Contents:
- Medical Video: What is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)? - DiaBiteSize
- What is diabetic ketoacidosis?
- What causes this condition?
- What are the symptoms?
- When should I see a doctor?
- Who is at risk for this condition?
- How is this condition diagnosed?
- How is this condition treated?
- 1. Insulin therapy
- 2. Electrolyte intake
- How to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis?
Medical Video: What is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)? - DiaBiteSize
Diabetes is a chronic disease that requires long-term treatment. If you don't get the right treatment, people with diabetes are prone to diabetes complications. One complication of diabetes that diabetics must watch out for is diabetic ketoacidosis.
What is diabetic ketoacidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious condition associated with diabetes. If your body does not have enough insulin to process blood glucose (sugar), then your body will burn fat as energy. As a result, acids called ketones form in the body. If left untreated, this ketone substance can poison you.
This condition can occur in people who have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. However, in many cases, people with type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of developing complications of diabetes one compared to people with type 2 diabetes.
Diabetic ketoacidosis can also appear if you are at risk of diabetes, but have not received a formal diagnosis. This can be the first sign of type 1 diabetes.
What causes this condition?
Diabetes ketoacidosis can be triggered by 3 things, namely:
- Forgot insulin injections
- Having a certain history of disease or infection that makes the body produce more hormones (such as adrenaline or cortisol) which can ultimately affect the workings of insulin in the body
- Physical or mental disorders
- Heart attack
- Alcohol or drug abuse
- Certain drugs such as corticosteroids and some diuretics
What are the symptoms?
Some typical symptoms of diabetes ketoacidosis are:
- Frequent urination
- Feel very thirsty even to become dehydrated
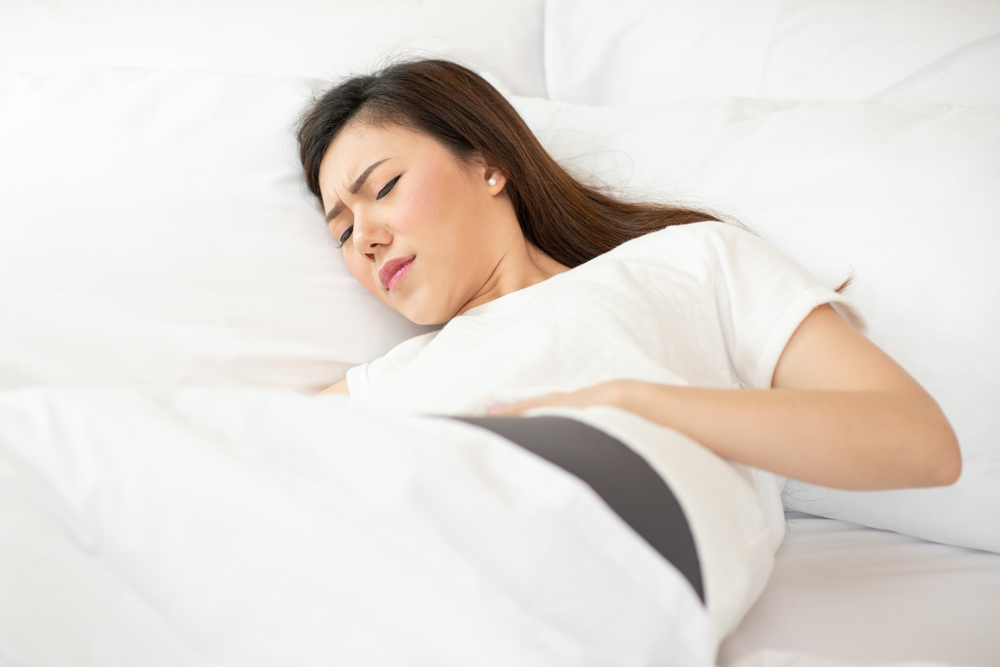
- Nausea
- Gag
- Stomach ache
- Confusion
- Blushing face
- Limp, lethargic, and not powerful
- Dry mouth and skin
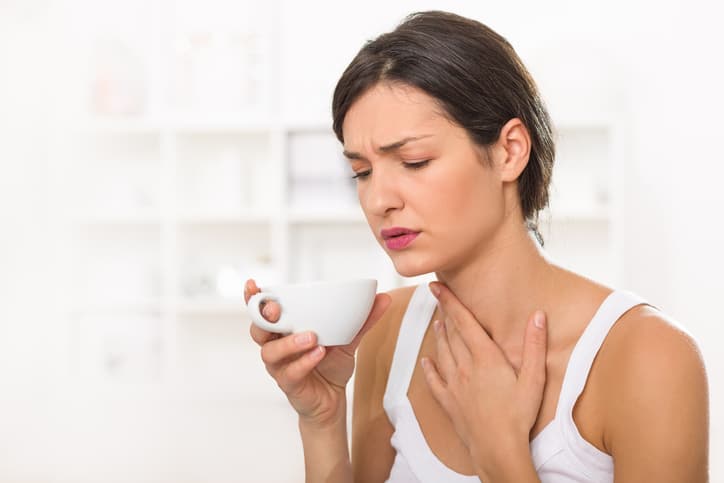
- Breathing (wheezing) or shortness of breath
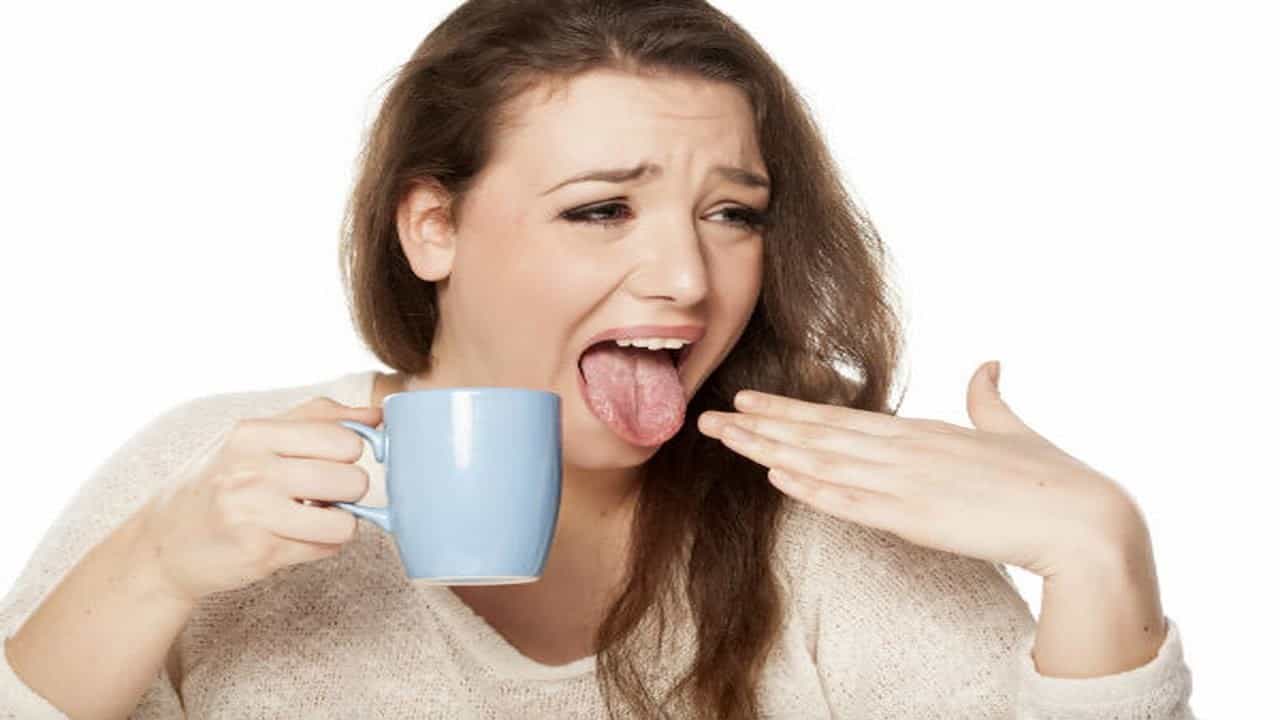
- The breath smell is rather sour, like fruit
When should I see a doctor?
Diabetic ketoacidosis is an emergency. If you have type 1 diabetes and a glucometer reading of more than 300 mg / dL, you should immediately take a urine test to see what level your ketone is. If a urine test shows moderate and high levels of ketone, you are at high risk of developing diabetic ketoacidosis. If you have this, you should immediately seek medical help. Because if not treated, diabetic ketoacidosis can cause coma or death.
Always seek medical attention if you experience nausea and vomiting without cause.
Who is at risk for this condition?
Your risk of developing diabetic ketoacidosis may be higher if you:
- Have type 1 diabetes
- Under the age of 19 years
- Has several forms of trauma, both emotional and physical
- Stressful
- Having high fever
- Have had a heart attack or stroke
- Smoke
- Drug or alcohol abuse
Although complications of diabetes one is rare in people who have type 2 diabetes, but this condition can also occur among them.
How is this condition diagnosed?
Testing for ketones in urine samples is one of the first steps to diagnosing diabetic ketoacidosis. Blood and sugar acidity tests are also often done. Other tests that your doctor may do such as:
- Blood potassium test to assess metabolic function
- Blood artery gas to determine the acidity of your blood
- Blood amylase test to test pancreatic function
- Chest radiograph to look for signs of infection such as pneumonia
How is this condition treated?
If you are diagnosed with this complication but have not been diagnosed with diabetes, your doctor will make a diabetes treatment plan to prevent ketoacidosis. While if your diabetic ketoacidosis is a result of infection or disease, your doctor may treat it with antibiotics.
In general, treatment options for diabetic ketoacidosis are:
1. Insulin therapy
Your doctor will likely give injections of insulin through an IV until your blood sugar level drops below 240 mg / dL. When your blood sugar levels are in a reasonable range, your doctor may let you continue using insulin as usual.
2. Electrolyte intake
Insulin that is lower than the normal level can cause electrolyte levels in your body to be abnormally low. Electrolytes are electrically charged minerals that help the body, including the heart and nerves - function properly. Electrolyte replacement is also usually done through infusion.
In addition to electrolytes, doctors also provide fluid intake (orally, if possible, or infusion) to replace fluids that are usually lost due to diabetic ketoacidosis. Fluid replacement also helps lower the amount of sugar in your blood.
How to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis?
There are many ways to prevent this one diabetes complication. One of the most important is proper diabetes care. This can be done by taking regular diabetes medication as prescribed by a doctor, eating healthy foods, and watching your blood sugar levels.
Other precautions include:
- Ensure that your blood sugar levels are in the normal range by checking it several times per day.
- Routine injection of insulin as directed by the doctor.
- Adjust insulin dosage based on activity level, disease, or other factors, such as what you eat.
- Make plans for emergencies related to what should be done if at any time you experience symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis.
- A urine test to see ketone levels when you are stressed or when you are sick.
- Look for medical care if your blood sugar level and ketone are higher than normal. Remember, early detection is important.