Contents:
- Medical Video: Basic First Aid Tips : How to Treat Burn Blisters
- Causes of burns
- Three groups of burns
- 1. Superficial burns (first degree)
- 2. Second degree burns (slightly deeper than first degree)
- 3. Third degree burns
- Surface area of burns
- Minor burns
- Moderate burns
- Severe burns
- How to deal with burns?
Medical Video: Basic First Aid Tips : How to Treat Burn Blisters
Burns can occur anywhere, especially for those of you who deal with fire and other heat sources every day, such as cooks, welders, factory workers who use electric fires, electricians, and so on. In addition, there are also many cases that occur due to accident, such as being exposed to hot water and oil splashes when cooking, and due to accidents such as fires due to explosions of gas cylinders, electricity, and others. PMI (Indonesian Red Cross) describes burns as a whole of injuries that occur due to exposure to high temperatures.
Before we know the various ways to deal with burns, it's good to know some of the following.
Causes of burns
We must recognize several sources of the causes of burns that are around us. The following are 4 causes of burns:
- Heat (temperature above 60 ° C), for example: fire, hot steam, hot objects
- Electricity, for example: household electricity, lightning
- Chemistry, for example: soda soda, water battery (zuur)
- Radiation, for example: sunlight (ultraviolet), radioactive material
Three groups of burns
Based on its depth, burns are divided into 3 levels, namely:
1. Superficial burns (first degree)
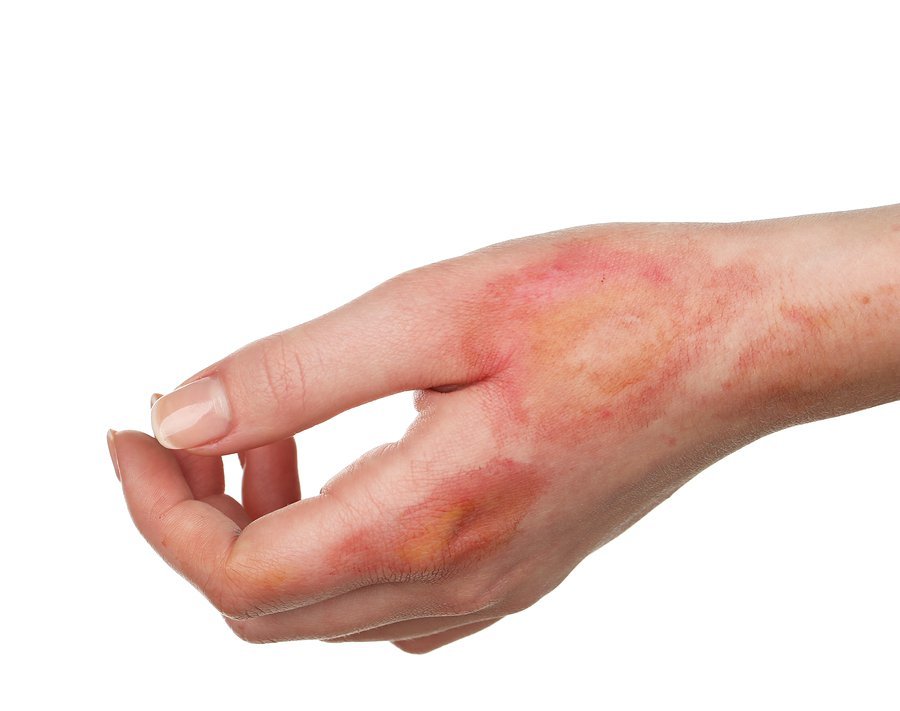
This burn only covers the uppermost layer of the skin (epidermal layer). Usually this burn is characterized by redness, pain, and sometimes swelling.
2. Second degree burns (slightly deeper than first degree)
This burn covers the outermost layer of damaged skin and disrupts the lower layer. This level of burns is the most painful type, with the appearance of bubbles on the skin filled with fluid, swelling, reddish skin or can also become white, moist skin, and damaged.
3. Third degree burns
In this level of burns, the layer affected by burns is unlimited, it can even reach the bones and internal organs. This burn is the most severe level. It is usually characterized by dry, pale or even white skin, but can also be charred and black. Unlike degrees one and two, this third degree burn does not cause pain.
Surface area of burns
In handling burns and determining the degree of burns, the body surface area that has burns is very important. Guidelines for estimating the area of a burning area can be done by law nine (rule of nine), namely by dividing the body area by a percentage of nine per body area.
Here is an explanation of the nine laws:
- Head (9%): front = 4.5%; back = 4.5%
- Body (36%): chest, stomach = 18%; back = 18%
- Arm (18%): front-rear upper arm (9%); front-rear forearm (9%)
- Legs (36%): front-rear upper limbs (18%); front and rear lower limbs (18%)
- Genitals (1%)
Another way to calculate the area of a burn is to compare the wound and the palm of the victim. The victim's palm is considered to have an area of 1% of the body surface area. It should be remembered that the calculation of the extent of burns is calculated based on each degree of burn. The degree of burns is determined by two main factors, namely the surface area of the body that has burns and its location.
Minor burns
- Third degree burns are less than 2% wide, except for the face, hands, feet, genitals, and airways
- Second degree burns are less than 15% wide
- First-degree burns are less than 50% wide
Moderate burns
- Third degree burns between 2% -10% wide, except for the face, hands, feet, genitals, and airways
- Second degree burns between 15% -30% wide
- First degree burns more than 50%
Severe burns
- All burns accompanied by airway injuries, soft tissue injuries, and bone injuries
- Second or third degree burns on the face, hands, feet, genitals or airway
- Second degree burns above 10%
- Second degree burns more than 30%
- Burns accompanied by motion injuries
- Burns surround the movement
How to deal with burns?
- Stream regular water to the injured area. If there is a chemical flowing water continuously for 20 minutes or more.
- Remove clothes and jewelry. If the clothes are attached to a burn, the surrounding clothing scissors do not stick, and do not force to remove them.
- Cover the burn, use a sterile wound cover, and do not break the bubble.
- Don't use butter, toothpaste, soy sauce, coffee, ice water.
- Refer immediately to a health facility.
READ ALSO:
- First Aid for Cyanide Poisoned People
- First Aid When Bitten by a Venomous Snake
- First Aid in Stroke