Contents:
- Medical Video: Dr. Hallberg on Ketogenic Interventions to Reverse Type 2 Diabetes (Ch 6)
- Benefits of the keto diet for diabetes
- The risk of keto diet for diabetes
- Then, what kind of diet is good for diabetics?
Medical Video: Dr. Hallberg on Ketogenic Interventions to Reverse Type 2 Diabetes (Ch 6)
The ketogenic diet (keto diet) is said to help people who want to lose weight quickly and can reduce blood sugar levels. Therefore, many assume that the keto diet for diabetes is very suitable. But is the ketogenic diet really safe for people with diabetes?
Benefits of the keto diet for diabetes
The ketogenic diet is a diet that has the principle of consuming high fat and carbohydrates in very low amounts. Carbohydrates that are allowed in this diet are less than 30 grams per day, while the remaining carbohydrate needs are replaced with fat intake. The keto diet is currently believed to be one of the effective diets to make your weight go down quickly. Although in the beginning, the ketogenic diet was applied as one of the treatments for treating epilepsy.
Because it can lose weight quickly and has a basic principle of low carbohydrates, this ketogenic diet is considered suitable for diabetics. People who have diabetes - whether it's type one diabetes or type two diabetes - don't have the ability or experience problems processing sugar in their bodies, so their blood sugar levels will always be high.
By consuming very low carbohydrates and relying on energy sources from fat, many consider that this diet can control blood sugar levels in diabetics and make them lose weight.
The risk of keto diet for diabetes
Until now the keto diet is still a debate, because some studies state that this diet is good to live with, but others find that many side effects arise.
Actually, the keto diet for diabetes is quite risky if done without the monitoring of a nutritionist. The ketogenic diet forces the body to quickly replace the energy source that must be obtained from carbohydrates into fat.
Indeed, fat reserves will decrease and then weight will also decrease. But behind the process of changing fat into energy, the body produces another substance called ketone. Ketones are acids produced if energy does not come from sugar (carbohydrates). Too much ketone in the body will cause other bodily dysfunction.
Short-term side effects that may occur in diabetics if applying the ketogenic diet are:
- Headache
- Frequent urination
- Having constipation, because by reducing carbohydrates you tend to reduce the intake of vegetables and fruit.
- Feeling often tired.
- Having nerve function disorders, such as forgetfulness.
While the long-term effects that can be experienced by people with diabetes are impaired kidney function, increase the risk of fractures, and risk of developing ketogenic diabetes.
Then, what kind of diet is good for diabetics?
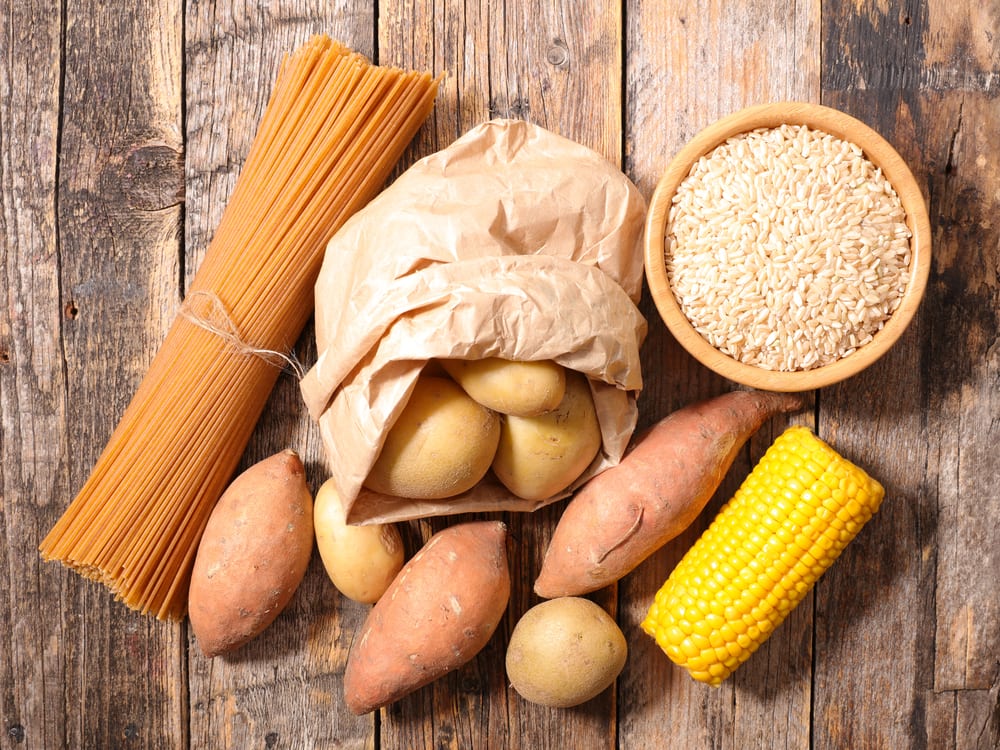
Despite having a disruption in processing sugar in the body, diabetics still need carbohydrates as their main source of energy. The minimum amount of carbohydrates that must be met by diabetics in a day is around 50% of total calorie needs. Or about 130 grams of minimum carbohydrate that must be present every day.
However, be careful with choosing the type of carbohydrate. Diabetics may no longer eat foods that contain simple carbohydrates, such as sugar, honey, sweetened condensed milk, or foods that have a sweet taste from sugar. Instead, they must meet the needs of complex carbohydrates obtained from rice, sweet potatoes, noodles, rice noodles. But even this may not be arbitrary. Pchoose a staple source of complex carbohydrates that contain lots of fiber such as whole wheat or brown rice. This type of food tends to have a low glycemic index that tends to be safe for the blood sugar levels of diabetics.
So in essence, it's not a problem of carbohydrate reduction that must be done by people with diabetes, but rather how to choose a good and proper carbohydrate so that blood sugar levels do not increase. This must also be accompanied by the selection of other food sources, which are certainly appropriate and in accordance with the needs of diabetics. Therefore, people with diabetes should first consult a nutritionist to get a food guide that suits their individual needs.