Contents:
- Medical Video: Don't Ignore These Early Symptoms of Kidney Disease
- What is gum disease?
- Signs and symptoms of gum disease
- How to diagnose gum disease?
Medical Video: Don't Ignore These Early Symptoms of Kidney Disease
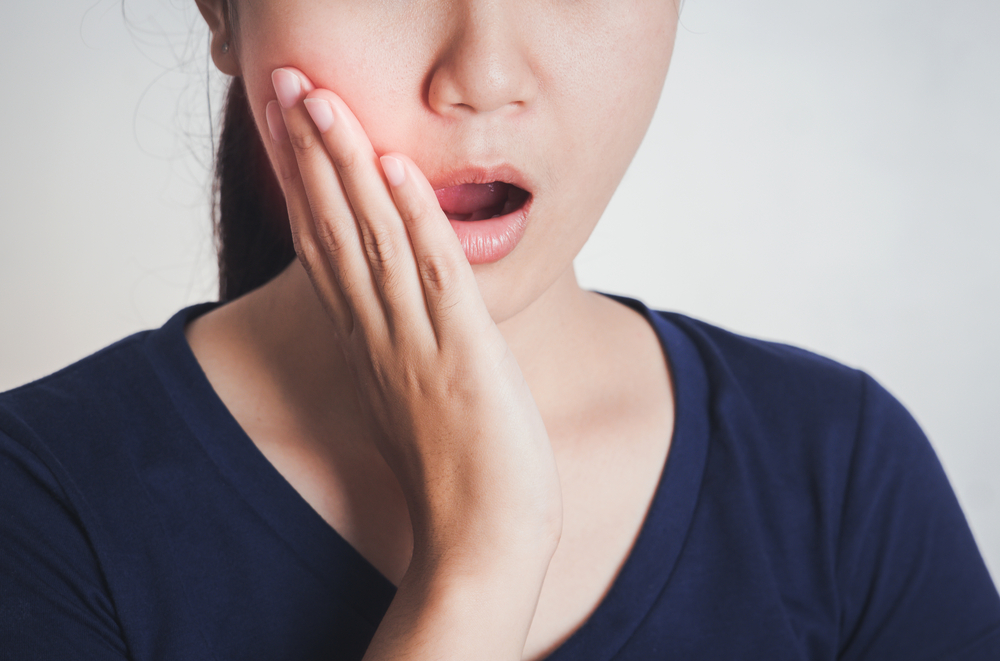
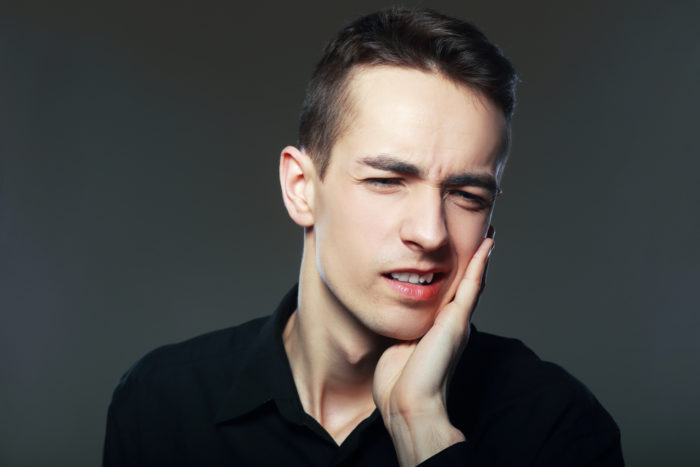
Gum disease is one of the dental and mouth problems that is often overlooked. Because gum disease does not always cause pain, even you may not realize that you are experiencing it. As a result, you will resume the lazy habit of brushing your teeth or eating sweet foods that can aggravate the symptoms of gum disease. What are the symptoms of gum disease? Find out through the following reviews!
What is gum disease?
Gum disease is mostly caused by poor oral hygiene. When you are lazy to brush your teeth and often eat sweet foods, bacteria are also easier to grow and develop into plaques. As a result, the bacteria will infect the gums slowly and damage the teeth.
Besides being lazy to brush your teeth, gum disease can be made worse by smoking habits. In fact, smoking can make the treatment of gum disease ineffective. In some conditions, you become more susceptible to gum disease when you have diabetes, take certain medications, experience hormonal changes in women, and because of genetic factors.
Reporting from the NHS UK, healthy gums are pink, tight gums, and become the place where teeth stick firmly. Healthy gums will certainly not bleed easily if you are exposed to toothbrush friction. Therefore, pay attention to any signs and symptoms of gum disease that might occur to you.
Signs and symptoms of gum disease
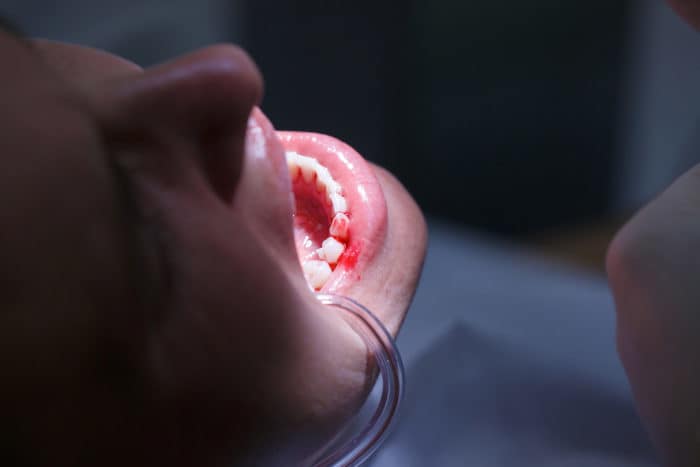
The most common symptom of gum disease is swollen gums, redness, until bleeding. If left unchecked, symptoms of gum disease will develop into periodontitis to acute gum disease.
The initial stages of gum disease are called gingivitis. Gingivitis is reversible or can be cured by routinely brushing your teeth properly and correctly. Symptoms of gingivitis are usually red, swollen, and easily bleeding gums when you brush your teeth or eat hard-textured food.
If the gingivitis is not treated, the bacteria that causes gum disease will spread to the tissues and bones that support the teeth. This condition is known as periodontitis or periodontal disease. Symptoms of advanced gum disease or periodontitis include:
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Bad taste in the mouth
- Tenuous teeth that make eating difficult
- Gum abscess or pile of pus that appears under the gums or teeth
In certain cases, the symptoms of gum disease that are left will get worse, becoming acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG). This condition is usually experienced by people who have never brushed their teeth and ignored a healthy lifestyle.
Symptoms of ANUG gum disease are usually more severe than other symptoms of gum disease, including:
- Bleeding gums
- Ulcers or wounds that cause prolonged pain
- The gums recede to cause the teeth to look longer than before
- Bad breath
- Metal feeling in the mouth
- Excessive saliva
- Difficulty swallowing or talking
- Fever
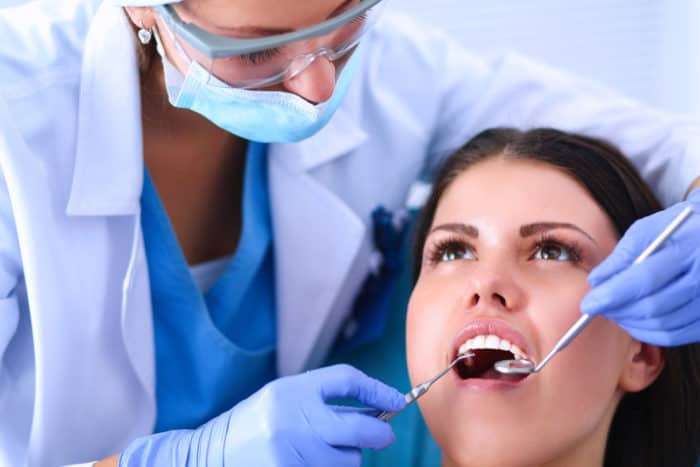
How to diagnose gum disease?
When you begin to notice the symptoms of gum disease, immediately have your teeth and gums checked with your doctor. During a dental examination, the dentist will usually assess the symptoms of gum disease by looking at:
- The level of bleeding and swelling of the gums
- Distance or space (pockets) between gums and teeth. Healthy gums have a bag measuring 1 to 3 millimeters (mm). The bigger and deeper in the gum pocket, the more plaque will enter and aggravate the gum disease
- Level of straightness of teeth growth
- Health of the jawbone, to help detect bone damage around the teeth
The main key to overcoming symptoms of gum disease is to routinely brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. In addition, make sure to check your teeth regularly with your dentist to help prevent the development of dental and oral diseases.