Contents:
Medical Video: Skin Tightening Treatment | No Need For Botox or Fillers Anymore | HIFU Treatment Review
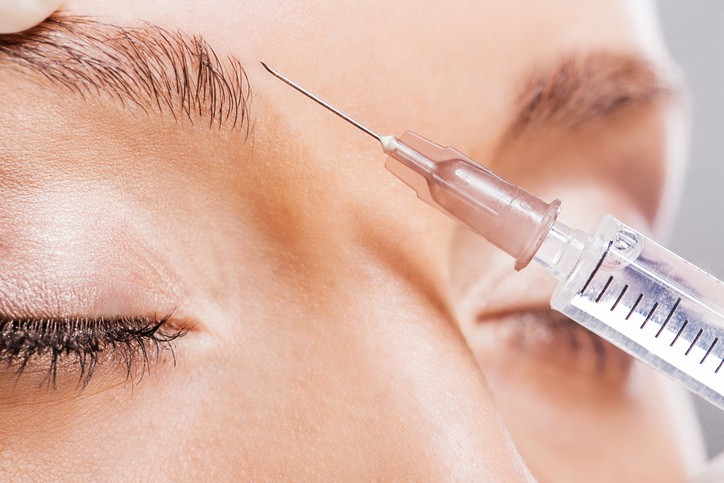
Botulinum toxin is a type of neurotoxin that functions to relax the muscles for months. Botox is famous in the world of beauty because of its effectiveness in minimizing the appearance of wrinkles around the eyes, face and neck. However, doctors also use Botox injections to treat various medical conditions.
The origin of Botox injections
Clostridium botulinum, an organism from which Botox originates, is found in non-active forms in the natural environment, including in forests and cultivated soils, also in lake, river, coastal, and free water sediments. These bacteria can also be found in the intestinal tract of mammals, fish, and also jaroan from other crabs and shellfish.
Natural Clostridium botulinum bacteria are relatively harmless. New problems will arise when the spores turn vegetative and the cell population rises to the point where bacteria begin to produce botulinum toxin, a neurotoxin that proves deadly: one gram of this nerve poison can kill as many as one million people - two kilograms can erase human populations on Earth . Botulinum toxin is also responsible for botulism.
How to work Botox injections
For muscles to contract, the nerves release chemical signals of acetylcholine at the junction where nerve endings and muscle cells meet. Acetylcholine attaches to nerve receptors in muscle cells, causing the muscles to contract - tensing and shortening.
Botulinum toxin is injected into humans in very small concentrations to stop the release of acetylcholine to cut the communication pathway between the nerves and muscles, so that it effectively thwarts the muscle contraction instructions and paralyzes them. The effect of botulinum toxin causes a decrease in abnormal muscle contractions, allowing the muscles to become less rigid.
Botox injections are mixed by diluting the botulinum toxin powder in salt water (sodium chloride) and injected directly into the neuromuscular tissue. It takes 24-72 hours for these neurotoxic effects to emerge, which reflects the time needed for poisons to interrupt the synaptosomal process. In rare cases, it may take 5 days for you to observe the optimal effect.
Use of Botox injections in the medical world
Botox is a purified derivative of botulinum toxin A, popular as a wrinkle treatment. Botox injections also have other medical uses.
1. Treating migraines
Migraines are severe nausea headaches accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to light and sound. Chronic migraines last for four hours or more, occurring at least every other day.
Botox can be considered if other migraine treatments are ineffective, cannot be tolerated, or cause too many side effects. When used, Botox is injected into the muscles of the head and neck every 12 weeks to prevent migraines from recurring frequently. Botox injections can reduce the effects of migraine symptoms.
Although this toxin is commonly used to treat migraines, Consumer Reports reports that Botox injections cannot prevent occasional migraines, based on an analysis of a 2009 randomized controlled trial involving 1,600 patients. Evidence to date also shows this treatment may not be effective for chronic tension headaches.
2. Control urinary incontinence (bedwetting)
The overactive urinary tract contracts involuntarily and often. This can cause loss of bladder control (urinary incontinence). The urologist can inject Botox into the bladder using a cystoscope, a special instrument inserted through the urethra. Botox injections can help the bladder contract to be more organized and normalize urination.
Studies have found that effective Botox injections reduce urinary incontinence, especially in people with a spastic bladder caused by spinal cord injury. In a small randomized controlled trial from the United Kingdom in 2009, this treatment proved to be able to improve quality of life in patients who have urinary incontinence without a definite cause.
A 2012 study published in the journal European Urology found that injecting botulinum toxin A (Botox) into the bladder wall was an effective way to treat debilitating conditions in which individuals had a sudden urge to urinate.
Botox injections are an option for treating this condition if other treatments are not effective. However, benefits begin to fade after about six months.
3. Overcome excessive sweating
Hyperhidrosis is another name to describe the condition when the armpit sweats excessively. This happens when the nerves in the armpit trigger sweat glands to produce sweat, even in the absence of normal triggers such as fear and shame - such as the face and hands sweating while eating.
Botox injections are given in areas with problems, such as the armpits, hands, feet or face. Botox works by blocking the signals that the brain sends to the sweat glands. This procedure can last up to eight months.
Some evidence suggests that these nerve toxin injections can control excess saliva in people with Parkinson's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
4. Repair squint eyes
With strabismus - also known as squint, tired or lazy - the eyes do not look at the object together. This is caused by the unbalanced working of the eye muscles, so that it contracts to pull one eye in the opposite direction. Strabismus can cause an inability to focus, blurred vision, double vision, lack of depth perception, and eye pain.
Botox can be injected into one eye muscle as a treatment option, usually if the squint develops rapidly without a clear cause. The injected liquid botox will relax the interested eye muscles, which allow the eye side to return straight to align itself.
However, Botox injections are usually provided for paralytic strabismus, not for strabismus in children.
5. Relieves muscle spasms
Botulinum toxin is used to relieve muscle spasms associated with various neurological conditions, such as spinal cord injury, cervical dystonia, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, stroke, hand tremors, and also blepharospasm (eye twitching). Botox injections can help stop the body's muscles from contracting or twitching involuntarily.
A number of medical evidence has been reported to support the benefits of botulinum toxin for lower leg spasms in children with cerebral palsy and upper leg muscle spasms in adults with stroke. Botox injections are especially proven to improve walking in children with tightened calf muscles.
READ ALSO:
- Why Women Are More Often Insomnia Than Men?
- 5 Most Popular Plastic Surgery for Men
- What Happens During Sex Change Surgery?