Contents:
- Medical Video: Learn To Use Garlic To Eliminate Vaginal Infections, Fungus And Odors!!
- What are the signs and symptoms of trichomoniasis in women?
- How is trichomoniasis diagnosed by a doctor?
- What is the cure for trichomoniasis?
- Can trichomoniasis be prevented?
Medical Video: Learn To Use Garlic To Eliminate Vaginal Infections, Fungus And Odors!!
Trichomoniasis is a venereal disease caused by a parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. Women are most often affected by this disease, although men can also be infected and transmit trichomononiasis to their partners through unsafe sexual contact. In women, these parasites attack the vagina, urethra (bladder tract), and bladder.
Although how many Indonesian women are infected with this disease can not be known for sure, trichomoniasis is one type sexually transmitted diseases which most often occurs in young women who are sexually active. It is important for you to know what are the signs and symptoms of trichomoniasis, along with the treatment steps.
What are the signs and symptoms of trichomoniasis in women?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says that trichomoniasis infection generally causes no symptoms. Therefore, most women who have these parasites do not know they have been infected. Even if it appears, symptoms of trichomoniasis can appear from five to 28 days or even several months after the first exposure to the parasite.
Symptoms in women can include:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge - foamy, greenish yellow, and foul-smelling or fishy; it may also contain blood
- Pain during urination and / or frequent urination
- Pain during sex
- Vaginal irritation - may be painful, sore, itchy, swollen
- Pain in the lower abdomen (rarely)
However, a number of these signs are also common in many other health conditions. The CDC added that symptoms might also come and go.
How is trichomoniasis diagnosed by a doctor?
Symptoms of trichomoniasis in women are often misdiagnosed as urethritis (bladder infection), so it is generally not treated appropriately and results in further complications - for example, increasing the risk of being infected with or spreading HIV in their sex partners.
Therefore, it is not possible to diagnose trichomoniasis based only on symptoms. Doctors must do a physical examination and lab tests in order to diagnose trichomoniasis
The doctor will take a sample of your vaginal fluid with a cotton swab or cotton bud, and examine it in the laboratory. Diagnosis of trichomoniasis can be ascertained if your vaginal discharge shows a pH level higher than 4.5 (normal vaginal pH level), and also the presence of T. vaginalis parasites. Trichomoniasis can also be diagnosed by trichomoniasis DNA or RNA tests, or culture cells. These parasites are more difficult to detect in men than women.
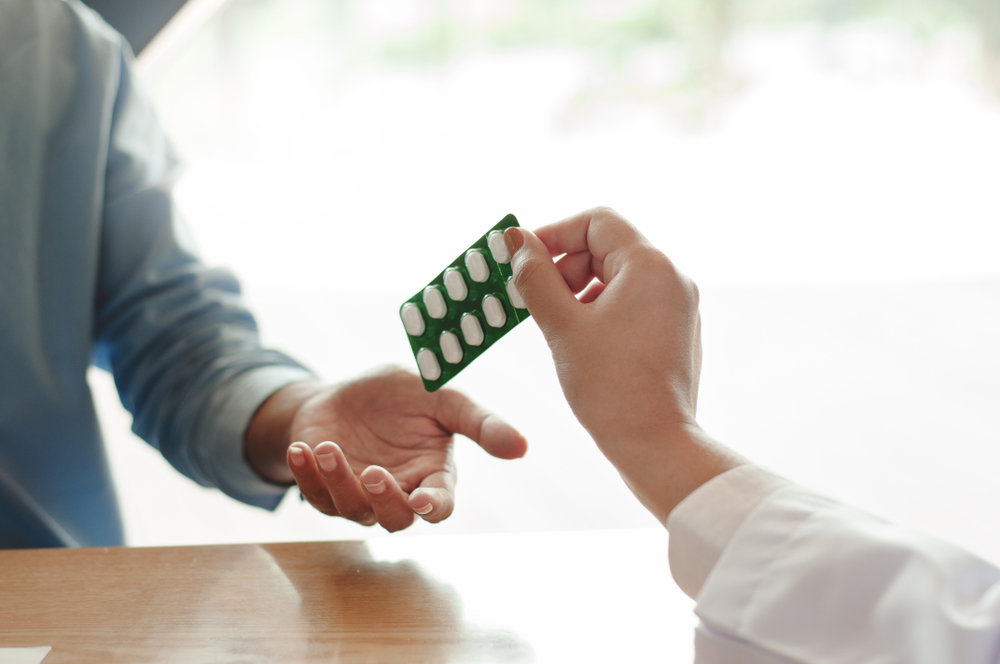
The good news, trichomoniasis can be treated with antibiotics. Ignoring symptoms only worsens the problem, and also complicates the exact diagnosis. The CDC says, untreated infections can last for several months or years. And if you become pregnant during these times, trichonomiasis can increase your risk for premature delivery and LBW babies.
What is the cure for trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis can be cured by prescribing antibiotics in the form of single dose pills (metronidazole or tinidazole) which can be consumed by mouth. Pregnant women may also take this medicine.
People who have undergone trichomoniasis treatment can be re-infected again, if involved in risky sex. About 1 in 5 people can be re-infected within 3 months after treatment. To avoid re-infection, make sure that your sex partner also has the same treatment, and waits for sex until all symptoms disappear (about a week).
Before taking the medication, be sure to tell your doctor about what medicines you and your partner are currently using. Some people who are drink alcohol within 24 hours after taking this medication can experience some uncomfortable side effects. You and your partner need to spend all doses of the drug so that its efficacy is effective. Make a doctor's appointment again if your symptoms come back.
Can trichomoniasis be prevented?
The only way to prevent fully trichomoniasis is to not have sex at all. If you are going to have sex, pay attention to the following:
- Use condoms correctly every time you have sex - latex condoms are the most effective condoms to reduce the risk of trichonomiasis infections and other STDs
- Limit the number of sex partners, and do not go back and forth between partners. Or, limit sexual contact with only one person who is guaranteed not to be infected
However, condoms do not cover everything, and it is still possible to get or spread this infection even when using a condom. If you think you have trichomoniasis, avoid sexual contact and visit a doctor.