Contents:
- Medical Video: Urinary Tract Infection | How To Prevent UTI (2018)
- Factors that make women experience urinary tract infections
- Anatomy of a woman's body
- Sexual activity
- Certain types of contraception
- Menopause
- How to prevent urinary tract infections?
- How do I know if I have a urinary tract infection?
Medical Video: Urinary Tract Infection | How To Prevent UTI (2018)
Urinary tract infections in women are more common than men. In fact, women can experience urinary tract infections more than once during their lives. Apparently, there are many factors that make women more likely to get urinary tract infections.
Factors that make women experience urinary tract infections
Urinary tract infections are infections that can occur in any part of your urinary system, which can affect the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Most infections usually attack the lower urinary tract, the bladder and urethra.
Well, this urinary tract infection usually attacks women more than men. Many factors in women that support the occurrence of urinary tract infections.
Anatomy of a woman's body
Women have a urethra (the last channel that removes urine outside the body) that is shorter than men, this makes it easier for bacteria to reach the female bladder In addition, the female urethra is also closer to the anus. Therefore, women are advised to rinse from front to back after urinating or defecating. This is done to prevent the transfer of bacteria from the anus to the urethra. Bacteria from the large intestine, such as E. coli bacteria, can move to the urethra when you rinse from back to front. These bacteria can then enter the bladder and cause infection. If the infection is not treated immediately, the infection can spread to the kidney area.
Sexual activity
Sexually active women have a higher risk of urinary tract infections than women who are not sexually active. Having a new sexual partner also increases a woman's risk of urinary tract infection. Sexual activity can also trigger the transfer of bacteria from the vagina to the urethra, so that it can cause infection in the urinary tract.
Certain types of contraception
Women who use diaphragm and spermicide contraceptives (creams that can kill sperm) have a higher risk of urinary tract infections. The diaphragm can compress the urethra and slow down bladder emptying. Urine that stays in the bladder allows bacteria to grow and cause infection. Meanwhile, spermicides can cause changes in the bacteria in the vagina. In addition, certain spermicides can irritate the skin, which can increase the risk of bacteria attacking the surrounding tissue.
Menopause
After menopause, estrogen levels in women are lower, resulting in changes in the female urinary tract. This makes women more prone to urinary tract infections.
How to prevent urinary tract infections?
Some things you can do to prevent urinary tract infections, namely:
- Urinate immediately if you feel the need to urinate, do not hold and rush. Make sure you empty your bladder completely.
- After finishing urinating or defecating or when cleaning your pubic area, rinse from front to back.
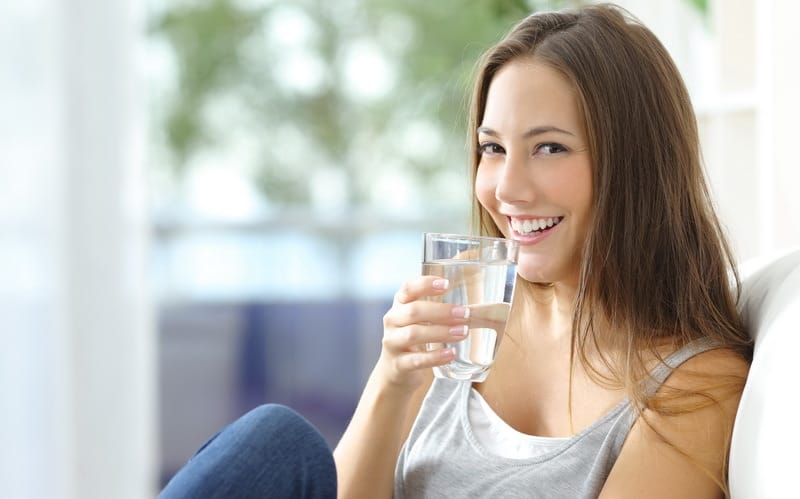
- Drink plenty of water, 8-10 glasses a day.
- You should take a shower or dip, not soak in bath tub.
- Avoid spray products to clean your female area, as well as products that contain fragrances. This product will only increase the risk of irritation.
- Clean your female area before and after sexual intercourse.
- Urinate after sexual intercourse to clean the urethra from bacteria that might enter it.
- Avoid using diaphragm contraceptives, non-lubricating condoms, or spermicide gels. This makes you more likely to experience urinary tract infections.
- Keep your pubic area dry by using cotton clothes or using more loose clothing. Avoid wearing tight jeans and nylon underwear because it can make your pubic area more moist, making bacteria easier to grow.
How do I know if I have a urinary tract infection?
If you experience things like the following, you should immediately check with your doctor. It is feared that you have a urinary tract infection.
- Feeling hot when urinating
- More often feel like urinating, even though the urine that comes out is only a little
- Pain in the pelvic area or lower abdomen, around the area of the pubic bone
- Your urine is more cloudy than usual, the color is darker, bleeding, or pungent
- Feeling tired or trembling
- Fever or cold, this is a sign that the infection has spread to the kidney area