Contents:
- Medical Video: Smoking Causes Cancer, Heart Disease, Emphysema
- How type 2 diabetes affects oral health
- The cause of diabetes is prone to mouth problems
- What are the symptoms of mouth and tooth disease?
- Dental and oral studies in people with diabetes say ...
- How do you prevent dental and oral diseases?
- How to treat dental and oral diseases?
Medical Video: Smoking Causes Cancer, Heart Disease, Emphysema
Diabetes has many dangerous complications. These complications include nerve damage, heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and even blindness. But what is often underestimated is complicationsoral and dental health. Diabetes not only causes bad breath, but also various other mouth problems.
How type 2 diabetes affects oral health
High blood sugar levels affect the body's ability to fight bacteria that can cause infection.According to the American Diabetes Association, people with diabetes have a higher risk of developing gum inflammation, gum disease and periodontitis (severe gum infection with bone damage).
Diabetes is also associated with an increased risk of occurrence oral thrush, type of fungal infection in the mouth. In addition, people with diabetes tend to have dry mouth. This condition has been associated with an increased risk of canker sores, toothaches, cavities, and dental infections.
Conversely, gum disease can also affect blood sugar control in the body.
The cause of diabetes is prone to mouth problems
Some people with diabetes actually do have a greater risk of developing oral health problems than normal people. For example, people who don't control their blood sugar levels are more likely to experience gum disease.
The bacteria that cause cavities are generally foods containing sugar that attach to the teeth. When your blood sugar is too high because of excess sugar or starch in food, there is an excess sugar intake available for bacteria as their food.
In addition, if you smoke and have diabetes, you are at a greater risk for oral health problems than someone who has diabetes and does not smoke.
Don't forget, too, according to the National Institutes of Health, there are more than 400 drugs that have been shown to cause symptoms dry mouth. This condition includes medicines commonly used to treat diabetes nerve pain, or neuropathy.
You can ask your doctor or pharmacist if your medication can increase the risk of dry mouth. If needed, the dentist can prescribe mouthwashes that can reduce the symptoms of dry mouth.
What are the symptoms of mouth and tooth disease?
People with diabetes sometimes do not always feel symptoms when they have dental and oral disease. Therefore, it is important to regularly check the dentist regularly. However, some symptoms can indicate that you have gum disease. These symptoms include:
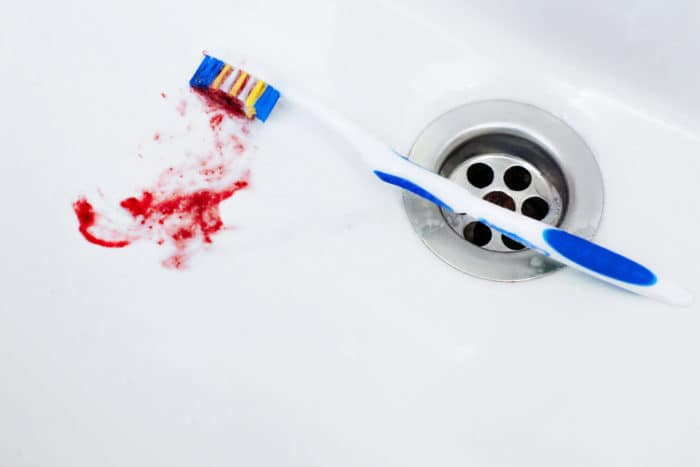
- Gums bleed, especially when you brush your teeth orflossing (using dental floss)
- Changes in tooth arrangement (malocclusion)
- Bad breath chronic, even after brushing your teeth
- Gums that look like they will escape from the teeth, which can cause your teeth to look longer or bigger
- Permanent teeth that begin to shake
- Red or swollen gums
Dental and oral studies in people with diabetes say ...
In 2013, there was a study of 125 people suffering from type 2 diabetes published in the journal BMC Oral Health. In the study, researchers measured factors of dental and oral problems, including missing teeth, the incidence of periodontal disease, and the number of teeth bleeding reported.
The study found that the higher their fasting blood glucose and the higher their hemoglobin A1C (measurement of a person's average blood sugar for three months); the more likely they are to have periodontal disease and tooth bleeding.
Those who did not report to their doctors and those who did not treat their teeth properly after being diagnosed with diabetes were more likely to experience tooth loss than those who routinely controlled their blood sugar levels.
How do you prevent dental and oral diseases?
The best way you can do to prevent complications associated with diabetes in your dental health is to routinely keep blood sugar levels normal. Check your blood sugar regularly and tell your doctor if you control sugar levels with diet, oral medications, or insulin have not shown maximum results.
You also need to be careful in treating your teeth, especially when brushing your teeth, flossingand examination to the dentist. You may need to ask your dentist to do more checks than recommended. If you see signs of gum disease, seek treatment for your teeth immediately.
Check your mouth to see problems every month. This examination includes looking for areas that experience dryness or white spots in your mouth. The bleeding area must also be considered.
If you plan on dental surgery but blood sugar is not controlled, you may need to delay this operation if it is not emergency. This can increase the risk of post-operative infections, if your blood sugar levels are too high.
How to treat dental and oral diseases?
Determining treatment for oral health conditions associated with diabetes usually depends on the condition and severity.
For example, periodontitis can be treated with scaling and management of tooth roots. This is an intensive cleaning method that removes tartar from the top to the bottom of the gum. Your dentist may also prescribe antibiotics.
People with severe periodontitis may need to undergo gum surgery but this is rarely done. This operation can prevent tooth loss or is known as toothless tooth.
By paying close attention to the control of diabetes and the health of your teeth, you can maintain healthy teeth and gums. Visit your dentist regularly and tell your diabetes problems, the symptoms you are experiencing, and the medication you are taking. This information can help your dentist provide the best care.