Contents:
- Medical Video: Superfoods for Growing Children
- What are the consequences if a child is deficient in vitamin B12?
- Signs of a baby lacking vitamin B12
- How much vitamin B12 does my child need?
- List of food sources of vitamin B12
Medical Video: Superfoods for Growing Children
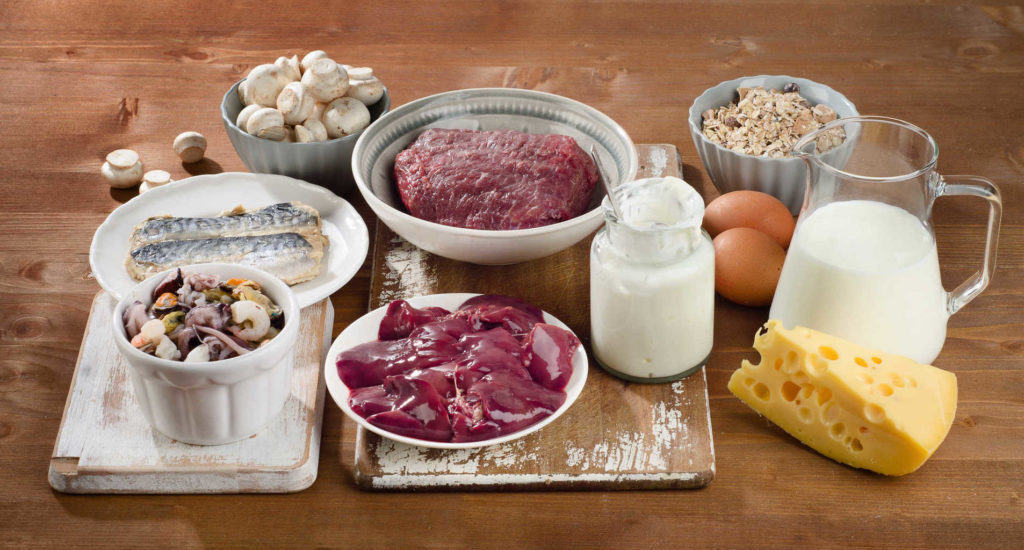
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) is synthesized by microorganisms and is found in animal products (meat, offal, fish, seafood, dairy products, and eggs). Some cereals and soy milk are also enriched by vitamin B12
B12 plays an important role in the production of red blood cells (haemotopoiesis) and the main nervous system. B12 is an enzyme.
What are the consequences if a child is deficient in vitamin B12?
Signs and symptoms of B12 deficiency in children are generally similar to the signs and symptoms of autism. Children with autism and brain damage due to B12 deficiency exhibit behavioral obsessive-compulsive disorders (OCD) and problems with speech, language, writing, and comprehension. B12 deficiency can also cause children to be alone and separate themselves from the surrounding environment. Unfortunately, very few children who show signs of autism receive adequate checks for B12 deficiency.
Signs of a baby lacking vitamin B12
Signs and symptoms in infants and children usually are:
- Delay or decline in development
- Apathetic and irritable behavior
- Hypotonia (decrease in muscle weight)
- Weak
- Tremor or tremble
- Movements that cannot be controlled
- Seizures
- Ataxia (a neurological disorder that affects balance, coordination, and speaking ability)
- Anorexia and other eating problems
- Failure to develop
- Abnormal body weight
- Abnormal head growth
- Difficult to socialize
- Bad motoric
- Language delay
- Speech impairment
- Low IQ or even mental retardation
- Anemia
- Macrocytosis (size of large red blood cells)
How much vitamin B12 does my child need?
Infants aged up to 6 months need 0.4 micrograms of B12 daily, and infants aged 7 - 12 months need 0.5 mcg of B12 per day. The recommended number of nutritional needs (RDA) for children aged 1-3 years is 0.9 mcg per day, and children aged 4 - 8 years need up to 1.2 mcg per day. Children aged 9-13 years will need B12 intake to reach 1.8 mcg, and for children aged 14 years and up to adults need 2.4 mcg B12 per day.
List of food sources of vitamin B12
Animal products are a rich source of food for B12, while the intake of vitamin B12 obtained from vegetables and fruits contains different levels, making it difficult for the body to digest. Good sources of vitamin B12 are dairy products, red meat, white meat (poultry), seafood, and eggs. However, do not worry if your child does not eat meat, some cereal products contain nutritious yeast enriched with vitamin B12 and other minerals. The same goes for processed soybeans.
Vitamin B12 levels contained in foods will vary depending on the size of fruit or vegetables.
Your child may eat less or exceed the average amount of food mentioned above, judging by his age and appetite. Estimate the nutritional content according to your child's needs.
| Source | Presentation Suggestions | Vitamin B12 MCG |
| Vegetables and fruits | This food group contains very little B12 | |
| Wheat products | This food group contains very little B12 | |
| Milk and processed milk | ||
| Milk | ||
| 3.3% gay, 2%, 1% | 250 mL (1 cup) | 1.2 – 1.4 |
| Skim | 250 mL (1 cup) | 1.3 |
| Buttermilk | 250 mL (1 cup) | 1.0 |
| Chocolate, milk | 250 mL (1 cup) | 1.0 |
| Cheese | ||
| Swiss / Emmental | 50 g (1½ oz) | 1.7 |
| Cheese Cottage | 250 mL (1 cup) | 1.5 |
| Feta, gouda, edam, gruyere, brie, cheddar, fontina, mozzarella, provolone | 50 g (1½ oz) | 0.7-0.9 |
| Sheet cheese, cheddar | 50 g (1½ oz) | 0.4 |
| Yogurt | ||
| Plain (regular, low fat) | 175 g (¾ cup) | 1.0 |
| Fruit bottom (regular, low fat) | 175 g (¾ cup) | 0.8-0.9 |
| Drinks made from yogurt | 200 mL | 0.6 |
| Alternative milk | ||
| Soybeans, fortification | 250 mL (1 cup) | 1.0 |
| Meat and alternatives | ||
| Offal | ||
| Liver (goat, lamb, deer, cow), cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 52.9-64.3 |
| Kidney goat, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 59.2 |
| Kidney, deer, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 27.7 |
| Giblets, turkey, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 24.9 |
| Kidney, beef, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 18.7 |
| Liver (chicken, pork), cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 12.6-15.9 |
| Pate (goose liver, chicken liver) | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 6.1-7.1 |
| Livestock Products (White Meat) | ||
| Turkey, chicken, cooked duck | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 0.2-0.3 |
| Red meat | ||
| Milled meat, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 2.4-2.7 |
| Cut (typical inside, typical outside, etc.), cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 1.3-2.5 |
| Pork | ||
| Cut (typical inside, typical outside, etc.), cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 0.8-1.1 |
| Milled meat, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 0.8-0.9 |
| Ham, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 0.7 |
| Bacon, strips, cooked | 3 slices (24 g) | 0.3-0.4 |
| Others | ||
| Caribou / stag, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 5.0 |
| Salami (beef, pork) | 75 g (2½ oz) or 3 slices | 1.1-2.1 |
| Sausage (pepperoni, chorizo, Polish, Italian, frankfurter) | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 0.9-1.5 |
| Meat process (pastrami, mortadella, bologna) | 75 g (2½ oz) or 3 slices | 1.1-1.3 |
| Wiener / hot dog | 1 wiener (45 g) | 1.2 |
| Fish and seafood | ||
| Mussels, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 74.2 |
| Oysters, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 18.2-26.3 |
| Green mussels, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 18.0 |
| Mackerel (King, Atlantic), cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 13.5-14.3 |
| Herring, cooked or smoked | 250 mL (1 cup) | 7.2-914.0 |
| Tuna, bluefin, raw or cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 8.2-9.3 |
| Roe fish, raw | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 9.0 |
| Crab, Alaska King, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 8.6 |
| Sardines, raw canned or cooked in tomato sauce | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 6.8 |
| Caviar (red, black) | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 6.0 |
| Trout, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 3.7-5.6 |
| Salmon, red / sockeye, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 4.4 |
| Salmon, pink / humpback, with bones, canned | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 3.7 |
| Salmon, Atlantic, wild, cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 2.3 |
| Tuna, small size, raw canned in water | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 2.2 |
| Alternative meat | ||
| White meat (chicken, fish sticks, wiener / frankfurter, meatballs), cooked | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 1.0-3.8 |
| Meatless luncheon slices | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 3.0 |
| Soya burger patty | 75 g (2 ½ oz) | 1.8 |
| Eggs, cooked | 2 large sizes | 1.5-1.6 |
| Etc | ||
| Almonds, oats or drinks made from rice, fortification | 250 mL (1 cup) | 1.0 |
| Red Star T6635 + Yeast (vegetarian special formula) | 2 grams (1 teaspoon of powder, or 2 tsp of coarse milled) | 1.0 |