Contents:
- Medical Video: How Risky Are Vaccines?
- How do vaccines work to prevent disease?
- Why are there parents who reject vaccines for children?
- Already vaccinated, but how come you still get sick?
- Is it true that vaccines contain pigs?
- What is the proof that the vaccine is safe to use?
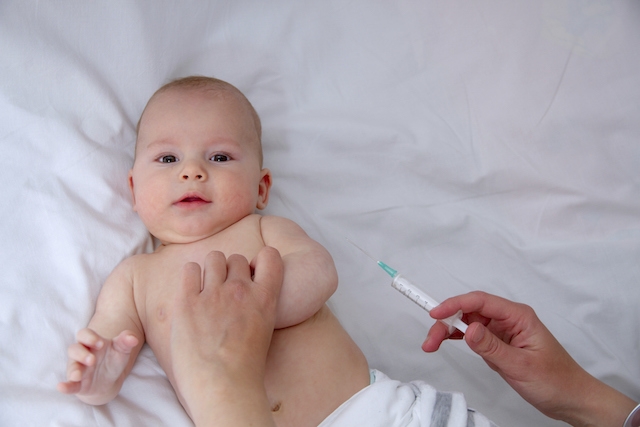
Medical Video: How Risky Are Vaccines?
Vaccines have long been found, but until now there are still many who are hesitant to give vaccines to their children. They still doubt the safety of vaccines, because there are many misunderstandings circulating in the community. Some think that even though they have been given a vaccine, they can still be sick. Or, there are also those who think that vaccines endanger the little one. But what?
A vaccine is an antigenic material that is used to produce active immunity to a disease. Provision of vaccines is intended to prevent or reduce the influence of infectious diseases.
How do vaccines work to prevent disease?
Vaccines work by training the immune system to recognize and fight pathogens, whether viruses or bacteria. To do this, certain molecules from pathogens must be inserted into the body to trigger an immune response, called an antigen.
By injecting antigens into the body through vaccination, the immune system can recognize pathogens that cause disease by producing antibodies. These antibodies will fight pathogens before they spread and cause disease. These antibodies also will later recognize the pathogen of the disease, if later it reappears.
Why are there parents who reject vaccines for children?
Studies published in BioMed Central in 2013 found several reasons why some parents refused to provide vaccines for their children. The results of the study showed that the decision was based on several factors, such as the parents' lifestyle, perceptions of the body and the child's immune system, perceptions of disease risk and vaccination side effects, perceived vaccine effectiveness, benefits of vaccination, negative experiences after vaccination, and parents' social environment.
Already vaccinated, but how come you still get sick?
Vaccination does not protect 100% of your child from disease. However, children who have been given a vaccine have more optimal immunity to an illness.
Actually, there are several factors that cause the administration of vaccines to be less effective in preventing illness, namely the completeness of immunization status, lifestyle, nutritional intake, and vaccine conditions given. Children who have been given a vaccine can still be infected with an illness, but the symptoms that are experienced tend to be much lighter compared to children who are not given a vaccine.
Is it true that vaccines contain pigs?
The vaccine does not contain pork. This information is obtained through the idai.or.id site. Through the site it is also known that even in the manufacture of the polio vaccine, the pig trypsin enzyme is used; but not all vaccines need it. The enzyme will also be cleaned or removed so as not to disturb the next stage of the vaccine production process.
Pig trypsin enzyme is only needed as a catalyst to break down proteins into peptides and amino acids which are germ food ingredients. But in the final results of the vaccine manufacturing process, there are absolutely no ingredients containing the enzyme. In fact, this vaccine antigen has no contact with the pig trypsin enzyme either directly or indirectly.
What is the proof that the vaccine is safe to use?
A study states that for each approved vaccine, the benefits of its use outweigh the risks. Usually, side effects that occur in the form of fever a few days after the vaccine, and can be lost after treatment.
Here are some evidence that vaccines are safe to use and have been effective in preventing diseases according to them Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in livescience.com:
- Over the past two decades, childhood vaccines have saved the lives of 732,000 U.S. children. and prevent more than 300 million children from getting sick.
- 90 percent of the side effects of using vaccines are harmless and very rare.
- More than 20 scientific studies have shown that there is no relationship between MMR vaccine and autism.
- The 2011 report from the National Academy of Medicine reviewed more than 1,000 vaccine studies and concluded that serious reactions to vaccines are very rare.
- A 2011 study found that the rotavirus vaccine prevented 65,000 children in the United States from being hospitalized with rotavirus since 2006.
- The HPV vaccine was introduced in 2006, and for the next four years, HPV infection rates among young women decreased by 56 percent, although the vaccination rate was relatively low in the teen age group.
- After the introduction of the chickenpox vaccine, cases of chickenpox dropped nearly 80 percent in the United States after more than a decade.
- The vaccine has successfully eliminated the polio and outbreaks smallpox.