Contents:
- Medical Video: Stroke - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options
- What are the symptoms of eye stroke?
- Causes of eye stroke
- Who is at risk for eye stroke?
- How to diagnose eye stroke?
- Treatment for eye strokes
- Preventive steps that can be taken
Medical Video: Stroke - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options
Eye stroke or known as retinal artery occlusion, is caused by a blockage in the blood vessels in the retina. Blood vessels function to bring nutrients and oxygen to all parts of the body. When blood vessels narrow or are blocked by a blockage, the blood supply will decrease or not at all. This will cause serious damage to the affected area, known as a stroke.
This condition blocks the blood supply to the retina, which is the inner layer of the eye that conveys light signals to the brain so that we can see objects around us. If the vessels in the retina are blocked, fluid from the vessels will leak to the retina so that swelling will occur. This will cause interference with vision.
What are the symptoms of eye stroke?
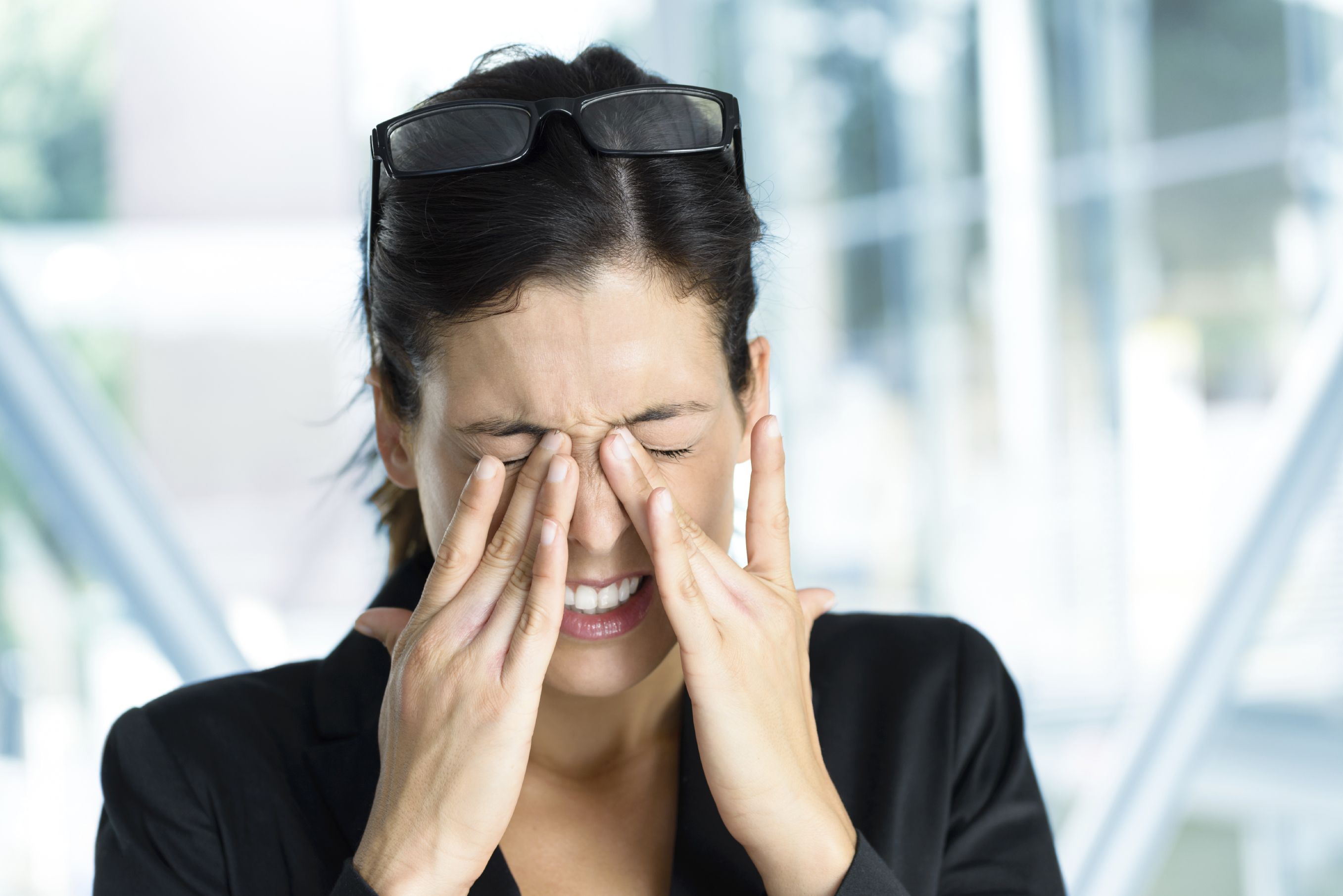
Symptoms that occur can occur slowly for hours or days, or can occur suddenly. You need to pay attention, a stroke usually occurs in one eye only. Here are some symptoms that might arise.
- Views like dizzy, or white spots appear on vision
- Pain or pressure in the eye
- Blurred vision that continues to worsen in part or all of your vision
- All vision loss can occur slowly or suddenly
If you experience the above symptoms, immediately consult your doctor. Without fast and proper treatment, strokes in the eye can cause you to lose vision (blindness) permanently.
Causes of eye stroke
Eye stroke occurs due to blockage of blood flow that damages the retina. This blockage usually occurs due to narrowing of the arteries or the presence of blood clots. Unfortunately, until now it is not known exactly why the eye organs can be affected by this condition.
Who is at risk for eye stroke?
Anyone can experience a stroke in the eye, but there are factors that make you more at risk to experience it. You who are more than 60 years old, have smoking habits, and are male sex are more at risk of this stroke.
Some health conditions that increase risk, namely:
- Diabetes
- Glaucoma
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- High cholesterol level
- Heart disease
- Narrowing of the carotid artery or neck artery
How to diagnose eye stroke?
If you experience sudden vision loss, you should immediately contact your eye doctor. The doctor will do a thorough examination to find out if you have an eye stroke. Your ophthalmologist will dilate your pupils with eye drops that allow for a more thorough examination of the retina and see if there are any signs of damage.
Treatment for eye strokes
Some medications that your eye doctor can give you within a few hours after symptoms occur, such as:
- Breathing deeply (inhaling) a mixture of carbon dioxide and oxygen, this can make the retinal artery widen
- Discard some of the liquid from the eye so that the blockage is away from the retina
- Clot-crushing drugs or clots in the blood
- Eye injection drugs such as corticosteroids or anti-vascular endothelial growth factor
- Laser therapy
- High pressure or hyperbaric oxygen
Other conditions that cause blood clots must also be treated. The faster the treatment is given, the greater your chance to save your vision. Some patients can look back after this stroke, even though vision is often not as good as it used to be.
Preventive steps that can be taken
- Control blood sugar levels if you are at risk or have diabetes.
- Treat glaucoma with drugs that keep your eye pressure under control.
- Make sure your blood pressure is always within normal limits.
- Check cholesterol levels regularly. If it's too high, diet and exercise can help reduce before taking drugs.
- Quit smoking.