Contents:
- What are the causes of endophthalmitis eye infections?
- What are the symptoms and characteristics of endophthalmitis?
- What examinations will the ophthalmologist do?
- What kind of treatment should be taken?
There are various types of infections that can attack your eyes. One of them is endophthalmitis. As one rarely heard disease, endophthalmitis is a severe eye infection that if not handled properly and quickly can cause blindness. What are the symptoms and what can be done to overcome them? Check out more detailed explanations in the following discussion.
What are the causes of endophthalmitis eye infections?
Broadly speaking, the causes of endophthalmitis eye infections can be divided into three, namely:
- External origin (exogenous) infection. Often occurs in puncture wounds that affect the eyes or can sometimes also occur after undergoing eye surgery. Through these two processes, bacteria enter the eye and cause infection.
- Infections originating in the body (endogenous). This infection is acquired because bacteria that are at the source of infection (for example in cavities) spread through blood to the eyes.
- The inflammatory process that occurs without the discovery of bacteria. This can be found in people who use planting lenses, have eyeball tumors, and in morgagni type cataract patients.
What are the symptoms and characteristics of endophthalmitis?
Some of the symptoms that are most often complained of by patients with endophthalmitis are:
- Unbearable pain in the eyeball
- Redness
- Excessive tear production
- Easy glare
- Blurred or unclear views
Whereas one of the easiest signs to recognize is the pupil (the black part of the eye) which turns yellowish due to the presence of pus.
If you experience the symptoms of endophthalmitis mentioned above, immediately consult your ophthalmologist to prevent the disease from worsening.
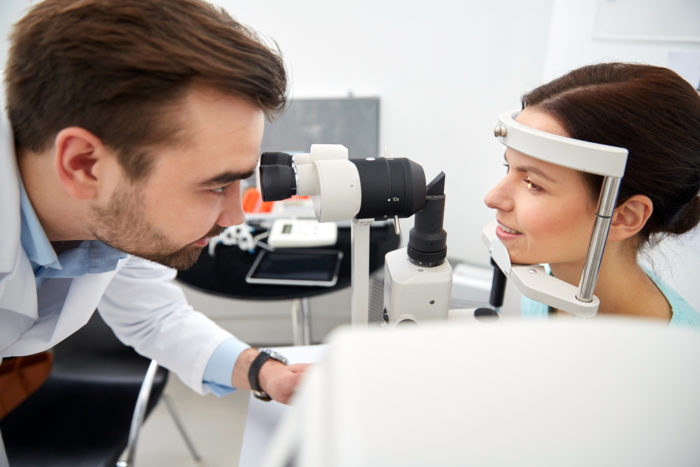
What examinations will the ophthalmologist do?
Examination begins by exploring your history to find out the main source of eye infections. Next will be a general examination of the eyes. This includes a sharp examination of the vision (vision) and examination of the front chamber. Ultrasonography sometimes needed in severe cases to be able to see the back of the eye.
In very serious cases, the ophthalmologist will remove the glass body as well as check the culture and gram to find out the bacteria that causes the infection.
What kind of treatment should be taken?
Treatment of endophthalmitis eye infections varies. Treatment depends on the severity of the disease during examination. Some types of treatment options are:
- Eye drops in the form of steroids, antibiotics and atropine.
- Injection drugs. Provision of systemic antibiotics from the fluoroquinolone group can be performed in cases of puncture trauma.
- Drinking medicine like steroids and antibiotics (moxifloxacin).
- Eye injection. In general, two types of antibiotics will be used. The act of injecting can be done simultaneously with taking glass body fluids to check the type of bacteria that causes the infection.
- Inject into the clear part of the eye (conjunctiva). This method can be done for antibiotics, but injections must be done repeatedly so that the drug levels are effective enough to kill the bacteria that causes infection.
- Operation removal of the glass body. If within 48-72 hours after treatment there is no progress or after being examined it turns out that your eye infection is severe enough, your doctor may recommend surgery.