Contents:
- Medical Video: How to Use Acupressure for Labor Induction
- What is labor induction?
- How is labor induction done?
- 1. Using prostaglandin
- 2. Using a Foley catheter
- 3. Wipe the lining of your cervix
- 4. Cleavage of the amniotic sac (amniotomy)
- 5. Using oxytocin
- When do you have to undergo labor induction?
- Are there risks from labor induction?
Medical Video: How to Use Acupressure for Labor Induction
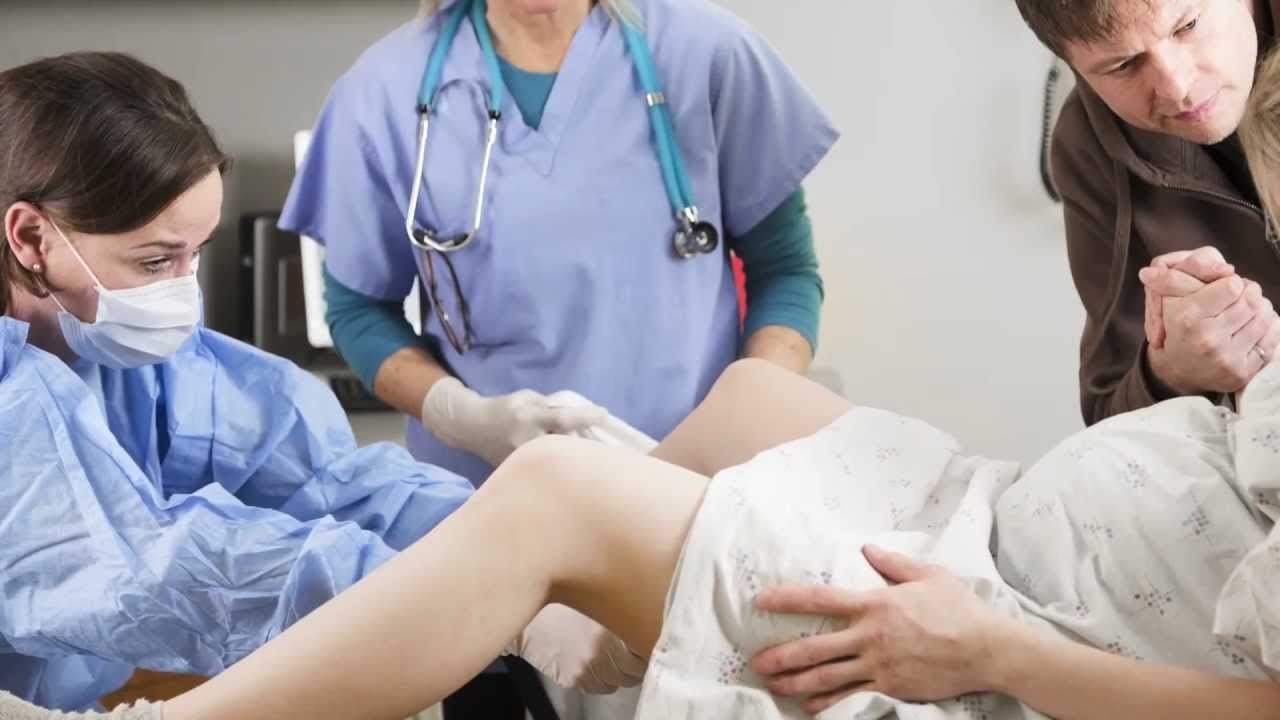
Childbirth is something that is awaited when the gestational age is nearing the date of birth of the baby. Waiting for childbirth might make you a little stressed and worried because you think too much about what will happen before, during, and after labor. Before labor, pregnant women may feel an unbearable heartburn. However, sometimes some mothers do not show signs of giving birth even though the time has come. At this time, the doctor may induce labor in pregnant women.
What is labor induction?
Labor induction is a procedure used to stimulate uterine contractions before labor begins on its own. If the signs of labor do not start on their own, labor induction may be done to stimulate the baby to be born quickly. The condition of pregnancy can be the reason why induction of labor is carried out, especially regarding the health condition of the mother or baby.
READ ALSO: Can Sex Trigger Childbirth Contractions?
How is labor induction done?
Labor induction can be done in various ways, such as administration of drugs or other methods. In what way the induction of labor is carried out depends on the readiness of the mother's body to give birth. If the condition of the mother's cervix has not begun to soften, thin, or open, it means that the mother's body is not ready to give birth.
Under these conditions, a pregnant woman may be given medication or a mechanical method to make the cervix ready for birth before starting labor induction. Some methods used to prepare the cervix and for labor induction are:
1. Using prostaglandin
To make the cervix thinner or open, your doctor may insert prostaglandin drugs into your vagina. This drug acts like the prostaglandin hormone so that it can help ripen the cervix for labor. Sometimes, this drug can also stimulate labor contractions.
2. Using a Foley catheter
In addition to drugs, stimulating labor can also be done with a tool. The doctor may insert a catheter with a special balloon to the end of your cervix. This balloon will be filled with water so that it suppresses your cervix, which will then stimulate the release of the hormone prostaglandin in the body. This causes the cervix to soften and open.
3. Wipe the lining of your cervix
If your cervix has opened slightly, you may not need to use drugs or catheters to stimulate the maturation of the cervix. You only need a little stimulation. The doctor may insert his finger into your cervix and manually separate the amniotic sac from your uterus. This makes the prostaglandin hormone released by the body, resulting in ripening of the cervix and possibly contractions.
READ ALSO: What Causes Rupture of Amniotic Before the Time?
4. Cleavage of the amniotic sac (amniotomy)
When your cervix is open a few centimeters and your baby's head has moved to your pelvis, but you have to wait a long time until the labor is ready, the doctor may break your amniotic sac with a small device. A ruptured amniotic sac can make you feel a contraction to give birth.
5. Using oxytocin
Oxytocin is used to stimulate or increase your contractions. The doctor will give oxytocin through low-dose intravenous fluids. How much oxytocin is needed will be adjusted to your needs.
When do you have to undergo labor induction?
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), induction of labor is only done when the baby's condition is more at risk to remain in the womb. Yes, labor induction is not always needed, there are various conditions that require you to induce labor. Some of the factors that determine whether you need labor induction or not are:
- Your health
- Baby health
- Gestational age and size of your baby
- Position of the baby in the womb
- Condition of the cervix
Some conditions that make labor induction must be done are:
- Your gestational age exceeds the date that should have been almost 2 weeks and you do not show signs of giving birth. A gestational age of more than 42 weeks will put you at greater risk for various problems, such as stillbirths.
- The amniotic sac has broken but you have not contracted. Induction is needed to reduce the risk of infection in your uterus or your baby. However, the doctor also looks at the gestational age and your baby is ready or not. If the baby is very premature, the doctor may not induce labor.
- You have an infection of the uterus or chorioamnionitis
- The baby in the womb has stopped growing
- Amniotic fluid is little or not enough to surround the baby (oligohydramnios)
- The condition of the placenta begins to worsen
- You experience placental abruption
- You have a history of stillbirths in a previous pregnancy
- You have medical conditions that are at risk for you and your baby, such as hypertension, preeclampsia or gestational diabetes
READ ALSO: Differences in gestational hypertension, preeclampsia and eclampsia
However, lately labor induction has also been done for other reasons that are not too urgent. Like because you live in a place far from health services, so you need to do an induction so that labor can be supervised by health workers. Another reason, namely to provide comfort to pregnant women so that they do not feel too much pain while waiting for labor, but generally this is not recommended.
Are there risks from labor induction?
Of course there is, induction of labor has a variety of risks. In fact, labor induction does not always work well. When induction of labor does not work for you, you may need another induction method or have to have a caesarean section. In addition, induction of labor can also last a long time, especially if your cervix is not ready. This might make you feel uncomfortable and nervous.
Some of the risks that can occur when you do labor induction are:
- Caesarean section. This is needed when labor induction does not work for you, especially if you have never given birth before and your cervix is not ready for birth. Complications from caesarean section here are higher than the planned caesarean section.
- Babies are stressed or have a low heart rate. This can happen because the drugs used during labor induction to stimulate contractions, such as prostaglandin and oxytocin, cause contractions to appear too strong and too often over a long period of time. This makes the supply of oxygen to your baby decreases, so that the baby's heart rate is low.
- Placental abruption or uterine rupture (uterine rupture). In rare cases, this can occur because prostaglandin and oxytocin drugs are used during labor induction. Caesarean section may be needed at this time to prevent more dangerous complications.
- Umbilical cord problems. Labor induction increases the risk of umbilical cord prolapse, where the umbilical cord precedes the fetus at birth so that the supply of oxygen to the fetus is disrupted.
- Bleeding after giving birth. Induction of labor can also increase the risk of your uterine muscle contracting poorly after labor (uterine atony). This causes serious bleeding after giving birth.
- Infection. The risk of infection in the mother and baby increases when you get labor induction.
Behind all the risks above, labor induction sometimes has greater benefits than the risk, so that induction of labor is still carried out. You should talk to your doctor about preparing for the birth of your baby, so that you can anticipate everything that is bad during childbirth.
READ ALSO: What Causes Heavy Childbirth Bleeding?