Contents:
- Medical Video: 5 Common Signs of Hypoxemia
- What is the difference between hypoxia and hypoxemia?
- How do you distinguish the two?
- What causes hypoxia?
- What are the symptoms of hypoxia?
- Steps for treating hypoxia
- How to prevent hypoxia?
Medical Video: 5 Common Signs of Hypoxemia
Ever heard of hypoxia or hypoxemia? Both hypoxemia and hypoxia are conditions where your body does not have enough oxygen. Both are very dangerous conditions; because without oxygen, the brain, liver, and other organs in the body will be damaged even a few minutes after symptoms appear.
Hypoxia and hypoxemia are often misunderstood as a common term, because they together describe an emergency due to lack of oxygen in the body. However, hypoxemia and hypoxia are two completely different conditions. Here's the explanation.
What is the difference between hypoxia and hypoxemia?
Hypoxemia is a low level of oxygen in the blood, especially in the arteries. Hypoxemia is a sign of a problem in the circulatory or respiratory system that can cause shortness of breath.
While hypoxia is a low level of oxygen in body tissues as a result of low oxygen levels in the air. Hypoxia can have an adverse effect on body tissues, because a lack of oxygen levels in the tissues will interfere with important biological processes in the body's tissues.
How do you distinguish the two?
Hypoxemia is determined by measuring oxygen levels in a blood sample taken from an artery or by measuring your blood oxygen saturation using a pulse oximeter. Normal arterial oxygen is 75 to 100 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
Normal arterial oxygen levels below 60 mmHg usually indicate that your blood needs oxygen supplements. While reading with an oximeter can be said to be normal ranging from 95 to 100 percent. An oximeter value below 90 percent indicates that your blood oxygen level is low. While hypoxia is an advanced condition of hypoxemia, so that if the oxygen level in the blood is low it increases the risk of hypoxia.
Hypoxia occurs as a result of hypoxemia, so in the end both of these are events that cannot be separated from each other
What causes hypoxia?
The main cause of hypoxia is hypoxemia. However, hypoxia can also be caused by a number of conditions that make a person at low oxygen levels, including being at a height, such as riding a mountain, being in a closed room without good air circulation, poisoning gases or chemicals, certain diseases - such as sleep apnea, asthma, anemia, emphysema, interstitial lung disease, etc.
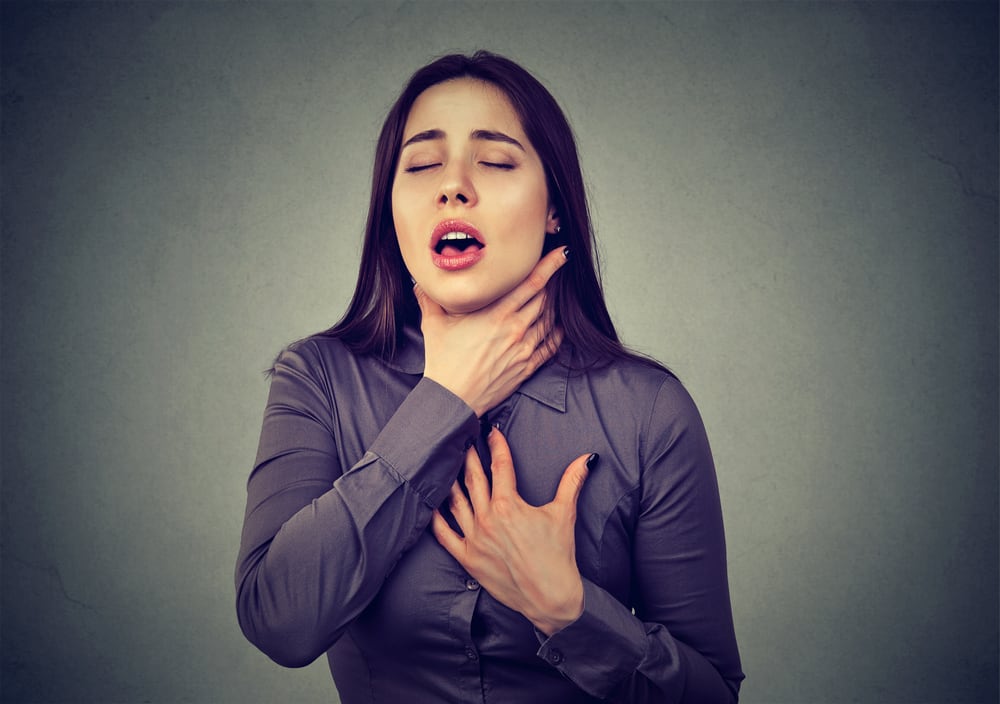
What are the symptoms of hypoxia?
Symptoms of hypoxia often appear suddenly and rapidly deteriorate (acute), or are chronic. Some of the most common symptoms of hypoxia are:
- Hard to breathe
- Cough
- Fatigue
- Fast heartbeat
- Hallucinations
- Breath sounds (wheezing)
- The skin changes color, becomes blue or purplish red
Often, ignorance makes someone who experiences hypoxia be given excessive oxygen assistance. In fact, excess oxygen can actually poison the body's tissues. This condition is called hyperoxia which can cause cataracts, vertigo, seizures, and pneumonia.
Steps for treating hypoxia
You are advised to consult a doctor if:
- Shortness of breath after you move or rest
- Shortness of breath during exercise or physical exercise
- Waking up from sleep due to shortness of breath (one of the symptoms of sleep apnea)
- Bluish lips and skin (cyanosis)
If you experience these symptoms or some of the symptoms mentioned above, immediately consult your doctor to get the right treatment. And even though the advanced symptoms are gone, you are still encouraged to routinely see a doctor.
How to prevent hypoxia?
Prevention of hypoxia can be done by avoiding causes or conditions that can reduce oxygen levels in your body. If hypoxia is caused by asthma, then to avoid a worse situation, you are encouraged to take asthma therapy - as recommended by the doctor. And to overcome chronic shortness of breath, try to stop being an active smoker, avoid passive smoke, especially from cigarette smoke, and do exercise regularly.