Contents:
- Medical Video: Schizophrenia Symptoms : Signs of Schizophrenia in Children With ADHD
- What are the causes of schizophrenia in children?
- 1. Genetic factors
- 2. Environmental factors
- What are the symptoms of schizophrenia in children?
- When should a child be taken to a doctor when experiencing symptoms of schizophrenia?
Medical Video: Schizophrenia Symptoms : Signs of Schizophrenia in Children With ADHD
The term schizophrenia may still be strange to your ears. People with schizophrenia are often called "crazy people" because they often hallucinate, do whatever they want, and find it difficult to distinguish between reality and imagination. This condition is more often found in adults. However, schizophrenia in children is in fact not an impossible thing. Even the symptoms are often not realized by parents.
What are the causes of schizophrenia in children?
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental disorder that can affect the sufferer's soul for life. People with schizophrenia often experience psychotic experiences, such as hearing intangible voices, hallucinations, delusions, and difficulty distinguishing between the real world and the imaginary world.
Schizophrenia in children generally occurs at the age of 7 to 13 years. Unfortunately, experts don't know the exact cause yet. They suspect there are two things that are the causes of schizophrenia in children, namely:
1. Genetic factors
Genes derived from families can be one of the causes of schizophrenia in children. The risk of schizophrenia in children can increase 5 to 20 times greater if the father or mother also has schizophrenia. In addition, if one of the twins is diagnosed with schizophrenia, the other twins are also at risk of developing schizophrenia by more than 40 percent.
2. Environmental factors
The risk of schizophrenia in children can increase if the mother is infected during pregnancy or has complications during childbirth. Especially if accompanied by genetic influences or inherited from their parents who turned out to also have schizophrenia. Again, experts still haven't found the exact cause.
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia in children?
Symptoms of schizophrenia in children are not the same as adults. This is because the child's brain is still developing during its growth period so the symptoms can vary, depending on the type of schizophrenia experienced by the child.
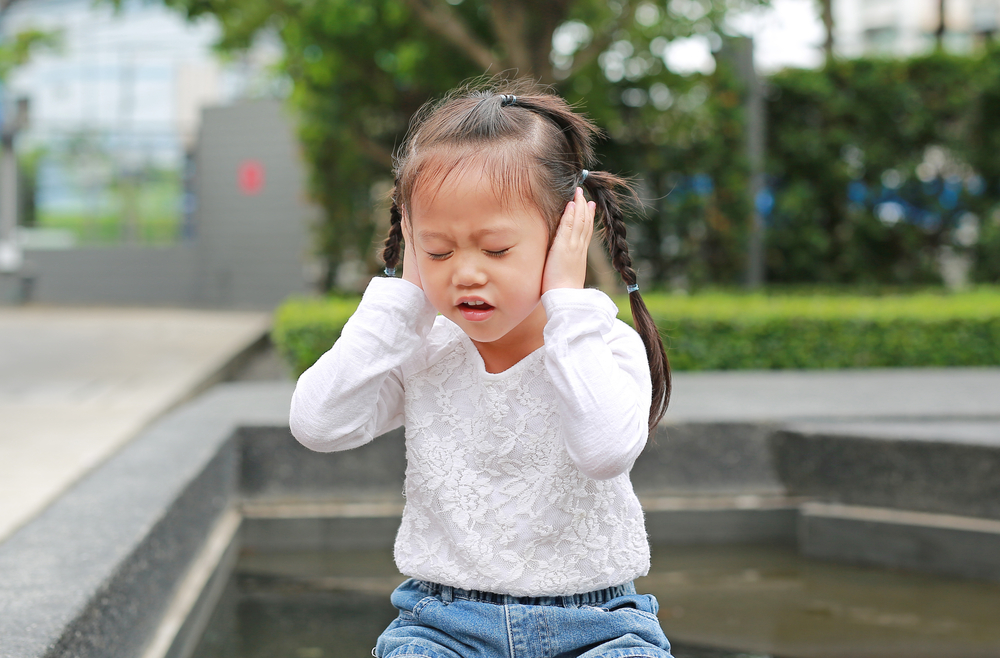
You should be aware of any changes in behavior in children that occur suddenly. For example, you know that your child tends to be active and easy to get along with his peers. However, your child suddenly withdraws from his environment and chooses to be alone.
Not only when at home, you also need to monitor the attitudes and behavior of children while at school. Because you are not likely to watch it directly, you can ask for help from the teacher to see changes in a child's behavior. For example, your child experiences extraordinary fear without cause and speaks carelessly or rambles.
In addition, other symptoms of schizophrenia in children include:
- Hallucinations, like seeing or hearing something that is not real
- Insomnia
- His attitude and manner of speaking are strange
- Cannot distinguish real and imaginary worlds
- Unstable emotion
- Excessive fear and assume someone else will harm it
- Don't care about himself
The age of children is indeed fair to have imagination and this is usually indicated by the feeling of having imaginary friends. For example, your child often talks with dolls or talks to himself in front of a mirror.
This does not mean your child is hallucinating or experiencing one of the symptoms of schizophrenia. However, if the child's behavior occurs continuously and is accompanied by the above signs, then this can only be suspected as a symptom of schizophrenia.
When should a child be taken to a doctor when experiencing symptoms of schizophrenia?

Many parents mistakenly consider schizophrenia in children as a symptom of bipolar disorder, depression, and autism. This cannot be entirely blamed because the symptoms of schizophrenia are indeed similar to some of these mental illnesses.
What's more, children still can't tell their parents about the symptoms of the disease that they have experienced so far. So, you can't ask, "Have you ever seen things other people don't see, child?" To diagnose symptoms of schizophrenia in children.
It's easy like this. Always monitor any changes in attitudes and behavior in children. This is important because the symptoms of schizophrenia in children develop gradually and over time the symptoms can be very clear.
If your child has two or more of the following symptoms:
- Delusion
- Hallucinations
- Talk irregularly and without expression
- Changes in behavior
- Be apathetic
- Limitations of speech
- Difficult to make a decision
It could be that your child has schizophrenia. Immediately bring your child to the nearest doctor or child psychologist to confirm the diagnosis. Your child may be advised to undergo therapy, take antipsychotic medication, or practice skills to reduce symptoms of schizophrenia.