Contents:
- Medical Video: Symptoms of Sudden Cardiac Arrest | Cedars-Sinai
- What are the causes of cardiac arrest?
- What happens during cardiac arrest (cardiac arrest)?
- What happens to the body after experiencing cardiac arrest
- Cardiac arrest must be treated immediately to prevent the risk of death
Medical Video: Symptoms of Sudden Cardiac Arrest | Cedars-Sinai
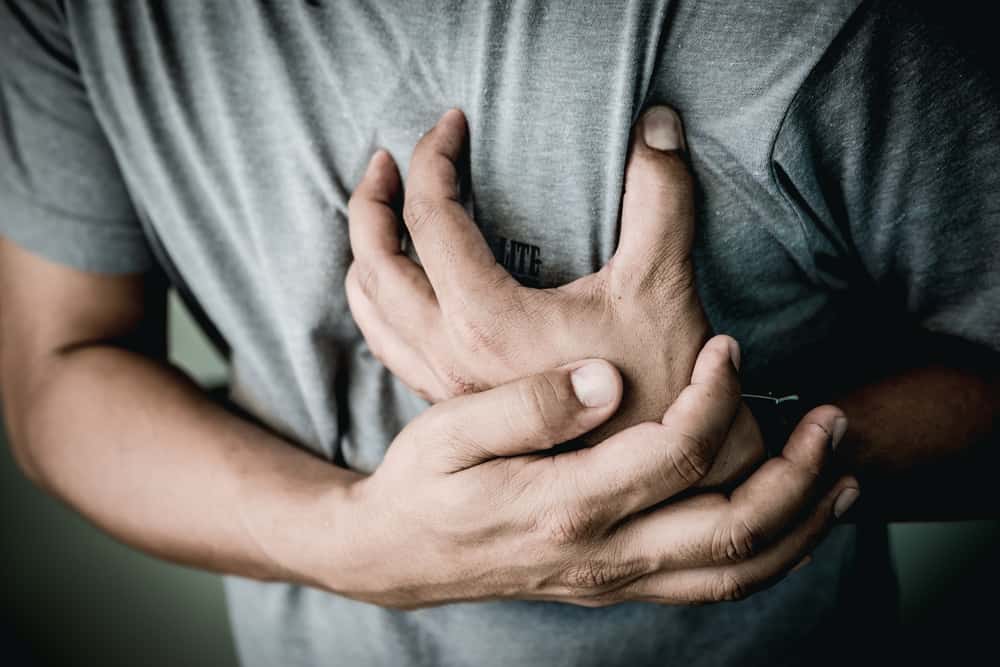
Cardiac arrest (cardiac arrest) is a fatal condition when the heart stops beating suddenly. The heart that stops beating automatically will not pump blood throughout the body. Death can occur in minutes because vital organs, especially the brain, do not receive enough fresh blood. Actually, what happens to the body minutes after a cardiac arrest?
What are the causes of cardiac arrest?
Most cases of cardiac arrest are caused by arrhythmias (abnormal heart rate or rhythm) due to an electrical force disorder in the heart muscle. This causes the blood flow from the heart to the whole body to stop.
Cardiac arrest (cardiac arrest) is more likely to be experienced by someone who has a congenital heart defect or whose heart has suffered serious damage, such as due to coronary heart disease. Trauma from injury can also cause sudden cardiac arrest, for example when electrocuted, drug overdose, overweight exercise, heavy blood loss, airway obstruction, traffic accidents, drowning and hypothermia.
What happens during cardiac arrest (cardiac arrest)?
In terms of the process of occurrence, cardiac arrest occurs very quickly and is characterized by the following signs:
- Breath breaks or doesn't breathe at all
- Pupils enter the skull
- Squeeze suddenly
- Unconscious
- The skin color becomes pale bluish
- Pulse or heart rate cannot be found
Cardiac arrest can cause organ dysfunction. If not treated immediately, cardiac arrest can lead to permanent damage and death.
What happens to the body after experiencing cardiac arrest
Stopping blood flow throughout the body can cause toxic substances left over from cell metabolism to gather in the blood. Within minutes, the cell will be damaged and then die. The first thing that happens after a cardiac arrest is the loss of consciousness due to the brain experiencing shock due to lack of oxygen. Usually, brain damage occurs after four to six minutes of cardiac arrest.
According to Dr. Sam Parnia, director of critical research on care and resuscitation at NYU Langone School of Medicine, New York, will body during cardiac arrest, humans will temporarily lose all reflexes from the brain.
That is why one of the initial symptoms when a person experiences a cardiac arrest that can be seen is a broken breath. This is caused by the cessation of the brain's function to instruct the lungs to take oxygen. A few minutes after cardiac arrest, you will stop breathing.
At the same time, two to 20 seconds after cardiac arrest, the cerebral cortex of the brain used to think will experience death slowly. Even though at this time breathing and heart rate have stopped, you are still conscious. Because the cerebral cortex is thought to be able to survive without oxygen.
Still according to Parnia, death is interpreted when the heart no longer beats. Once this happens, blood no longer flows in the brain. That is, brain function will be totally stopped and will lose all brain stem reflexes, including the pupillary reflex in the eye. This is what causes most cases of cardiac arrest to end in death.
Cardiac arrest must be treated immediately to prevent the risk of death
Even though cardiac arrest causes cessation of blood flow, you actually still have the opportunity to send blood to the brain, even though only 15% of the total brain needs to function normally.
This can be done through cardiac resuscitation aka CPR. This method is quite helpful to slow brain cell death, but it is still not enough to start the brain back to work. The longer you delay CPR, the brain cell death will occur faster.