Contents:
- Medical Video: Female Reproductive Anatomy
- Hand drawings and their functions
- 1. Bones and joints
- 2. Muscle
- 3. Nerves
- 4. Blood vessels
- 5. Ligaments and tendons
Medical Video: Female Reproductive Anatomy
One of the unique anatomy of the human body is the hand. It requires proper alignment and control so that your hands can function properly. Yes, hands have a very vital function to support your life everyday starting from carrying things, holding objects, holding things, and so on. Uto get a brief explanation of the hand drawings and the functions of each part, see the review below.
Hand drawings and their functions
The structure of the human hand can be divided into several categories which include:
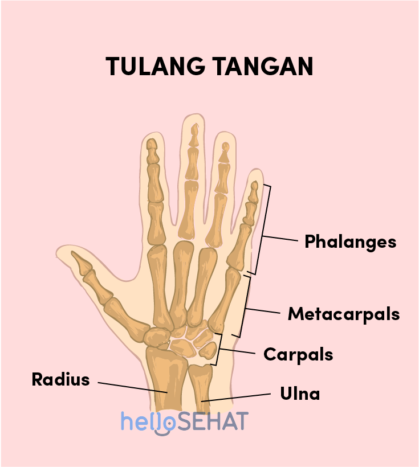
1. Bones and joints
There are 27 bones on your wrist and palm. Seen from the picture of the hand above, there are eight small bones on the wrist itself called carpal (carpals) Carpal is supported by two forearm bones, pengumpil bones (radius), and cubit bone (ulna) forming the wrist joint.
Metacarpal is a long bone in the hand that is connected to the carpal and phalanges (finger bone). Top metacarpal forming knuckles that join the wrist. On the side of the palm, metacarpal covered with connective tissue. There are five metacarpal which forms the palm. You can feel and see it when you clench your fists.
Every metacarpal connected to bone phalanges, namely the finger bones. There are two bones fingerin each thumb and three finger bones in each other finger (index finger, middle finger, ring finger, and little finger). We can see it through the fingers.
Hinge joints formed between the finger bonesand metacarpal makes you more flexible moving your fingers and grasping something. This joint is called a joint metacarpophalangeal (MCP joint).
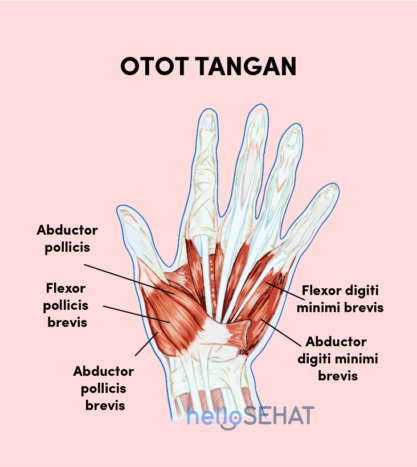
2. Muscle
Muscles that work in the hand can be divided into two groups, namely:
- Extrinsic muscle. This muscle is located in the front and rear compartments of the forearm. This muscle function is useful to help straighten or flex the wrist.
- Intrinsic muscle. Intrinsic muscle is located in the palm. This muscle functions to provide strength when your fingers do fine motor movements. Fine motorism itself is an ability associated with physical skills involving small muscles and eye and hand coordination, for example grasping, pinching, clenching, gripping, and other movements carried out by the hand.
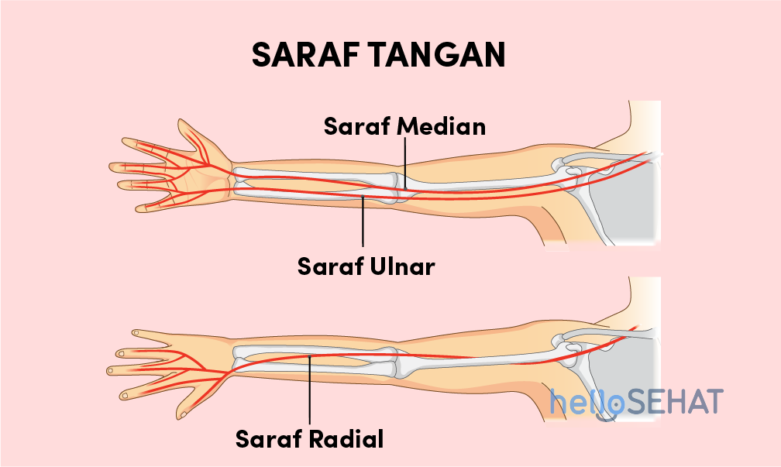
3. Nerves
The nerves that are along the arms and fingers begin to unite in the shoulder, including the radial nerve, median nerve, and ulnar nerve.All of these nerves travel to the side of the hand alongside the blood vessels.
Nervecarrying signals from the brain to the muscles to move the muscles in the arms, hands, fingers and thumb. Nerves also carry signals back to the brain so you can feel sensations such as touch, pain, and temperature.
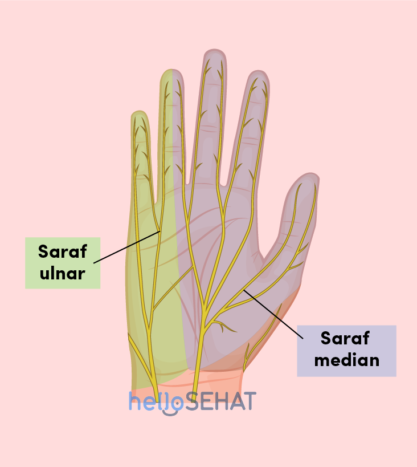
In general, the following are pictures of hands and nerves and their functions:
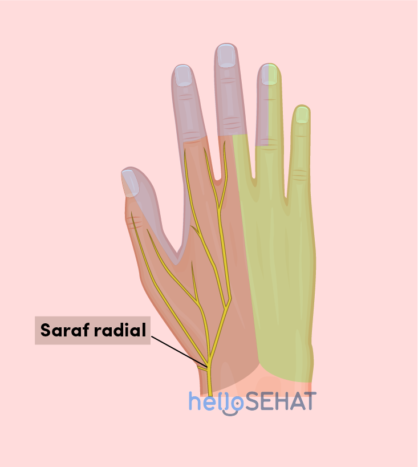
Sthe median nerve crosses through the structure on the tunnel-shaped wrist called carpal tunnel (carpal tunnel). This nerve functions to move the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and half the ring finger. This nerve also sends nerve branches to control the thumb muscles. These famous muscles help move the thumb and touch the thumb pad to the end of each finger on the same hand. This movement is called opposition thumb, aka opposition thumbs up.
While the ulnar nerve is a nerve along the back of the inner elbow, it penetrates the narrow gap between the forearm muscles. This nerve functions to move the finger part little finger and half ring finger. These nerve branches also supply the small muscles in the palm and muscles that pull the thumb into the palm.
The number of nerves along the arms and hands makes the area vulnerable to problems. Too long a pressure on the wrist or on the palm can cause tingling, numbness, or stabbing pain like a needle stick. The most common part of the pain is the thumb, fingers and palm area.
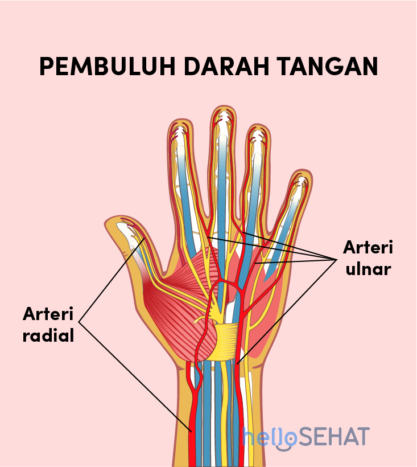
4. Blood vessels
Is available two blood vessels in your arms and hands, namely the radial artery and the ulnar artery. The largest blood vessel along your arms and hands is the radial artery. This artery carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the pengumpil bone (radius) up to the thumb. You can find the radial artery and feel it right on your wrist. While the ulnar vessels are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to cubits (ulna), to the middle finger, ring finger, and little finger.
As seen from the hand image above, kedua these veins are curved together in the palm, to supply blood to the front of the hand, fingers, and thumb. Other arteries travel across the back of the wrist to supply blood to the back of the hand, fingers, and thumb.
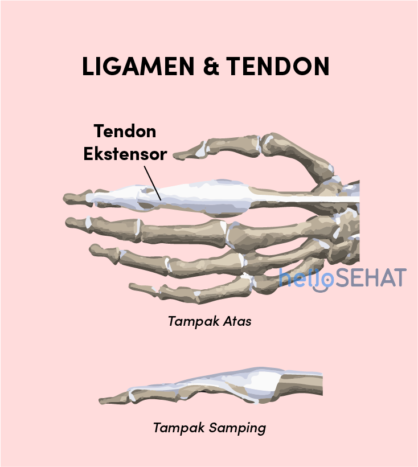
5. Ligaments and tendons
Ligaments are hard tissues that connect between one bone and another and stabilize your joints. Two important structures, called collateral ligaments, are found on both sides of each finger and joint of your thumb. The function of the collateral ligament is to prevent abnormal sideways bending of each finger joint.
While tendons, or better known as veins, are a group of connective tissue that is strong fibrous and attached to the muscles. Tendons have the function of connecting muscle tissue to bone. Tendons that allow each finger and thumb to be straightened are called extensor tendons. While the tendons that allow each finger to bend are called flexors.
The hand structure that appears from the hand image above shows how complex and complex the limbs are. Problems that occur in a small part of the hand may interfere with overall hand function. For this reason, paying attention to all activities carried out by hand carefully is important to be able to maintain its normal function.