Contents:
- Medical Video: Nourishing Babies
- Benefits of breastfeeding for mother and baby
- Benefits of breastfeeding on the risk of heart disease and stroke
- How can breastfeeding reduce the risk of disease?
- How long is breastfeeding ideal for heart health?
Medical Video: Nourishing Babies
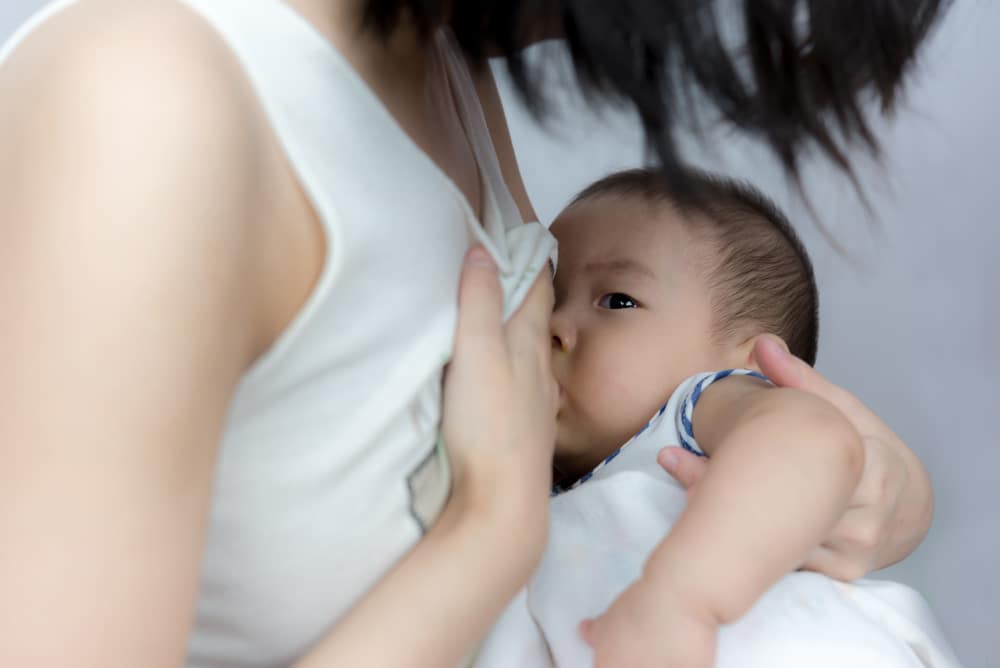
Giving breast milk (ASI) is known to have a myriad of benefits for both babies and mothers. Recent research shows that breastfeeding can also reduce a woman's risk of heart disease and stroke. To find out more about the benefits of breastfeeding to avoid heart disease and stroke, read the full information below.
Benefits of breastfeeding for mother and baby
Breast milk can give the baby the body's resistance to viruses and bacteria so that the immune system becomes better and stronger. Babies who get breast milk are also more protected from some diseases than babies who don't get breast milk. For example the risk of asthma, allergies, ear infections, and respiratory infections. A number of studies also show that breast milk can increase intelligence and good weight gain during growth.
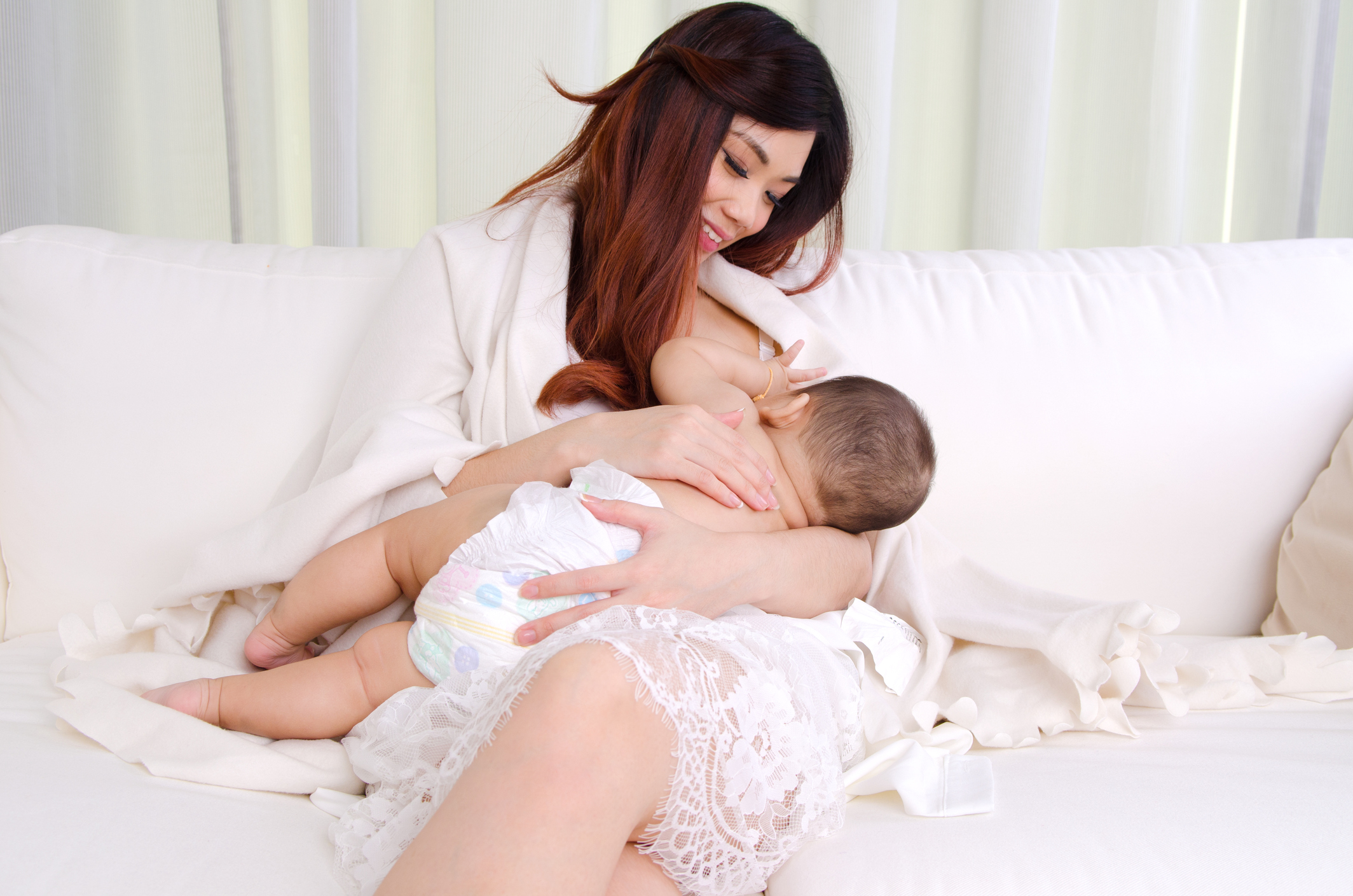
The benefits of breastfeeding for the mother can help reduce maternal weight after giving birth, reduce the risk of osteoporosis, obesity, and several types of cancer, such as breast and ovarian cancer.
Benefits of breastfeeding on the risk of heart disease and stroke
Currently, a recent study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association states that breastfeeding can reduce a woman's risk of heart disease and stroke, even in the long term after giving birth.
The study involved about 290,000 women in China aged between 30-79 years who did not have heart disease or stroke at the start of the study. The researcher collected data in the form of labor history, breastfeeding, medication, and lifestyle. The study participants were then observed for eight years. During that period, as many as 16,700 women were affected by heart disease and nearly 24,000 women had strokes.
After adjusting the results of these studies with other risk factors, namely smoking, hypertension (high blood pressure) and physical activity, the expert team found that breastfeeding mothers had a 9 percent lower risk of heart disease and a 8 percent lower risk of stroke compared to mothers who never breastfeed.
The benefits of breastfeeding for heart and brain health are cumulative. That is, the longer a mother breastfeeding her baby, the risk for heart disease or stroke will be smaller. Every additional six months of breastfeeding, the risk of heart disease will decrease by 4 percent and the risk of stroke is reduced by 3 percent.
How can breastfeeding reduce the risk of disease?
Sanne Peters, a researcher at Oxford University, said that breastfeeding can affect the risk of heart disease by changing the body's metabolism in the mother after giving birth. During pregnancy, the mother's body will collect fat in order to ensure that the developing baby gets enough nutrients and also for preparing breastfeeding when the baby is born.
Previous research has shown that fat accumulation is lost faster during breastfeeding. If mothers do not breastfeed when their babies are born, they will have fat reserves that they do not need. This can cause weight gain and increase risk factors for heart disease, such as atherosclerosis.
How long is breastfeeding ideal for heart health?
Until now it is still unclear whether there is an ideal period of breastfeeding to get the biggest benefits of breastfeeding for heart health.
The World Health Organization or WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding (ASI as the only food source) for at least six months. After the age of 6 months, the child is given additional complementary foods (MP ASI) and breastfeeding can be continued until the child is two years old.