Contents:
- Medical Video: Benefits of Epilepsy Surgery
- What are the goals of surgical treatment of epilepsy?
- Who can undergo epilepsy surgery?
- What is the epilepsy surgical procedure like?
- 1. Resective surgery
- 2. Corpus callosotomy
- 3. Hemispherectomy
- The risk of epilepsy surgery to watch out for
- 1. Memory disorders
- 2. Changes in behavior
- 3. Double vision
Medical Video: Benefits of Epilepsy Surgery
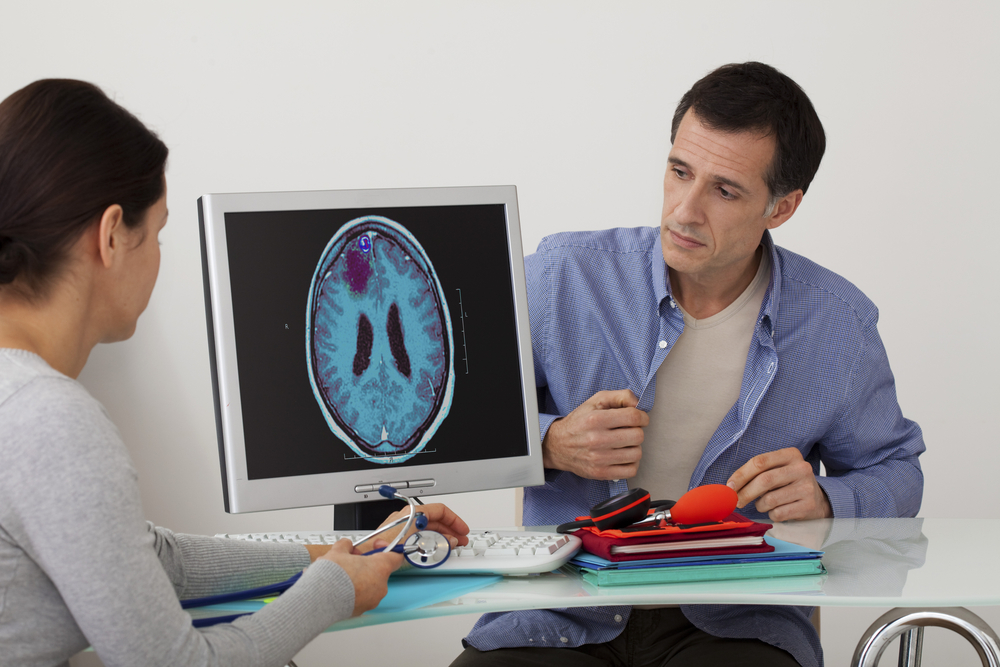
Epilepsy, or better known as epilepsy, is a chronic disease caused by a central nervous system disorder that triggers recurrent seizures even to loss of consciousness. As a first step, doctors will usually provide epilepsy drug therapy to control seizures. However, if the drug is no longer effective, then the treatment of epilepsy will be directed at surgical procedures, aka surgery.
Before you decide to undergo epilepsy treatment through surgery, it's good to first understand the ins and outs of epilepsy surgery through the following article.
What are the goals of surgical treatment of epilepsy?
Epilepsy drug therapy is actually quite effective in controlling seizures in people with epilepsy. Unfortunately, many cases of epileptic seizures that do not work are treated with epilepsy from a doctor. In fact, about 30 percent of patients are not strong with the side effects of drugs, such as headaches, uncontrolled shaking (tremor), rash, anxiety, and so on.
As a solution, patients will be advised to undergo epilepsy treatment through the surgical route, also called epilepsy surgery. There are three main goals of epilepsy surgery, including:
- Lifting the area of the brain that triggers seizures
- Blocking the brain's nerve pathways that cause seizures.
- Inserting certain devices into the brain to reduce the impact of epilepsy on the patient's health, namely brain damage, bone damage, and sudden death.
Who can undergo epilepsy surgery?
Basically, treatment of epilepsy with surgery may be done in epilepsy patients of all ages. However, the main requirements are:
- Patients experience epileptic seizures that cannot be controlled by drug therapy.
- Patients experience brain tumors, blood vessel abnormalities, or strokes that trigger seizures.
It should be noted that treatment of epilepsy by surgery can only be done if the area of the brain causing the seizure does not hold vital functions in the body, such as centers of gesture, language, or touch. If the area of the brain is affected by surgery, the patient can become difficult to move and difficult to speak.
What is the epilepsy surgical procedure like?
Not all patients will undergo the same epilepsy surgery procedure. This depends on how severe the seizures you experience and the location of the cause of the seizure itself.
Quoted from the Mayo Clinic, there are three types of epilepsy surgery that are most often performed, namely:
1. Resective surgery
This type of surgery is most often done to control epileptic seizures.Resectivesurgerydone by lifting a little area of the brain, usually the size of a golf ball, which triggers seizures.
2. Corpus callosotomy
Operation corpus callosotomy more often done in children who experience severe seizures. The trick is to cut the nerve tissue that connects the right and left hemispheres of the brain which causes spasms. This can help reduce the severity of seizures in children.
3. Hemispherectomy
Look like cospus callosotomy, procedurehemispherectomy also more often done in children who experience seizures due to damage to one hemisphere of the brain, whether right or left side. Epilepsy surgery is done by lifting the outer layer in half the brain.
The good news is, most epilepsy operations produce satisfactory results. Most patients no longer experience epileptic seizures after surgery. Even if they still experience seizures, the duration will be much reduced and fairly rare.
Even so, doctors will continue to give epilepsy drugs over the next year to help control epileptic seizures. However, if you actually experience epileptic seizures that are difficult to control after taking medication, you should reduce the dose or even stop taking epilepsy medication.
The risk of epilepsy surgery to watch out for

Just like other types of surgery, surgical treatment of epilepsy also has risks and side effects that must be considered. This can vary for each person because it depends on the type of epilepsy surgery and how many areas of the brain are removed.
Some of the possible risks and side effects of epilepsy surgery include:
1. Memory disorders
The area of the brain's temporal lobe is responsible for processing memories while combining them with sensation, sound, vision, touch, and emotion. Epilepsy surgery performed in this area of the brain can make it difficult for patients to remember, speak, or understand the information provided.
2. Changes in behavior
The frontal lobe area is the part of the brain that is located behind the forehead. Its function is to control thoughts, reasoning, and behavior. If epilepsy surgery is done in this area of the brain, patients tend to lose control, drastic changes in mood, to depression.
3. Double vision
Double vision can occur if epilepsy surgery is performed in the temporal lobe of the brain. You might also have difficulty seeing objects remotely due to the side effects of epilepsy surgery.
To speed up recovery from these side effects, patients are advised to take care of 3-4 days after surgery under the supervision of a doctor. You may experience pain and swelling in certain parts of the body for several weeks afterwards. The important thing is routine control to monitor your health condition postoperatively.