Contents:
- Medical Video: Causes & Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes - Manipal Hospital
- What is type 2 diabetes?
- Why do I have type 2 diabetes?
- Various complications of diabetes to watch out for
Medical Video: Causes & Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes - Manipal Hospital
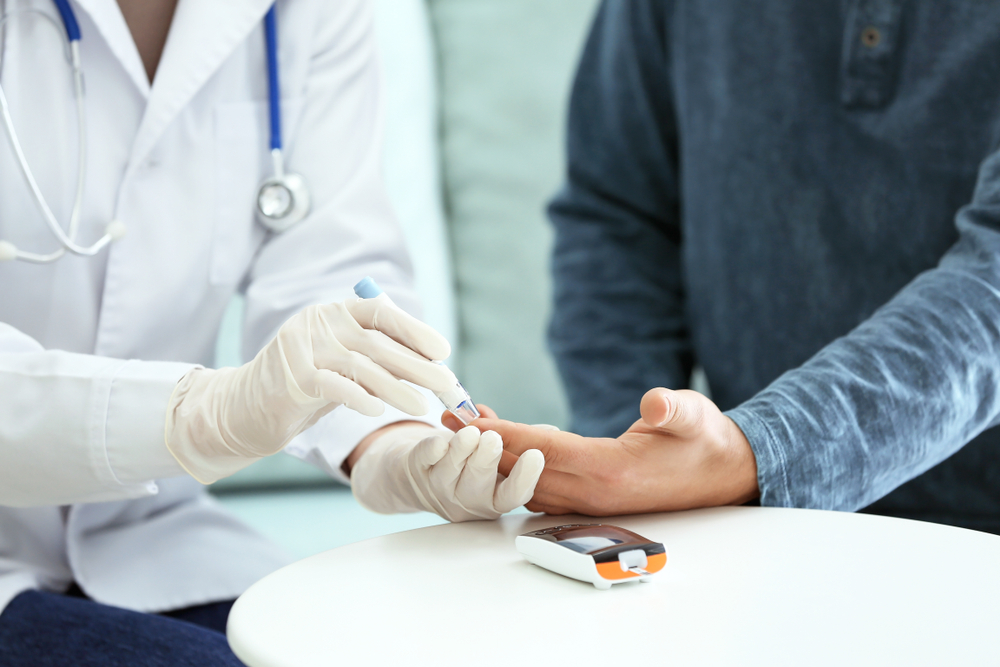
Diabetes, aka diabetes, is a chronic disease. This disease is characterized by high blood sugar (glucose). Type 2 diabetes is a common form of diabetes mellitus. Without proper diagnosis and treatment, this disease can cause serious health problems.
What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes, also known as adult-onset diabetes or diabetes that is not insulin dependent is a condition when your body has enough insulin but is unable to use it properly. This disease is different from type 1 diabetes, where the pancreas cannot produce insulin.
In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas actually works normally but somehow cells in the body cannot use glucose in the blood as an energy source. As time goes by, the glucose in your blood increases so much that it will endanger the body.
About 90 to 95 percent of diabetic patients are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. The disease often attacks in adulthood, aged 40 years or more. But the risk of developing type 2 diabetes can increase with obesity in childhood.
Why do I have type 2 diabetes?
Before knowing why type 2 diabetes occurs, you must know how glucose metabolism in your body works.
Saliva and chemicals in the stomach convert the food you eat into glucose (a form of sugar), which is the main source of energy for body cells. Your liver also stores a certain amount of sugar, but in the form of glycogen. If you don't pay attention to your food intake correctly or glucose in your blood is low, the glycogen will be destroyed and turn into glucose.
Blood flow absorbs sugar and takes it to cells in need, but cells cannot use this energy without the help of insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas.
The pancreas receives a signal that glucose is in your blood and produces more insulin. By allowing glucose to enter the body's cells, insulin will reduce the amount of blood sugar and automatically the production of insulin in the pancreas decreases.
If the cell cannot recognize insulin, this hormone cannot help cells use glucose as energy. As a result, glucose will continue to dwell in your blood and eventually accumulate. Your pancreas will produce more insulin because there is high glucose in the blood, while the body's cells cannot use it to absorb glucose. This disorder causes symptoms of type 2 diabetes.
Researchers are still looking for a full picture of the causes of type 2 diabetes. However, having excessive weight is a major risk of this disease.
Various complications of diabetes to watch out for
The most likely complication of uncontrolled diabetes, be it type 1 or type 2, is necrosis. Complications of diabetes can make you paralyzed. Without proper treatment and treatment, your body's cells will not be able to use glucose in the bloodstream and will die slowly. Necrosis usually occurs in the lower body, such as the legs.
Apart from necrosis, you may be able to have a serious illness, diabetic ketoacidosis. In diabetic ketoacidosis, ketones accumulate in the blood. Ketones contained in the blood will change blood acid. This condition is dangerous because it can affect organs including the brain and can endanger the sufferer if it is not immediately diagnosed and hospitalized.
Other serious complications of diabetes are:
Cardiopathy
Diabetes can increase the risk of various other cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart disease, stroke, arterial narrowing (atherosclerosis), and high blood pressure.
Neuropathy
Excessive sugar can harm small blood vessels (capillaries) that nourish your nerves, especially in the legs. This can cause tingling, numbness, burning or pain from the tip of the foot and radiating upwards.
Poorly controlled blood sugar can cause you to numb at the feet of one or both legs. Damage to nerves that affect the digestive tract can cause several problems such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation. For men, the problem can be erectile dysfunction.
Nephropathy
The kidneys contain many clusters of blood vessels that filter out waste from your blood. Diabetes can harm this delicate filtering system. Some damage can result in kidney failure or recoverable end-stage kidney disease, but this requires dialysis or kidney transplantation.
Eye damage
Diabetes can harm blood tissue in the retina (diabetes retinopathy), and is likely to cause blindness. Diabetes can also increase severe damage to vision, such as cataracts and glaucoma.
Foot damage
Nerve damage or blood flow in the legs can increase the risk of foot complications. If not treated, scratches and sores on the legs can become serious infections, which are difficult to treat and can result in leg amputation.
Mouth and Skin Conditions
Diabetics can cause you to be susceptible to skin problems, including bacterial and fungal infections.
Pregnancy Complications
High sugar levels can be dangerous for children and babies. You have a high risk of miscarriage, birth, and birth defects if your sugar level is not controlled properly.
For the mother, diabetes can increase the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetes retinopathy, high blood pregnancy, and preeclampsia.