Contents:
- Medical Video: Benefits Of Breastfeeding For Mother - Manipal Hospital
- Benefits of breastfeeding for mothers
- 1. Helps burn body fat after giving birth
- 2. Encourage the release of good hormones
- 3. Maintain heart health
- 3. Reducing the risk of breast cancer and ovarian cancer
Medical Video: Benefits Of Breastfeeding For Mother - Manipal Hospital
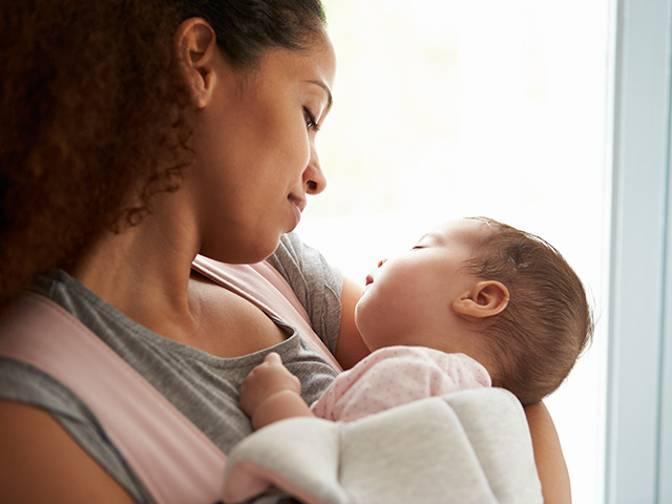
Breastfeeding is one way to fulfill the nutrition of a newborn baby. By giving breastmilk for at least six months, this can increase the endurance of the baby's body, help develop the body and brain and provide long-lasting immunity until a child grows up. However, not only that, the benefits of breastfeeding in mothers are equally numerous, and can last a long time,
Benefits of breastfeeding for mothers
Although breastfeeding is recommended, not all mothers can give breast milk because of some obstacles both in the condition of the mother and baby, such as if the baby is born prematurely. Breastfeeding can also be seen as an option that depends on the decision of the baby's mother. But here are some benefits of breastfeeding that can be obtained by a mother.
1. Helps burn body fat after giving birth
Weight gain is normal for pregnant women. When pregnant, the body stores more food in the form of fat. Weight gain can also be caused by changes in diet to meet the nutritional needs of pregnant women and infants. But not only fulfillment of nutrition during pregnancy, weight gain is also prepared for breastfeeding after giving birth.
With breastfeeding, the mother's body will burn more calories than usual or around 480 calories per day during breastfeeding. It can also overcome excess fat around the abdomen after going through the pregnancy process.
One study showed that breastfeeding mothers experienced a reduction in fat and more weight compared to mothers who gave formula milk to their children. Fat around the abdomen itself is a form of metabolic syndrome which can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes in women, especially after entering menopause.
2. Encourage the release of good hormones
The breastfeeding process triggers the mother's body to release the hormone prolactin and oxytocin. Prolactin acts as a trigger for relaxation and also prevents the ovum from ovulating for some time so that the menstrual cycle can be temporarily delayed. While oxytocin acts as a trigger for closeness between mother and baby. In addition, oxytocin also helps the uterus to return to its normal size after childbirth, and this is needed to prevent postpartum bleeding.
3. Maintain heart health
A study released in 2010 showed that mothers who breastfeed have a lower risk of experiencing cardiovascular disease. Conversely, the risk of the disease is more common in women who have not breastfed for more than three months.
One explanation of this is that breastfeeding can reduce cholesterol triglyceride levels which increase due to changes in diet and body increases during pregnancy. Nursing mothers also tend to have higher levels of good cholesterol (HDL) while breastfeeding. The process of breastfeeding can also reduce blood pressure because it can produce a sense of calmness from the hormone oxytocin which also plays a role in controlling stress.
3. Reducing the risk of breast cancer and ovarian cancer
The process of breastfeeding is known to reduce two types of cancer, namely breast cancer and ovarian cancer. The benefits of breastfeeding against protection from breast cancer have been widely proven by research, even in a study, breast cancer that is inherited in the family also has a reduced risk when a woman is breastfeeding.
Nevertheless, the mechanism related to this matter cannot yet be known for certain. There is a possibility that this is related to hormonal conditions of a woman where the cessation of the menstrual cycle after childbirth can reduce excess estrogen levels and reduce the risk of breast cancer.
Whereas in ovarian cancer, the benefits of breastfeeding are related to increasing the body's resistance to the appearance of cancer cells. Breastfeeding can trigger a small infection known as mastitis. These infections play a role in strengthening the body's resistance with the appearance of antibodies that can prevent the emergence of tumor cells in the future. Women who do not breastfeed will not have these antibodies and are more at risk for ovarian cancer. Several studies have also shown that ovarian cancer is more common in women who have never breastfed.