Contents:
- Medical Video: Congenital Hypothyroidism
- What are the signs and symptoms of congenital hypothyroidism?
- How do doctors diagnose congenital hypothyroidism?
Medical Video: Congenital Hypothyroidism
The thyroid gland is a gland located in the lower neck. This gland serves to make hormones that contain iodine. These hormones function to regulate growth, brain development, and body metabolism.
The disruption of the production of this hormone can inhibit the growth of children, disrupt the respiratory system, the heart and nervous system, body temperature, muscle strength, skin health, weight, cholesterol levels, and brain development disorders such as mental retardation. Unfortunately, this disorder can be congenital. This condition is known as congenital hypothyroidism.
What are the signs and symptoms of congenital hypothyroidism?
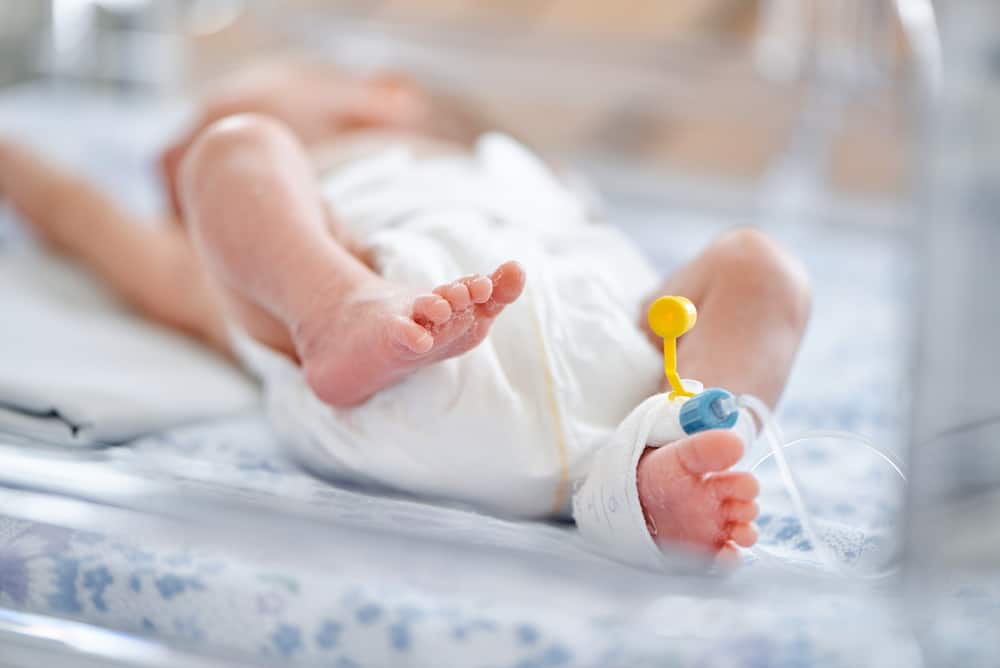
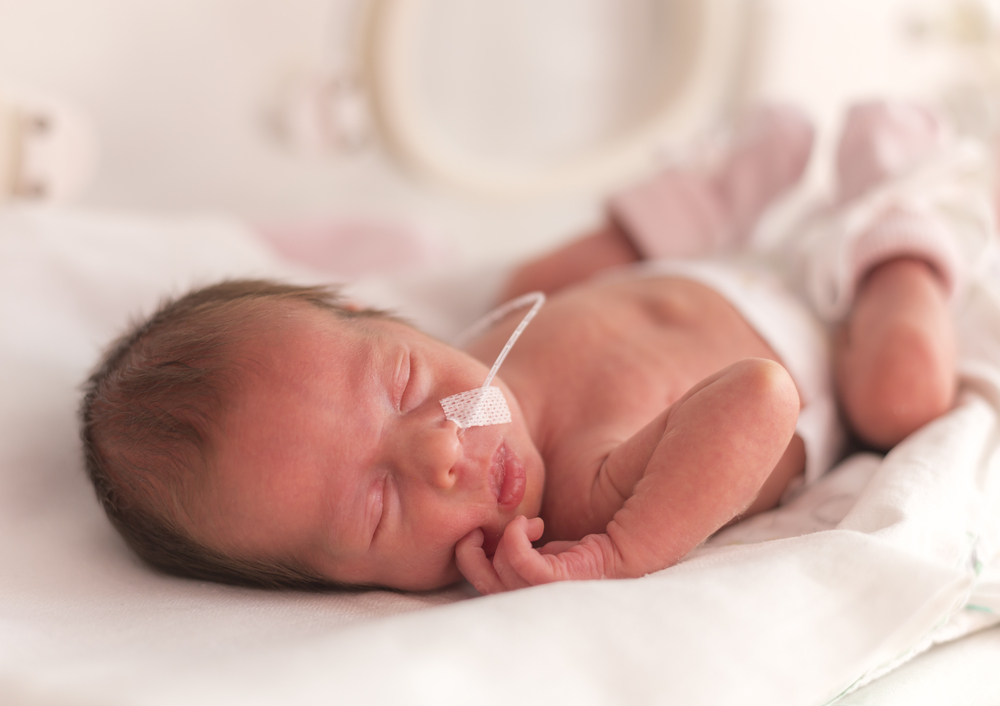
Symptoms of congenital hypothyroidism that often occurs in infants are prolonged jaundice (skin and yellow eyes), prolonged sleep and decreased activity, difficulty eating, dry skin, and constipation (constipation). Babies may also look lethargic and easily choke.
Signs that appear in congenital hypothyroid children are umbilical hernias, macroglossia, bulging abdomen, and cold and speckled skin. You can also observe the child's face and see something strange. For example the distance between the right and left eye is too wide or the area between the child's eyebrows (above the nose) looks very large.
While other symptoms that will appear along with the growth of children include:
- Stunted growth (the child's body is very short)
- Head larger than normal size
- Anxious, like not powered
- Weak muscles
- Slow reflex
- Too late learning to sit and stand
- A voice that sounds harsh and too late to speak
- The development of sexual organs is blocked or does not occur at all
- The mouth is often open because of the size of a large tongue
- Swelling of the eyelids, back of the hand, or genital area
- Pulse feels slow, heart rate is weak
How do doctors diagnose congenital hypothyroidism?
Congenital hypothyroidism is one of the main causes of mental retardation in children that can be prevented and has a good prognosis. In 1993, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommended a congenital hypothyroid examination in all newborns. Early detection of congenital hypothyroidism is one of the many screening tests performed on newborns.
What is used for screening is blood from the heels collected on special filter paper. Blood will be routinely taken between the 2nd day to the 5th day, can also use blood from the umbilical cord. In some programs a second sampling is also carried out when patients are between 2 and 6 weeks old.
Initially screening is done by testing the levels T4. If the results obtained are below the normal level, then the next testThyroid-Stimulating Hormone or TSH. With the increasing accuracy of the TSH test, this TSH test is also performed to detect congenital hypothyroidism.
After obtaining unnatural screening results, a confirmation test is performed again. A confirmation test will check TSH, fT4, or total T4 combined with T3 resin uptake.
According to the recommendations of the Indonesian Pediatrician Association (IDAI) in 2012, congenital hypothyroid screening is performed on all newborns by:
- Take capillary blood samples from the lateral surface of the baby's foot or medial part of the heel, on the 2nd to 4th day after birth.
- Capillary blood drops into special filter paper.
- The filter paper is sent to a laboratory that has a TSH inspection facility.
Infants with a positive screening test are immediately recalled for serum TSH and T4. If the TSH results are high and the FT4 is low or the FT4 results are low and regardless of TSH, the doctor will immediately give thyroxine.