Contents:
- Medical Video: Checking Your Blood Glucose | Diabetes Discharge | Nucleus Health
- What is glucose?
- Know how glucose works
- What is normal glucose level?
- Controlling glucose is the main key for diabetic patients
- What should you do if your blood glucose level is too high or too low?
Medical Video: Checking Your Blood Glucose | Diabetes Discharge | Nucleus Health
You may have heard about glucose, but still confused to distinguish it from blood sugar or sugar from food. Yes, glucose is a medical term that is still often misunderstood. To straighten our understanding of glucose, see what glucose is and its function for the body in the following full explanation.
What is glucose?
Glucose is a source of energy for the human body. Glucose provides energy for all cells in the body to stay alive and function properly. Glucose is obtained from the food you eat, especially from carbohydrate sources such as rice, bread, fruits, vegetables, and sugar. Glucose moves through the bloodstream to body cells, so it is better known as blood glucose or blood sugar.
Even though it has an important role in the body, glucose levels must remain stable, should not be excessive or lacking. Glucose that is too high or low can cause serious health problems.
Know how glucose works
After eating, the body begins to produce glucose which then flows in the blood. Ideally, the body processes glucose several times a day. In the body of a healthy person, the way glucose works is:
- Food drops through the esophagus to the stomach
- Acid and enzymes in the stomach break down food into small parts
- Glucose is produced
- Glucose enters the intestine and is absorbed
- Glucose enters the bloodstream
- The hormone insulin is produced by the pancreas
- Insulin helps glucose enter the cell
- Cells that get glucose will work properly
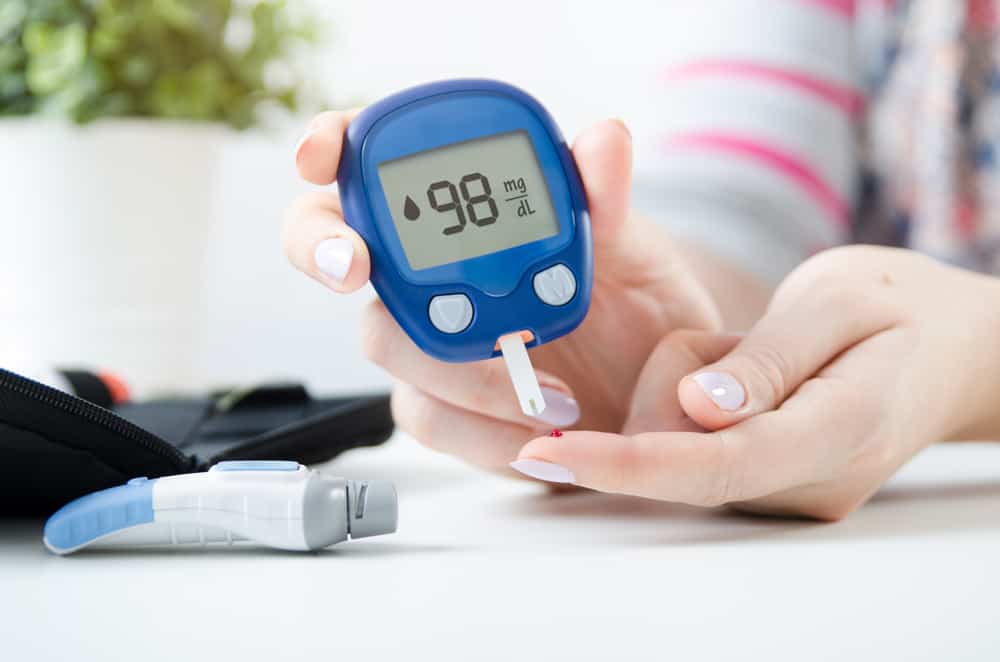
What is normal glucose level?
To keep the body healthy and functioning effectively, it is important to maintain glucose levels in the normal range. This is especially important for people with type 1 or 2 diabetes mellitus.
Before eating, healthy glucose levels are between 90-130 milligrams per deciliter (mg / dL). This number is measured by a special device and is known as fasting blood sugar. Whereas one or two hours after eating, normal glucose levels are below 180 mg / dL.
Things that can increase glucose are:
- Eat heavily or eat in large portions
- Stressful
- Certain health conditions
- Sedentary lifestyle (not moving)
- Forgot to take diabetes medication or inject insulin
Controlling glucose is the main key for diabetic patients
Normally, blood sugar levels rise after you eat. Then within a few hours the glucose level will go down because it has entered the cell, no longer in the bloodstream.
If you excess glucose in a chronic way, the doctor will divide the type of disease into two types:
Type 1 diabetes, which is where the body lacks insulin. In this situation, the immune system attacks and destroys the pancreatic cells, causing abnormalities in insulin production.
Type 2 diabetes where the body's cells do not respond to insulin. As a result, the pancreas must work harder to produce more insulin.
In the end, the pancreas is damaged and can no longer produce enough insulin to meet the body's needs. Without enough insulin, glucose cannot enter the cell, so the blood sugar levels remain high.
If blood sugar stays high for a long time, blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood to the organ will be damaged. As a result, you are also more at risk for the following diseases.
- Heart disease, heart attack, and stroke
- Kidney illness
- Neurological disease
- Eye disease called retinopathy
What should you do if your blood glucose level is too high or too low?
When glucose levels rise, insulin produced naturally by the pancreas will reduce it again. In people with diabetes, the solution is to give artificial insulin. In milder cases, moving actively and exercising can reduce blood sugar.
There are also some people who suffer from hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia is a condition in which glucose levels drop below 70 mg / dL. Hypoglycemia can occur when people with diabetes forget to take medication. Hypoglycemia can also occur when a person eats less than usual but exercises desperately. The solution is to eat or drink juice so that blood sugar can rise again.
Low blood sugar levels can cause loss of consciousness. You should immediately seek medical help if this happens.
Hello Health Group does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.