Contents:
- Medical Video: Pill Camera Swallowed | Follow Through Gut | Guts | Brit Lab | BBC
- Get to know bacteria in the intestine
- Benefits of intestinal bacteria for our body
- How can bacteria in the intestine affect brain function?
Medical Video: Pill Camera Swallowed | Follow Through Gut | Guts | Brit Lab | BBC
Did you know that it turns out that the stomach, intestines, and various organs that function in the digestive system have a direct relationship to the formation of cognitive and intelligence of children? Various studies even state that the stomach is the second brain of the human body. How can the stomach "shape" children's intelligence?
Get to know bacteria in the intestine
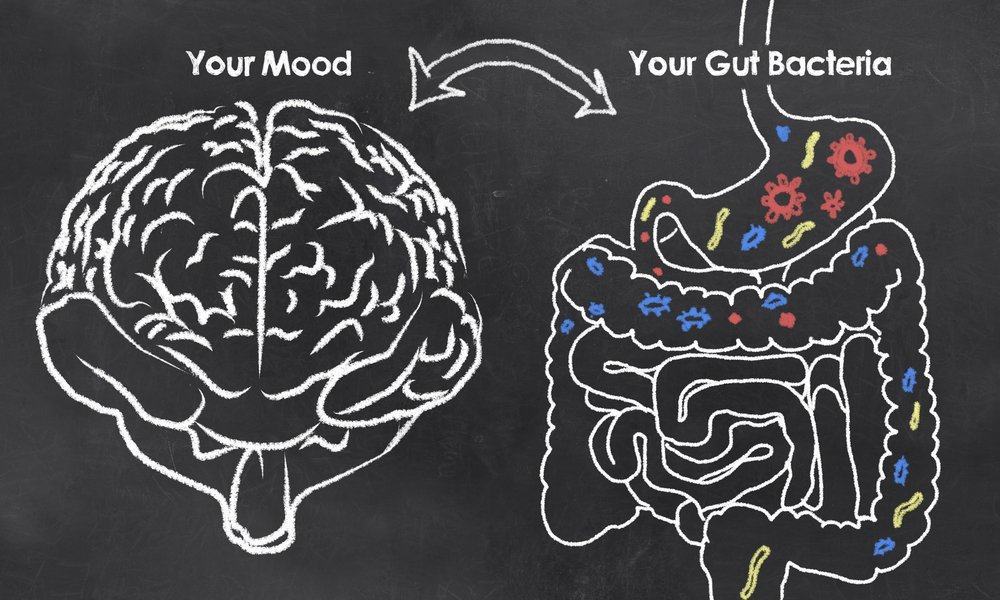
The theory that connects the digestive system to the brain is called gut brain axis. The digestive organs not only function to digest and absorb nutrients from food that enters the body. However, in the intestine, there are various microbes or good bacteria that have various health benefits.
Shortly after birth, bacteria in the intestine grow and develop to form colonies. Various theories say that bacteria in the intestine appear through breast milk given to babies. The study, reported in Environmental Microbiology, shows that bacteria are sent by mother to baby through the milk they give and can help keep the baby's immune system into adulthood later.
There are other studies that say that bacteria in the intestine have been formed from since the baby is still in the womb. This study proved it through experiments in mice, which found that bacteria were kind Enterococcus and Staphylococcus already formed in the womb. Meanwhile, breastfeeding in infants supports bacterial growth and development, and the opposite occurs when babies are given formula milk. Formula milk is considered to be unable to support the growth of this bacterium so it is not good for baby's growth.
Benefits of intestinal bacteria for our body
Until we grow up, the bacteria in the intestines will grow and develop. Even if calculated, the weight of bacteria in the intestine can be up to 2 kg, which consists of at least 1000 types of bacteria formed from 3 million genes. What's more, everyone has their own intestinal bacteria, different and unique. Two-thirds of the total bacteria in the intestine are formed from the characteristics and lifestyle of each individual, depending on the air they breathe everyday, food and drinks consumed every day, and various other environmental factors.
Then what is the function of good bacteria in the intestine? It turns out that many things that these bacteria can do, not only digest food, but also maintain the immune system, produce various vitamins and minerals produced from the digestive process, and help improve intelligence and cognitive abilities. The more types of bacteria an individual has, the better the impact on health. Even considered to be able to prevent someone from being exposed to various chronic diseases such as coronary heart disease, stroke, diabetes mellitus, and cancer.
How can bacteria in the intestine affect brain function?
The intestine, called the second brain, turns out to have the ability to communicate directly with the brain, the center of all bodily functions. In addition, the intestine is also considered to be able to feel and provide a direct response to what is happening to the body. Have you ever felt you were in a state of panic or pressure and suddenly your stomach felt sick, wanted to vomit, and was uncomfortable? That is one response given by the intestine because you are feeling stressed. The intestine can feel what you feel so that the symptoms appear without cause. Communication that occurs in two directions, between the brain and the intestine, involves various types
Simply put, the intestine will send a good signal to the brain when it is filled with foods of good quality, which then affect brain development. Vice versa, when the brain is not in good condition, such as stress or stress, then the signal will be sent to the intestine and affect the composition of the bacteria which in turn has an impact on the process of absorption of nutrients.
The American Psychological Association (APA) states that bacteria in the intestine produce various neurotransmitters, namely substances used by the brain to regulate a person's mental and psychological processes, including memory, learning ability, and mood. In fact, 95% of the hormone serotonin, which is a hormone that functions to regulate mood, cognitive abilities, and one's appetite, produced by bacteria in the intestine. In 2014, a study found that bacteria were both effective in reducing stress and anxiety levels and people who had a smaller number of good bacteria experienced higher stress levels.
These good bacteria in the digestive system are also said to be associated with a decrease in the incidence of autism in children. A study conducted at Arizona State University which looked at the number and method of working bacteria in the intestines in the autism group, proved that autistic children had a lower number of bacteria in the intestine compared to normal children, the bacteria were Prevotella, Coprococcus, and Veillonellaceae. From this research, it was concluded that good bacteria in the intestine are related to brain function, especially in terms of emotions and cognitive abilities.
READ ALSO
- Differentiating Stomach Pain Due to Gas, Appendicitis, or Kidney Stone
- Foods to Avoid If You Have Intestinal Inflammation
- Benefits of Lemon Water for Overcoming Ulcer