Contents:
- Medical Video: Understanding COPD
- Definition
- What is COPD?
- Cause
- What are the causes of COPD?
- Risk factor
- Who is at risk for COPD?
- Signs and symptoms
- What are the symptoms of COPD?
- Complications
- What complications can occur?
- Diagnosis and test
- How is COPD diagnosed?
- Treatment and Control
- COPD is an incurable disease, really?
- What can you use to relieve COPD symptoms?
- How to control COPD?
Medical Video: Understanding COPD
Definition
What is COPD?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or COPD is a respiratory disease that causes a person to have difficulty due to blocked airways in the lungs. COPD is a progressive disease, meaning that the disease will worsen over time.
In 2012, more than three million people died from COPD. That number is equivalent to 6 percent of deaths worldwide in that year. COPD itself consists of two main types. Some can only have one, while others have both. Two types of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease that occur, namely:
- Chronic bronchitis. Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial duct wall (throat branch). This disease causes the walls of the bronchial tubes in the lungs to become red, swollen, and filled with mucus. It is this mucus that then blocks the napad tract and makes breathing more difficult.
- Emphysema. Emphysema gradually damages the air sac (alveolus) in the lungs, making you even more short of breath. Damage to the air sac will make the number of alveoli in your lungs less. As a result, oxygen will be difficult to enter and carbon dioxide is also difficult to get out. This condition is also a cause of exhalation becomes more difficult.
During the breathing process, there are the main parts of the lungs that work, namely the bronchial duct (the throat branch or also called the airway), the alveoli (air sacs), and the trachea (trachea).
When inhaling, air moves from the trachea through the bronchi to then to the alveoli. From the alveolus, oxygen moves into the blood while carbon dioxide comes out of the blood. That's how the norm of breathing should be. However, in COPD people the process does not go smoothly. Disorders that arise from this disease can cause shortness of breath. This causes the lungs to lack oxygen, as well as other organs. If this happens, you should immediately seek medical help as early as possible.
Cause
What are the causes of COPD?

COPD is caused by blockage or damage to lung tissue. This type of damage usually occurs when you regularly breathe irritants for a long time. Common irritants can include:
- Cigarette smoke (both those who are active smoking and passive smoking) - long-term smoking is the cause of 80 to 90 percent of COPD cases
- Smoke, gas, steam, or chemicals
- Dust
- Indoor pollution (such as solid fuels used for cooking and heating)
- Outdoor pollution
- Dust and occupational chemicals (steam, irritants and smoke)
- Lower respiratory infections that often occur during childhood
Risk factor
Who is at risk for COPD?
The main risk of COPD is smoking. Besides smoking, there are other irritants and pollutants that can damage the lungs. You can find more pollutants in developing countries. Following are other risk factors that can increase the risk of COPD:
- people aged 65-74 years
- non-Hispanic white race
- people who are unemployed, retired, or unable to work
- people with education below high school
- people with low income
- people who are divorced, left dead, or separated
- smokers who are still active or ex-smokers
- people with a history of asthma
Signs and symptoms
What are the symptoms of COPD?
COPD affects the respiratory system so that it can cause many signs and symptoms that cause respiratory problems. COPD can cause the following signs and symptoms:
- chronic cough (prolonged)
- cough with the production of mucus that can be clear, white, yellowish or green - although rare, mucus can have blood spots
- increased respiratory infections (such as flu and runny nose)
- shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- feeling of tightness in the chest
- wheezing
- fatigue
- mild and hot-cold fever
At first, you may not feel any symptoms. Or, even if the symptoms appear you only experience mild symptoms so you don't realize you have COPD. This disease is a progressive disease, meaning that the new symptoms are really disturbing if the disease has lodged long enough in your body.
When your COPD symptoms have developed over the years, eventually the symptoms begin to affect your level of activity and quality of life. It is at this time that you may only really realize that there is a problem in your lungs.
Some severe symptoms may require treatment at the hospital. You must seek emergency treatment if you experience the following problems:
- Difficulty breathing or talking.
- Your lips or nails turn blue or gray (this is a sign of low blood oxygen levels).
- You are not mentally alert.
- Your heart beats very fast.
- Recommendations for treatment for worsening symptoms do not work.
There may be symptoms that have not been mentioned. However, if you have concerns about other symptoms, consulting a doctor is the right choice to answer your doubts.
Complications
What complications can occur?
COPD is a disease that is at risk of causing complications. There are several complications that might risk you getting COPD, including:
- Heart problem: COPD can cause an irregular heartbeat and change. This condition is called arrhythmia. Another heart problem that may also be at risk in people with COPD is heart failure.
- High blood pressure: COPD can cause high blood pressure in the blood vessels that supply blood to the lungs. This condition is called pulmonary hypertension.
- Respiratory infections: When you have COPD, you may be affected more oftencolds, flu, or even pneumonia (serious lung infection caused by a virus or fungus). This infection can make your symptoms worsen or cause further lung damage. That is why it is important for COPD patients to receive flu vaccines each year. Also consult with your doctor about the need to get a pneumonia vaccine. Your chances of getting a cold or pneumonia will decrease if you get this vaccination.
Diagnosis and test
How is COPD diagnosed?
COPD is a disease that occurs slowly. This disease is usually diagnosed in people over the age of 40 years. Your doctor will diagnose COPD based on signs and symptoms, medical and family history, and your test results.
The doctor may ask whether you smoke or have had contact with lung irritants, such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, chemical fumes, or dust. The doctor will also examine you and the stethoscope to hear wheezing or other abnormal sounds in the chest.
Here are some tests that can be done to diagnose COPD:
Lung function tests
Lung function tests will measure how much air you can breathe and exhale. This test can also find out how fast you can exhale, and how well your lungs deliver oxygen to the blood.
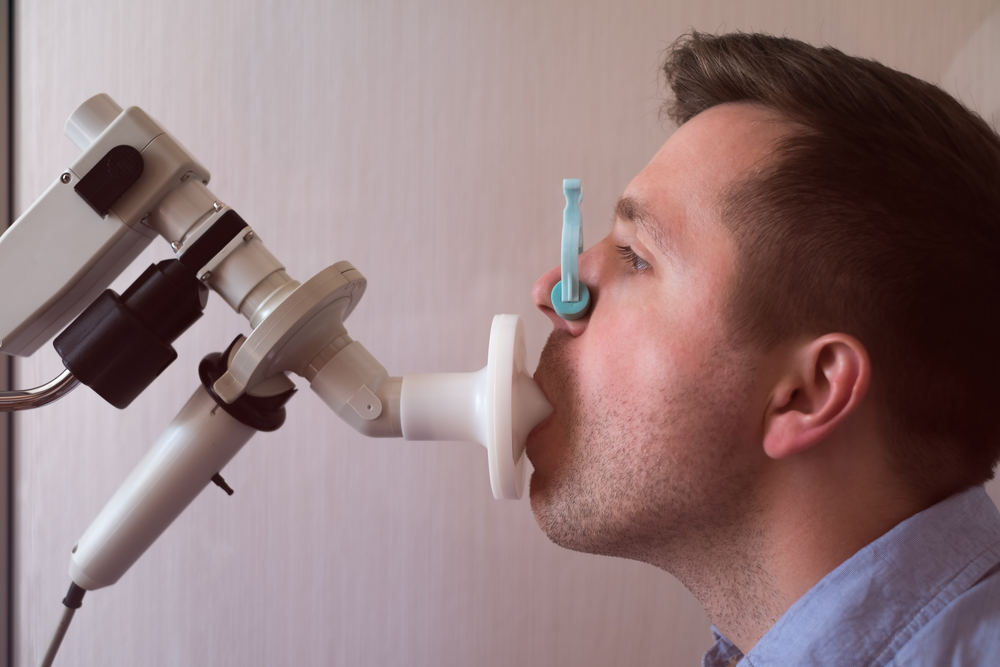
Spirometry
This one test is used to measure your ability to breathe. The diagnosis of COPD through this test is done by taking a deep breath and exhaling it as tightly as possible on a device called a spirometer. This tool measures how much air you exhale and how quickly you can exhale.
Chest radiograph or CT scan
This test provides a picture of the structure in the chest, such as the heart, lungs, and blood vessels. This description can provide information about the presence of signs of COPD or not.
Blood test
Blood tests are performed to measure oxygen levels in the blood. Blood is collected using a blood sample taken from an artery. The results of this test can show how severe your COPD is and whether you need treatment.
Treatment and Control
COPD is an incurable disease, really?
Yes, unfortunately, there is no cure for COPD. The best method for dealing with COPD is prevention and control. That is, what we can do with COPD is to prevent damage and the symptoms do not worsen. The goals of COPD treatment include:
- Relieve symptoms
- Slow the progression of the disease
- Improve the ability to stay active
- Prevent and treat complications
What can you use to relieve COPD symptoms?
Drugs
- Bronchodilators: this drug can make you breathe easier by relaxing the muscles in the lungs and widening the airways
- Bronchodilator combination with inhaled corticosteroids: steroid-type drugs are given with the aim of reducing lung inflammation
Vaccine
Getting a vaccine regularly every year is also one step that can be done to prevent worsening conditions and symptoms of COPD. Some vaccines that you might need to get include:
- Flu vaccine
- Pneumococcal vaccine, which functions to prevent diseases caused by so-called bacteria Streptococcus pneumoniae or pneumococcus) This vaccine is useful to prevent pneumonia
Oxygen therapy
One therapy that needs to be done is oxygen therapy, especially if the condition is severe enough. COPD is a disease that causes a person to have difficulty taking oxygen. In severe conditions, a person sometimes needs additional oxygen through regular oxygen therapy.
Operation
Surgery is usually the last choice for people who suffer from severe symptoms that do not improve by taking medication. The most frequent operations associated with emphysema, including bullectomy and lung volume reduction (LVRS) surgery. Lung transplantation can be an option for people who suffer from very severe COPD.
- bullectomy, namely removal of bubbles in the air bag (bullae) in the lungs
- lung volume reduction surgery
- lung transplant
How to control COPD?
Lifestyle changes and treatment can make you feel better, stay active, and slow down the progression of COPD. Some of the ways you can control COPD are as follows:
Stop smoking and avoid lung irritants
If you smoke, stop. Smoking is a major cause of COPD. Consult your doctor about programs and products that can help you stop smoking.
Try to avoid lung irritants that can contribute to COPD. The irritants that contribute to COPD are cigarette smoke, air pollution, chemical fumes, and dust.Keep this irritant away from your home. If you are doing a home renovation, move away for a while until the activity is complete.
Close the window and if possible stay at home when there is a lot of air pollution or outside dust.
Get constant medical help
It's important to get uninterrupted medical care, especially if your doctor requires you to take certain medications throughout your life. Take all medicines according to your doctor's prescription. Be sure to repurchase before it runs out. Bring a list of all the drugs you use while undergoing a medical examination.
Consult your doctor about whether you should get a flu vaccine (influenza) and pneumonia vaccine. In addition, ask him about other diseases that are at increased risk of developing COPD, such as heart disease, lung cancer, and pneumonia.
Overcome disease and symptoms
Take a meal program to get enough calories and nutrients your body needs, because when you suffer from COPD, you can have difficulty eating.
Stay active by doing physical activity regularly. Physical activity can strengthen the muscles that help you breathe and improve your overall health. However, you should consult your doctor first about what types of activities are safe for you.
Place objects that you often need in one place to easily reach them.Look for very simple ways to cook, clean, and do other homework. For example, you might need to use a small table or wheeled tray to move items and stakes or long-handled pins to reach objects.
Ask for help to move things at home to an easily accessible place so you don't have to climb the stairs often.
Choose clothes that are loose and wear clothes and shoes that are easy to wear and remove.Depending on the severity of the disease, you may need to ask for help from family and friends in doing daily work.
Get ready for an emergency
Record and save the doctor's telephone number, hospital, and someone who can take you to the hospital in an easily accessible place.Call your doctor if you feel that your symptoms are worsening or if you experience signs of infection, such as fever.
Hello Health Group does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.