Contents:
- Medical Video: Chest Physiotherapy, by Susan Hamilton, MS, RN, for OPENPediatrics
- What is pneumonia?
- Symptoms of pneumonia in children
- How to prevent pneumonia in children?
Medical Video: Chest Physiotherapy, by Susan Hamilton, MS, RN, for OPENPediatrics
Based on data from the World Health Organization (WHO), pneumonia in children is the cause of 16 percent of deaths of children under five in 2015. Pneumonia in children is even claimed to be the cause of death of children every 20 seconds. Here are some symptoms of pneumonia in children that you should know about.
What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is a condition in which one of your lungs becomes inflamed. The cause can be caused by many things such as fungi, bacteria, and viruses. But most cases of pneumonia are generally caused by a bacterial infection in your lungs. Generally pneumonia symptoms develop within one to two days, then experience a slowdown after a few days.
This infection begins with disrupting your upper respiratory system (nose and throat). Then the infection will move towards the lungs, which then inhibits the movement of air in the lungs, so you will increasingly experience difficulty in breathing. Most pneumonia can be treated until healed within one to two weeks (pneumonia due to viruses generally takes longer). But your condition will certainly be worse if you experience pneumonia coupled with the presence of other diseases in your body.
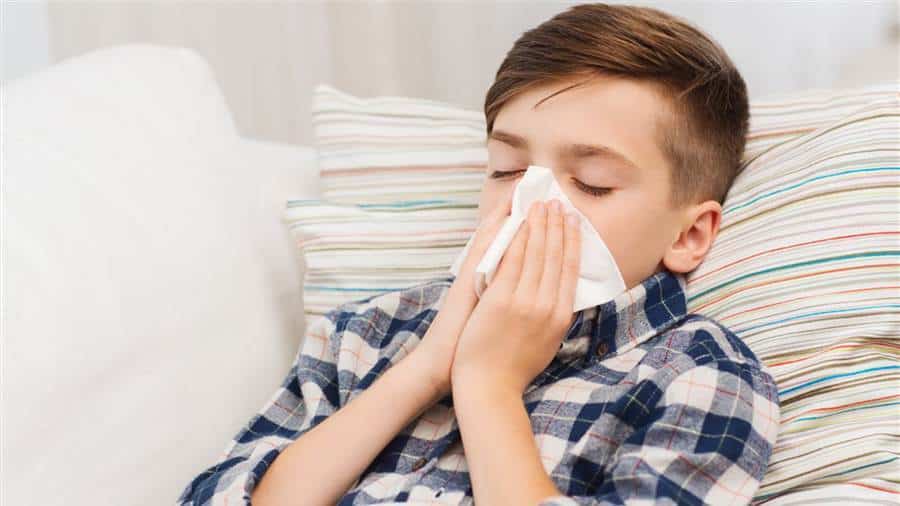
Symptoms of pneumonia in children
Somewhat different from pneumonia in general, pneumonia in children in some cases is not marked by an increase in the tempo of breathing, especially if the pneumonia attacks the lower lung. Symptoms that occur are generally just fever, vomiting and pain in the lower abdomen.
Some other symptoms that indicate your child is attacked by pneumonia include:
- Fever,
- Cough, which may be dry and may also phlegm followed by mucus or mucus in green or yellow.
- Breathing in a high tone,
- Difficulty breathing. Generally your child will still feel difficulty breathing even when he is resting.
- Throws up,
- Pain in the chest.
- Abdominal pain that can occur due to your child's efforts that are too hard to breathe normally.
- Decreased activity.
- Loss of appetite.
- In more severe conditions your child's lips and nails will turn blue.
- Sweating
How to prevent pneumonia in children?
At the age of children, pneumonia can be prevented by routinely getting a vaccine that will usually be given since he was about two months old. But as mentioned above, pneumonia will have a worse impact when the attack comes along with other diseases. Especially if comorbidities are chronic diseases that come with relapses such as heart disease or asthma.
Although pneumonia is not an infectious disease, the microorganisms that cause this disease can spread through droplets of water when sneezing or coughing. So that your child should:
- Shut your mouth every time someone with cough pneumonia or sneezes nearby
- Wash hands with soap, to prevent the spread of any bacteria or viruses.
Some other conditions can also increase your child's chances of developing pneumonia. Such conditions are like living in areas with high levels of pollution and having parents of active smokers.