem.
2. Nutritional status
Children who are malnourished tend to experience permanent tooth growth delays. Because the child's teeth and gums don't get enough nutrients to maximize their growth. As a result, the child's teeth grow late.
3. Gender
Girls generally speak faster than boys. In fact, this in fact also affects dental health and gums.
Girls on average begin to grow milk at the age of four to six months, earlier than boys. Thus, the possibility of permanent dentition also tends to be faster and easier than boys.
4. Body posture
Children who have large postures tend to be more likely to grow permanent teeth than children who are small in posture. In addition, premature babies tend to experience delays in permanent teeth growth than babies who are quite months old.
5. Certain diseases
In rare cases, the problem of permanent teeth is difficult to grow due to the condition of hardened gums. When the child's gums harden, permanent tooth seeds will find it difficult to find a way out in order to grow and replace the dislodged milk teeth. As a result, the permanent growth of a child's teeth is hampered.
In addition, hormonal factors are also considered to play a strong role in the development of teeth. This is why children who experience thyroid disease tend to experience slower tooth growth than healthy children.
So, how can a child's permanent teeth grow again?
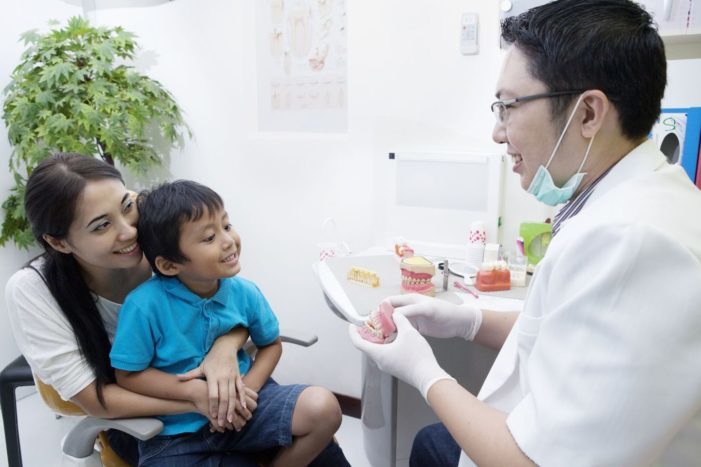
Maintaining children's dental health is not only the responsibility of your child, but it is your main task. That is why children need to check their teeth regularly every six months, as recommended by the Ministry of Health. Not only to maintain dental health, it can also prevent dental problems in children as early as possible.
If the tooth of the toothless child takes too long, immediately take your child to the dentist. The doctor may see the completeness of a child's toothpaste with the help of X-ray X-rays. If there are still teeth in the location of the tooth dislodging, then you only have to wait until the permanent teeth grow.
However, if the tooth is toothless for a long time because the gums tend to be hard, the doctor may give a small incision to facilitate permanent teeth to grow. However, again this is quite rare in children.