Contents:
- Medical Video: Common Cough or COPD
- First understand what chronic bronchitis is
- Then, what is emphysema?
- Chronic bronchitis can develop into emphysema
- So, what's the difference between chronic bronchitis and emphysema?
- 1. The part of the lung that is attacked by disease
- 2. Symptoms are different
- Symptoms of bronchitis and emphysema resemble other chronic diseases
- How are these two diseases diagnosed?
Medical Video: Common Cough or COPD
Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are part of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The second main cause of this disease is smoking, and the symptoms that appear are similar. No wonder many people still often mistakenly consider these two diseases to be the same. So, what's the difference between chronic bronchitis and emphysema? Come on, see the following review.
First understand what chronic bronchitis is
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (bronchial), airway tubes that branch off towards the right and left lungs. The bronchus serves to channel the air coming in and out of the lungs.
There are various causes of bronchitis, ranging from infection to exposure to air pollution. However, the main cause is smoking. Less than 10 percent of cases of bronchitis are caused by bacterial infections.
If untreated, inflammation of the bronchi can become chronic and can last for months to years. The intensity of the symptoms is also more severe than that of acute inflammation.
This is because gradually, inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes will increase the production of lung mucus which makes it difficult for you to breathe freely. In fact, this disease can cause permanent airway damage.
Then, what is emphysema?
Emphysema is a disease caused by gradual swelling of the alveoli. Alveoli is an air sac in the lungs. Emphysema causes the alveoli to weaken and eventually collapse.
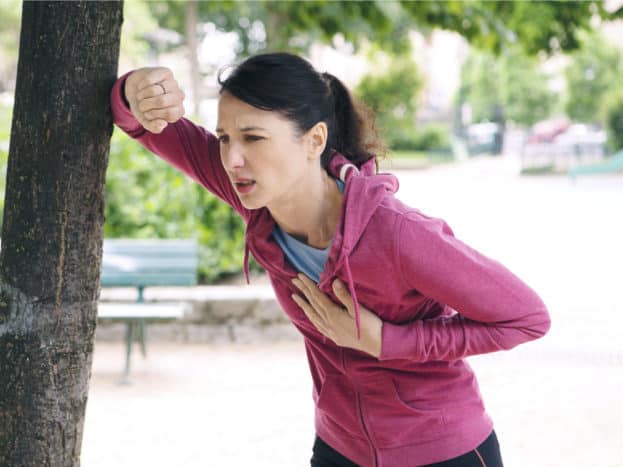
This condition can make the lungs constrict, so that gas exchange (oxygen and carbon dioxide) is disrupted or does not occur at all. As a result, the amount of oxygen that should reach the bloodstream is very limited. This makes it difficult for people with emphysema to breathe, especially when exercising.
Smoking is the main cause of emphysema. Other risk factors include a deficiency of an enzyme called alpha-1-antitrypsin, air pollution, airway reactivity, heredity, and age. Adult men are among the most vulnerable groups to experience emphysema.
Chronic bronchitis can develop into emphysema
These two lung diseases are included as progressive diseases. That is, it takes a long time for bronchitis or emphysema to cause real symptoms. That's why most of the cases have only been detected when the conditions have worsened. Moreover, your condition can also get worse over time if you don't get the right treatment.
Many people who get chronic bronchitis but don't get treatment eventually develop emphysema too.
So, what's the difference between chronic bronchitis and emphysema?
Bronchitis and emphysema are both lung diseases whose main cause is smoking. However, these two diseases still have their own differences that you need to understand and be aware of.
1. The part of the lung that is attacked by disease
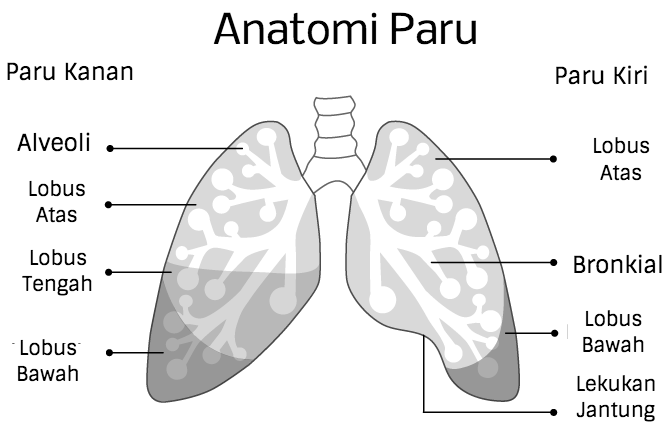
Bronchitis and emphysema attack different parts of the lung. Bronchitis infection will cause inflammation in the lining of the bronchial tubes, the airways that branch off towards the right and left lungs. As explained above, the bronchi should function to channel the air coming in and out of the lungs.
While emphysema will cause damage to the alveoli. Alveoli is a collection of small sacs where exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide with blood.
2. Symptoms are different
People who suffer from bronchitis and emphysema both have lower stamina and are easily exhausted after activity. This is because both diseases make the lungs expand perfectly to take oxygen. So, you will find it difficult to breathe freely and your blood will contain less oxygen.
However, the symptoms of the symptom are shortness of breath. Emphysema will cause shortness of breath which can worsen day after day. Initially shortness of breath will only be felt after walking away. However, over time it can also be experienced while sitting relaxed or not doing any physical activity.
In addition to shortness of breath, people with emphysema will experience other symptoms, such as:
- The level of alertness decreases.
- The nails turn blue or gray after physical activity.
- Difficult to carry out activities that are hard because of shortness of breath getting worse.
- Weight loss.
- Faster heartbeat.
Chronic bronchitis does not cause shortness of breath. Generally people with bronchitis will experience shortness of breath when the cough gets worse. The cough is the body's way to reduce excess mucus. However, because bronchitis keeps the lung constantly producing continuous mucus, coughing will also become more frequent and severe.
People with this disease usually have shorter breaths than shortness of breath and other symptoms, such as:
- Fever and chills
- Cough continues to worsen; cough up a lot of phlegm.
- Chest pain.
Symptoms of bronchitis and emphysema resemble other chronic diseases
There are several diseases that have symptoms similar to the two diseases above, such as:
- Heart disease.
- Pulmonary collapse (atelectasis).
- Lung cancer.
- Pulmonary embolism.
How are these two diseases diagnosed?
In addition to seeing the symptoms, you need to check with your doctor to get the right diagnosis. There are no specific tests to detect the presence of emphysema or bronchitis. However, the doctor will usually review your medical history and conduct a physical examination, such as:
- Imaging test, either chest x-ray or lung CT scan.
- Lung function tests to find out how well your lungs are working and you will measure the strength of air flow in the lungs with a spirometer
- Analysis of blood gases to find out pH, oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
- Alpa-1-antitrypsin (AAT) test to find out how high the AAT level is, a protein that protects the lungs from remaining elastic. People who lack this protein can get emphysema even if they don't smoke.
The treatment will be adjusted to the cause and severity of your symptoms.