Contents:
- Medical Video: Hemorrhagic Stroke (Brain Hemorrhage)
- Why can a stroke cause brain damage?
- 1. Inflammation
- 2. Excess calcium and lack of sodium
- 3. The formation of free radicals
- 4. Unbalanced pH
- Various changes that occur due to post-stroke brain damage
- Cerebrum (right and left brain)
- Cerebellum (upper and front brain)
- Brainstem (brain stem)
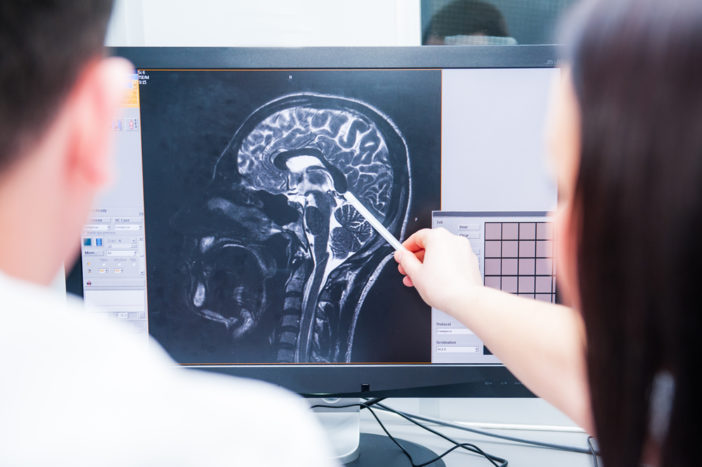
Medical Video: Hemorrhagic Stroke (Brain Hemorrhage)
Stroke causes various serious effects on health, one of which is the brain. Brain damage due to stroke occurs due to a disturbed and not smooth blood supply. The effect of stroke on the brain that can cause damage to cells in the brain that causes interference with the senses, motor skills, behavior, language skills, memory, and the speed of stimulation in response to something. So, what happens to the brain when someone has a stroke?
Why can a stroke cause brain damage?
The brain needs a blood supply to keep working properly. Well, if the blood flow is insufficient, the condition and work of the brain changes. Here are some things that cause brain damage due to stroke.
1. Inflammation
When poisons attack the brain during a stroke, then naturally these body organs will try to repair themselves. However, not infrequently this business can actually cause excessive inflammation.
As a result, brain tissue will be flooded with fluids and white blood cells that are responsible for fighting infection. Well, this condition can cause swelling (edema) which can damage normal brain function.
2. Excess calcium and lack of sodium
When the brain experiences damage from a stroke, calcium in the body can leak and enter brain cells. When the blood supply to the brain is insufficient the sign of oxygen intake decreases.
As a result, calcium levels become unbalanced. Meanwhile, brain cells are designed not to respond to large amounts of calcium. As a result, brain damage cannot be avoided.
In addition, sodium also functions to keep brain function normal. But when a stroke strikes, sodium in the brain becomes unbalanced until it can change the contents of brain cells and make them damaged.
3. The formation of free radicals
Meanwhile, other factors that contribute to brain damage during stroke are free radicals. Free radicals produced during a stroke can quickly damage the tissue nearby. If that happens, even healthy brain cells will be affected and experience malfunction.
4. Unbalanced pH
Brain cells that do not get a blood supply that makes the brain experience a lack of energy to carry out its functions. As a result this will trigger the formation of strong acid molecules that can affect the pH of the brain. Excess acid molecules can be dangerous and can cause brain injury.
Various changes that occur due to post-stroke brain damage
Generally, stroke only affects one side of the brain. That means if a stroke attacks the left side of the brain, then you will experience various problems with the right side of your body and vice versa.
However, not infrequently strokes can also affect both sides of the brain. The effects of stroke on the brain will usually cause a loss of normal function in some parts of the body. The effect produced will vary according to which brain region is attacked, whether in the cerebrum (right and left brain), cerebellum (upper and front brain), and brainstem (brain stem).
Quoted from Hopkinsmedicine.org, the following are various changes that occur due to post-stroke brain damage according to the affected part.
Cerebrum (right and left brain)
The following are the effects of stroke on the right and left brain, including:
- Having problems in moving the body.
- Cognitive disorders such as the process of thinking and memory.
- Having problems with language skills.
- Difficulty eating and swallowing.
- Visual impairment.
- Disorders of sexual ability.
- Problems with bowel and bladder control.
Cerebellum (upper and front brain)
Following are the effects of upper and front strokes in the brain, including:
- Problems of coordination and balance.
- Dizzy
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
Brainstem (brain stem)
The following are the effects of stroke on the brain stem, including:
- Problems with breathing and heart function.
- The inability of the body to control temperature.
- Problems with balance and coordination.
- Difficulty chewing, swallowing, and talking.
- Visual impairment.